马拉松 | 121-75-5
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.4
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:11
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.8
-
拓扑面积:128
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:8
ADMET
安全信息
-
储存条件:储存注意事项:应将物品存放在阴凉、通风良好的专用库房内,并实行“双人收发,双人保管”制度。远离火种与热源,确保容器密封。需与氧化剂及碱类分开存放,严禁混储。配备相应种类和数量的消防器材。储存区应备有泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
由五硫化二磷和甲醇合成二甲基二硫代磷酸酯,然后与顺丁烯二酸二乙酯加成得到马拉硫磷。将顺丁烯二酸二乙酯(以100%计为380kg)投入1000L搪玻璃反应锅内搅拌,控制温度在45℃以下,投入350kg五硫化二磷。慢慢滴加甲醇,控制温度为48-55℃,约2h加完250kg甲醇。加毕,保持65-75℃反应8h。此过程产生硫化氢和逸出甲醇蒸气,经冷凝器使甲醇回流,硫化氢则用碱液吸收。反这过程需在负压下进行。反应完成后,冷却至40-50℃,静置分层使杂质沉淀。上层原油先后进行水洗、碱洗、水洗,然后在真空脱水锅中进行脱水,在85℃以下(真空度93.3kPa)使原油中的水分蒸发1.5-2h,得到马拉硫磷原油。原料消耗定额:顺酐430kg/t、五硫化二磷470kg/t、乙醇420kg/t、甲醇390kg/t。
合成制备方法由五硫化二磷和甲醇合成二甲基二硫代磷酸酯,然后与顺丁烯二酸二乙酯加成得到马拉硫磷。将顺丁烯二酸二乙酯(以100%计为380kg)投入1000L搪玻璃反应锅内搅拌,控制温度在45℃以下,投入350kg五硫化二磷。慢慢滴加甲醇,控制温度为48-55℃,约2h加完250kg甲醇。加毕,保持65-75℃反应8h。此过程产生硫化氢和逸出甲醇蒸气,经冷凝器使甲醇回流,硫化氢则用碱液吸收。反这过程需在负压下进行。反应完成后,冷却至40-50℃,静置分层使杂质沉淀。上层原油先后进行水洗、碱洗、水洗,然后在真空脱水锅中进行脱水,在85℃以下(真空度93.3kPa)使原油中的水分蒸发1.5-2h,得到马拉硫磷原油。原料消耗定额:顺酐430kg/t、五硫化二磷470kg/t、乙醇420kg/t、甲醇390kg/t。
用途简介马拉硫磷是一种高效低毒杀虫、杀螨剂,防治范围广泛。不仅适用于稻、麦、棉等作物的种植,还因其毒性较低、残效时间较短而被用于蔬菜、果树、茶叶以及仓库防虫。主要防治对象包括稻飞虱、稻叶蝉、棉蚜、棉红蜘蛛、麦粘虫、豌豆象、大豆食心虫、果树红蜘蛛、蚜虫、粉蚧壳虫、巢蛾、蔬菜黄条跳、菜叶虫、茶树上的多种蚧类,以及蚊、蝇幼虫和臭虫等。
用途马拉硫磷是一种高效低毒杀虫、杀螨剂,防治范围广泛。不仅适用于稻、麦、棉等作物的种植,还因其毒性较低、残效时间较短而被用于蔬菜、果树、茶叶以及仓库防虫。主要防治对象包括稻飞虱、稻叶蝉、棉蚜、棉红蜘蛛、麦粘虫、豌豆象、大豆食心虫、果树红蜘蛛、蚜虫、粉蚧壳虫、巢蛾、蔬菜黄条跳、菜叶虫、茶树上的多种蚧类,以及蚊、蝇幼虫和臭虫等。此外,马拉硫磷还可作为农药杀虫剂使用。
