N,N-dimethylacetamide hydrochloride | 920-54-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.52
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.75
-
拓扑面积:20.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:aluminum (III) chloride 、 N,N-dimethylacetamide hydrochloride 反应 1.67h, 以90.3%的产率得到N,N-dimethylacetamidium chloroaluminate参考文献:名称:[EN] SYNTHESIS OF NON-CYCLIC AMIDE AND THIOAMIDE BASED IONIC LIQUIDS
[FR] SYNTHÈSE DE LIQUIDES IONIQUES À BASE DE THIOAMIDE ET D'AMIDE NON CYCLIQUES摘要:非环状酰胺或硫酰胺基离子液体及其制备方法被披露。公开号:WO2017011232A1 -
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:通过乙烯基硅烷偶联反应将有机官能团固定在固体载体上的过渡金属催化摘要:已经开发出一种新颖有效的接枝方法,用于将功能性有机分子共价键合到二氧化硅或玻璃表面。该协议采用乙烯基硅烷与表面羟基的过渡金属催化反应。二甲基二乙烯基硅烷可在此过程中用作连接体,其中一个乙烯基用于与功能性有机分子直接形成 CC 键,另一个用于将烷基甲硅烷基固定在固体载体的羟基表面上。DOI:10.1021/ja102741k
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:Process for preparing polymorphic form II of sertraline hydrochloride摘要:本发明涉及一种制备盐酸塞来曲普兰II型的新工艺。公开号:US20060229472A1
文献信息
-
Heterobinuclear Alkyl Complexes of Rhodium and Iridium. Migratory Insertion or Ir-to-Rh Migration of a Methyl Group in Reactions with Small Molecules作者:Frederick H. Antwi-Nsiah、Okemona Oke、Martin CowieDOI:10.1021/om9505874日期:1996.2.6The reaction of [RhIr(CO)3(dppm)2] (dppm = Ph2PCH2PPh2) with methyl triflate yields [RhIr(CH3)(CO)3(dppm)2][CF3SO3] (2), having the methyl group and two terminal carbonyls on Ir and one carbonyl on Rh. An Ir → Rh dative bond is proposed, giving Rh+ a 16e square-planar configuration. Reaction of 2 with hydrogen at ambient temperature yields [RhIrH(CO)2(μ-H)2(dppm)2]+ and methane. At 0 °C the intermediate[RhIr(CO)3(dppm)2 ](dppm = Ph 2 PCH 2 PPh 2)与三氟甲磺酸甲酯反应生成[RhIr(CH 3)(CO)3(dppm)2 ] [CF 3 SO 3 ](2),在Ir上具有甲基和两个末端羰基,在Rh上具有一个羰基。提出了Ir→Rh的键,给出了Rh + 16e的方形平面构型。2在室温下与氢反应生成[RhIrH(CO)2(μ-H)2(dppm)2 ] +和甲烷。在0°C下,观察到中间体[RhIrH(CH 3)(CO)2(μ-H)(dppm)2 ] [CF 3 SO 3 ],该中间体在H 2下加热后生成三氢化物和CH 4。用HCl和CF 3 SO 3 H质子化2产生[RhIr(CH 3)(CO)2(μ-H)(μ-Cl)(dppm)2 ] +和[RhIr(CH 3)(CO)2( μ-H)(μ-CO)(dppm)2 ] +2。反应2与一氧化碳反应会分解成几种不明的
-
Bridging Methylene to Bridging Acyl Conversion in Heterobinuclear Rh/Ru Complexes: Models for Adjacent-Metal Involvement in Bimetallic Catalysts作者:Bryan D. Rowsell、Robert McDonald、Martin CowieDOI:10.1021/om040051v日期:2004.8.1methylene-bridged complex [RhRu(CO)4(μ-CH2)(dppm)2][CF3SO3] (1) at −80 °C yields an asymmetrically bridged methyl complex in which the methyl ligand is σ-bound to Ru while being involved in an agostic interaction with Rh. Warming to −40 °C results in migration of the methyl group to a terminal site on Rh, and further warming to 0 °C results in migratory insertion to give the acetyl-bridged complex [RhRu(OS所述的质子化的亚甲基桥连的络合物[RhRu(CO)4(μ-CH 2)(DPPM)2 ] [CF 3 SO 3 ](1)在-80℃下产生一个非对称地桥接甲基络合物,其中配位体甲酯是σ与Ru发生有害相互作用时与Ru结合。升温至−40°C导致甲基迁移至Rh的末端位点,进一步升温至0°C导致迁移插入,从而获得乙酰基桥接的复合物[RhRu(OSO 2 CF 3)(CO)2(μ-C(CH 3)O)(μ-CO)(DPPM)2 ] [CF 3 SO 3 ](4),其中乙酰基碳与Rh结合,而其氧与Ru结合。在环境温度下,羰基从4丢失,得到[RhRu(OSO 2 CF 3)(CO)2(μ-C(CH 3)O)(DPPM)2 ] [CF 3 SO 3 ](5)。碳13 NMR光谱和两种乙酰桥产物的X射线结构均表明酰基碳具有显着的卡宾特征。试图获得甲基和随后乙酰物种通过亚甲基插入合适的前体的金属氢化物键[RhRu(X)(CO)4(μ-H)(DPPM)2
-
Dihydride formation versus H<sub>2</sub>-elimination in the protonation of the heterobimetallic FePt complex (CO)<sub>3</sub>Fe(μ-H)(μ-PCy<sub>2</sub>)Pt(PEt<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>作者:Hilary A. Jenkins、Stephen J. Loeb、David G. Dick、Douglas W. StephanDOI:10.1139/v90-136日期:1990.6.1
The reaction of Li[Fe(CO)4(PCy2)] with trans-PtCl(H)(PEt3)2 results in the formation of the hydride complex (CO)3Fe((μ-H)((μ-PCy2)Pt(PEt3)2, 1. This heterobimetallic, phosphido-bridged complex reacts with one equivalent of HBF4•Et2O to give the complex [(CO)3Fe(μ-H)2((μ-PCy2)Pt(PEt3)2][BF4], 2, which contains two bridging hydride ligands. This species is isolated and fully characterized by 31P1H} and 1H NMR and infrared spectroscopy. In contrast, 1 reacts with one equivalent of HCl•DMA (DMA = dimethylacetamide) to give the complex (CO)3ClFe(μ-PCy2)Pt(PEt3)2, 3. This species is the result of oxidative addition of HCl with subsequent reductive elimination of H2(g). This complex is fully characterized by 31P1H} and 1H NMR, infrared spectroscopy and an X-ray crystal structure determination. 3 crystallizes in the space group [Formula: see text] with a = 10.037(4) Å, b = 10.644(3) Å, c = 17.137(9) Å, α = 102.80(3)°, β = 76.74(3)°, γ = 103.99(3)°, V = 1702(1) Å3, and Z = 2. The structure was refined to R = 2.54% and Rw = 2.73% for 4056 reflections with Fo2 > 3σ(Fo2). Keywords: heterobimetallic, hydride, phosphide, protonation.