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (-)-S-malathion 145307-17-1 C10H19O6PS2 330.363 (R)-马拉硫磷 (+)-R-malathion 141318-03-8 C10H19O6PS2 330.363 —— 1-carboethoxy-2-carbomethoxy-1-[(dimethylphoshinothioyl)thio]ethane 71133-16-9 C9H17O6PS2 316.336 —— 2-carboethoxy-1-carbomethoxy-1-[(dimethylphoshinothioyl)thio]ethane 33779-98-5 C9H17O6PS2 316.336 —— (R)-malathion β-monoacid —— C8H15O6PS2 302.309 马拉硫磷beta-单酸 malathion monocarboxylic acid 1642-51-9 C8H15O6PS2 302.309 2-二甲氧基硫代膦酰硫基丁二酸二甲基酯 dimethoxythiophosphorylsulfanyl-succinic acid dimethyl ester 3700-89-8 C8H15O6PS2 302.309 —— (R)-malathion α-monoacid —— C8H15O6PS2 302.309 马拉硫磷alpha-单酸 Malathion monoacid 1190-29-0 C8H15O6PS2 302.309 —— Diethyl 2-dihydroxyphosphinothioylsulfanylbutanedioate 68906-22-9 C8H15O6PS2 302.3 2-二甲氧基硫代膦酰硫基丁二酸 malathion dicarboxylic acid 1190-28-9 C6H11O6PS2 274.255 马拉氧磷 malaoxon 1634-78-2 C10H19O7PS 314.296 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:微波辅助碳酸丙烯酯中有机磷农药的亲核降解摘要:在化学反应研究中,碳酸丙烯酯正在成为挥发性有机溶剂的合适绿色替代品。在这项研究中,提出了一种以碳酸亚丙酯为溶剂,对五种有机磷农药杀螟硫磷、马拉硫磷、二嗪农、对硫磷和对氧磷进行亲核降解的有效方法。研究了改变亲核试剂性质的影响和微波 (MW) 加热的影响。在微波加热下进行温度筛选(50°C-120°C)。农药降解紧随其后的是31P NMR和转化程度(%)通过磷信号的积分计算。请记住,最近有报道称一些离子液体具有亲核作用,在这项工作中,我们首次报道了使用基于氨基酸的离子液体(如 Bmim[Ala])作为亲核试剂降解有机磷农药以及作为反应介质的生物基溶剂(碳酸亚丙酯)与微波加热相结合。DOI:10.1039/d0ob01620a
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
Thieno-pyrimidine compounds having fungicidal activity
表征谱图
-
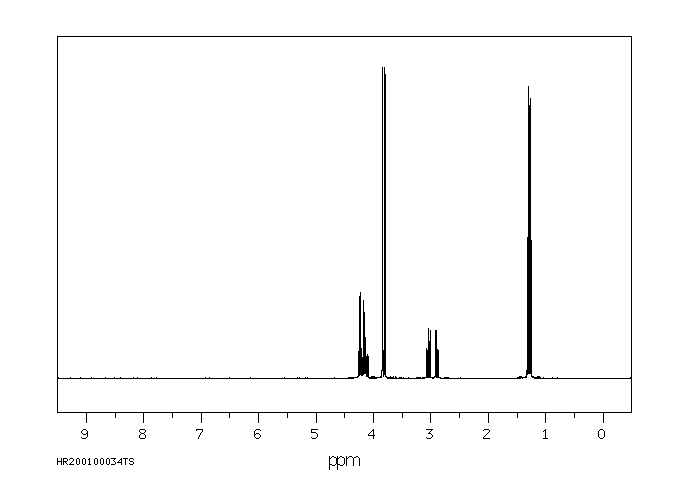
氢谱1HNMR
-
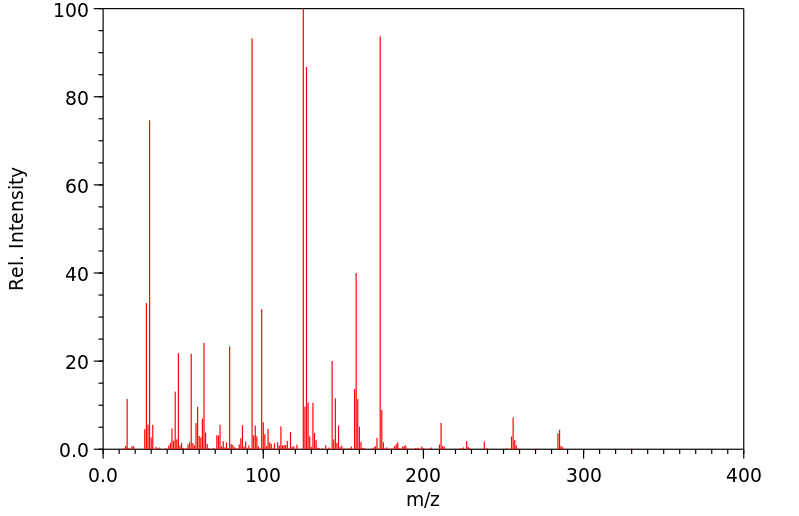
质谱MS
-
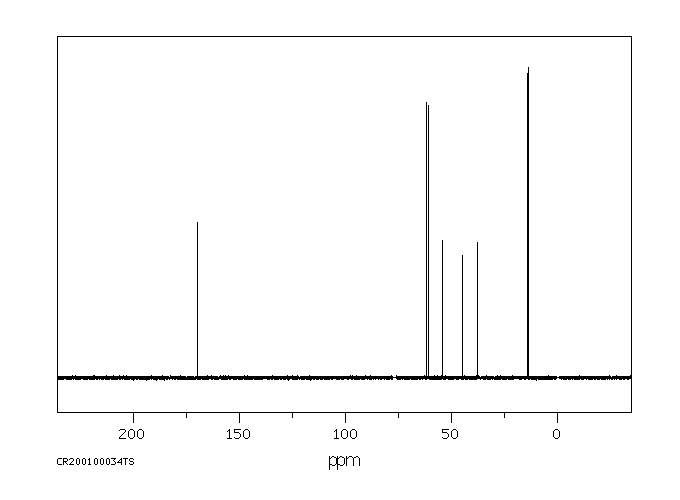
碳谱13CNMR
-
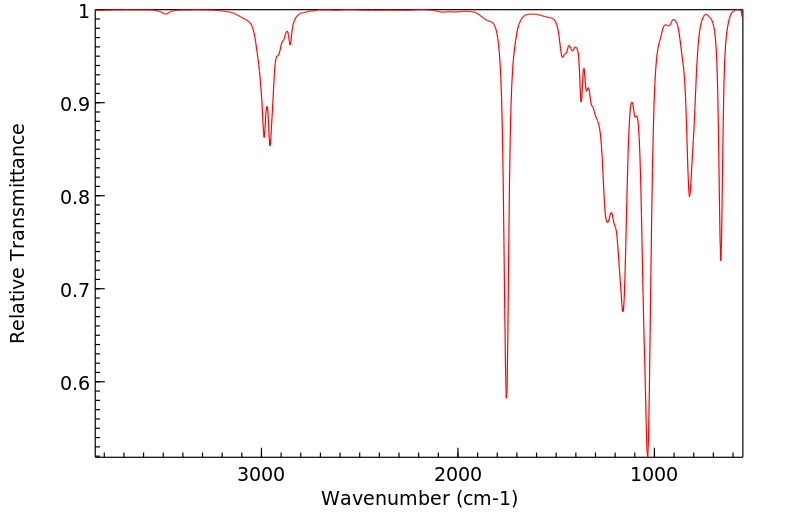
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息