Li[Fe(CO)4(PCy2)]与trans-PtCl(H)(PEt3)2反应,生成了氢化物配合物(CO)3Fe((μ-H)((μ-PCy2)Pt(PEt3)2),代号为1。这种杂双金属,膦桥配合物与HBF4•Et2O反应,生成了配合物[(CO)3Fe(μ-H)2((μ-PCy2)Pt(PEt3)2][BF4],代号为2,其中含有两个桥式氢配体。这种物种通过31P1H}和1H NMR以及红外光谱进行了全面表征。相比之下,1与HCl•DMA(DMA=二甲基乙酰胺)反应,生成了配合物(CO)3ClFe(μ-PCy2)Pt(PEt3)2,代号为3。这种物种是HCl的氧化加成产物,随后通过还原消除H2(g)而形成。这种配合物通过31P1H}和1H NMR、红外光谱以及X射线晶体结构测定得到了全面表征。3以[Formula: see text]空间群结晶,a=10.037(4) Å,b=10.644(3) Å,c=17.137(9) Å,α=102.80(3)°,β=76.74(3)°,γ=103.99(3)°,V=1702(1) Å3,Z=2。该结构的R值为2.54%,Rw值为2.73%,对于F o2>3σ(F o2)的4056个反射进行了修正。关键词:杂双金属,氢化物,膦化物,质子化。 -
Process for preparing penicillin antibiotics申请人:Glaxo Laboratories Limited公开号:US03971775A1公开(公告)日:1976-07-27.alpha.-Aminoacylpenicillin antibiotics such as ampicillin and amoxycillin may be prepared in particularly simple manner by a process which comprises preparing a solution of 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) in a water-immiscible organic solvent by treating 6-APA with an excess of a strong tertiary amine base in the presence of said solvent; neutralising the residual strong tertiary amine base in said solution; reacting the neutralised solution with a solution in a water-immiscible organic solvent of an acylating agent which is a mixed anhydride of a lower alkoxyformic acid and an N-protected derivative of an .alpha.-aminoacid wherein the N-protecting group is acid-labile, to yield a solution of an N-protected .alpha.-aminoacylpenicillin derivative; contacting the resulting solution with water and a strong acid to cleave the acid-labile N-protecting group; and isolating the thus-obtained .alpha.-aminoacylpenicillin from the resulting water-containing system. The use of water-immiscible solvents in the process obviates the need for a solvent evaporation stage during isolation of the .alpha.-aminoacylpenicillin product and thus renders the process of particular advantage in plant-scale operations..alpha.-氨基酰青霉素类抗生素,如氨苄青霉素和阿莫西林,可以通过以下简单的方法制备:首先将6-氨基青霉烷酸(6-APA)与过量的强三级胺碱在不溶于水的有机溶剂中反应,以制备6-APA的溶液;然后中和溶液中残留的强三级胺碱;接着将中和后的溶液与不溶于水的有机溶剂中的酰化试剂反应,该酰化试剂是较低的烷氧基甲酸和一种α-氨基酸的N-保护衍生物的混合酸酐,其中N-保护基为酸敏感,以产生一种N-保护的α-氨基酰青霉素衍生物的溶液;然后将所得溶液与水和强酸接触,以裂解酸敏感的N-保护基;最后从所得含水体系中分离出α-氨基酰青霉素。该过程中使用的不溶于水的溶剂消除了α-氨基酰青霉素产品的分离过程中需要蒸发溶剂的需求,因此在工厂规模的操作中具有特殊优势。
-
Heterobinuclear Hydrido, Alkyl, and Related Complexes of Rh/Os. Site-Specific Reductive Elimination of Methane from a Rh/Os Core and the Structures of [RhOs(CH2CN)(CO)3(dppm)2] and [RhOs(CH3)(CO)3(dppm)2]作者:Brian T. Sterenberg、Robert W. Hilts、Giovanni Moro、Robert McDonald、Martin CowieDOI:10.1021/ja00106a028日期:1995.1This paper reports the synthesis and characterization of a series of hydride, alkyl, alkenyl, and related heterobimetallic complexes of Rh and Os and the site-specific reductive elimination of methane from hydride methyl complexes. Reaction of [RhOs(CO)(3)(NCMe)(mu-H)(dppm)(2)](2+) (3, dppm = Ph(2)PCH(2)PPh(2)) with NaC=CH in acetonitrile yields the acetylide complex [RhOs(C2H)(CO)(3)(dppm)(2)] (6)and the cyanomethyl complex [RhOs(CH2-CN)(CO)(3)(dppm)(2)] (7). The same reaction under CO instead results in deprotonation of one dppm group to give [Rhos(CO)(4)(dppm-H)(dppm)] (8, dppm-H = bis(diphenylphosphino)methanide). The methanide carbon can be alkylated to give [RhOs(CO)(4)(Ph(2)PCH(CH3)PPh(2))(dppm)](+) (9) or protonated to give the known compound [RhOs(CO)(4)(dppm)(2)](+)(2). The methyl complex [RhOs(CH3)(CO)(3)(dppm)(2)] (10) is prepared by several routes, and upon protonation yields [RhOs(CO)(3)(mu-H)(mu(2)-eta(3)-(o-C6H4)PhPCH(2)PPh(2))(dppm)](+) (14) via methane loss. If the reaction is carried out at -80 degrees C and slowly warmed, three hydride methyl intermediates are observed at different temperatures, yielding information about the reductive elimination from these heterobinuclear species, which appears to occur from the Os center. An alkenyl complex analogous to the alkyl species 7 and 10 can be obtained by the reaction,of [RhOsH(CO)(3)(dppm)(2)] (1) with dimethyl acetylenedicarboxylate resulting in insertion into the Os-Il bond and migration of the resulting alkenyl group to Rh yielding [RhOs(MeO(2)CC=C(H)CO(2)Me)(CO)(3)(dppm)(2)] (18). Protonation of 18 yields [RhOs(R)(CO)(3)(mu-H)(dppm)(2)](+) (19) and alkylation yields [RhOs(R)(CH3)(CO)(3)(dppm)(2)](+) (20, R = MeO(2)CC=C(H)CO(2)Me). Compound 20 has the vinylic moiety bound to Rh with the methyl group on Os. The structures of 7 and 10 have been established by X-ray crystallography. Compound 7 crystallizes in the monoclinic space group C2/c with a = 18.313(3) Angstrom, b = 13.279(2) Angstrom, c = 22.492(5) Angstrom, beta = 115.89(1)degrees, and Z = 4; compound 10 crystallizes in the triclinic space group P1 with a = 11.102(2) Angstrom, b = 11.684(3) Angstrom, c = 10.954(3) Angstrom, alpha = 111.79(2)degrees, beta = 93.16(2)degrees, gamma = 68.18(2)degrees, and Z = 1. Both compounds are disordered at an inversion center, although only the metals and the carbonyl and alkyl groups are disordered. Both models refined acceptably: R = 0.046, R(w) = 0.058 (7); R = 0.047, R(w) = 0.077 (10). The geometries of the two complexes are almost identical, having the cyanomethyl or methyl group terminally bound to Rh and having the three carbonyls on Os. One carbonyl forms a semibridging interaction with Rh.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
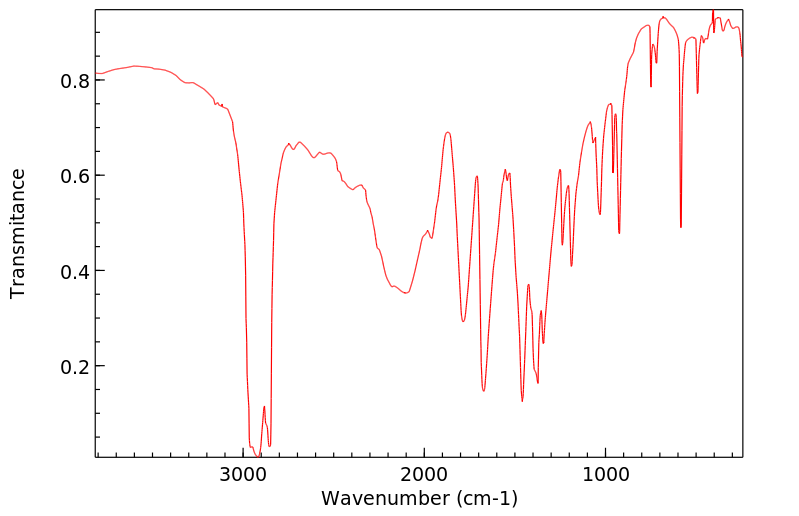
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息