1-(溴甲基)-4-[2-[4-(溴甲基)苯基]乙基]苯 | 6337-67-3
中文名称
1-(溴甲基)-4-[2-[4-(溴甲基)苯基]乙基]苯
中文别名
——
英文名称
4,4'-bis(bromomethyl)bibenzyl
英文别名
1,2-bis(4-(bromomethyl)phenyl)ethane;1,1'-Ethane-1,2-diylbis[4-(bromomethyl)benzene];1-(bromomethyl)-4-[2-[4-(bromomethyl)phenyl]ethyl]benzene
CAS
6337-67-3
化学式
C16H16Br2
mdl
——
分子量
368.111
InChiKey
GKYPYQQVLLXFDQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:95 °C
-
沸点:403.0±35.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.521±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):5.3
-
重原子数:18
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.25
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,2-二苯乙烷 1,1'-(1,2-ethanediyl)bisbenzene 103-29-7 C14H14 182.265 4-[2-(4-甲酰基苯基)乙基]苯甲醛 bibenzyl-4,4'-dicarbaldehyde 1220-08-2 C16H14O2 238.286 —— {4-[2-(4-hydroxymethyl-phenyl)ethyl]phenyl}methanol 88579-94-6 C16H18O2 242.318 1,1'-(1,2-乙二基二-4,1-亚苯基)二-乙酮 4,4'-diacetylbibenzyl 793-06-6 C18H18O2 266.34 1,4-二(溴甲基)苯 1,4-bis(bromomethyl)benzene 623-24-5 C8H8Br2 263.96 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 对二甲苯二聚体 [2.2]Paracyclophan 1633-22-3 C16H16 208.303 —— [2.2.2.2]paracyclophane 283-81-8 C32H32 416.606 4-[2-(4-甲酰基苯基)乙基]苯甲醛 bibenzyl-4,4'-dicarbaldehyde 1220-08-2 C16H14O2 238.286 —— <2.2.2>m,p,p-cyclophane 214972-59-5 C24H24 312.455 —— <24>paracyclophanediene, isomer 2 79238-91-8 C32H28 412.574 —— 1-(Azidomethyl)-4-[2-[4-(azidomethyl)phenyl]ethyl]benzene 865439-25-4 C16H16N6 292.343
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:1-(溴甲基)-4-[2-[4-(溴甲基)苯基]乙基]苯 在 sodium azide 作用下, 以 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 10.0h, 以97%的产率得到1-(Azidomethyl)-4-[2-[4-(azidomethyl)phenyl]ethyl]benzene参考文献:名称:Size-Specific Ligands for RNA Hairpin Loops摘要:The targeting of one mRNA in the transcriptome requires small molecules that bind with substantial affinity and specificity. As such, compounds with specificity for individual RNA secondary structural motifs could be useful for targeting RNA. Described herein is the synthesis of a combinatorial library of 105 dimers of deoxystreptamine and the subsequent identification of compounds with specificity for specific RNA hairpin loop sizes, including tetraloops and octaloops. Such compounds will be useful for the perturbation of RNA function in vivo.DOI:10.1021/ja051685b
-
作为产物:描述:4,4'-(ethene-1,2-diyl)dibenzoic acid 在 lithium aluminium tetrahydride 、 氯仿 、 硫酸 、 三溴化磷 作用下, 生成 1-(溴甲基)-4-[2-[4-(溴甲基)苯基]乙基]苯参考文献:名称:Macro Rings. I. Preparation and Spectra of the Paracyclophanes摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01156a059
文献信息
-
Rotaxane or Pseudorotaxane? Effects of Small Structural Variations on the Deslipping Kinetics of Rotaxanes with Stopper Groups of Intermediate Size作者:Ansgar Affeld、Gosia M. Hübner、Christian Seel、Christoph A. SchalleyDOI:10.1002/1099-0690(200108)2001:15<2877::aid-ejoc2877>3.0.co;2-r日期:2001.8Secondly, stopper flexibility has an important influence on the deslipping rate. Thirdly, exchange of a carbonamide for a sulfonamide in the wheel significantly reduces the entropic costs of the deslipping, resulting in a pronounced deslipping rate enhancement. Fourthly, intramolecular hydrogen bonding within the wheel decelerates deslipping by a factor of more than 104.三个系列的轮烷已通过滑动合成(轴和轮混合熔化)、通过识别大环轮内部的酰胺基团或通过阴离子模板法(其中塞子酚盐与轮以氢键键合)的方式合成。然后通过与半轴的反应连接。大多数这些轮烷使用的 3,5-二叔丁基苯基塞子足够大,可以隔离它们,但在适当的条件下仍允许车轮从轴上滑落。所有轮烷的脱滑活化参数均来自 1 H NMR 动力学测量值,并已根据 Arrhenius 方程和 Eyring 理论进行评估。小的结构变化会对激活参数产生惊人的影响。首先,在一些例子中,轴长影响防滑屏障,但止动器和车轮的尺寸互补性保持不变。其次,塞子的柔韧性对脱滑率有重要影响。第三,在车轮中用碳酰胺交换磺酰胺显着降低了脱滑的熵成本,从而显着提高了脱滑率。第四,车轮内的分子内氢键使滑移减速超过 104 倍。
-
Deoxystreptamine Dimers Bind to RNA Hairpin Loops作者:Xianjun Liu、Jason R. Thomas、Paul J. HergenrotherDOI:10.1021/ja048936l日期:2004.8.1RNA is known to have multiple roles in critical cellular functions. Thus, there is great potential for RNA-binding small molecules as both therapeutic agents and cellular probes. Unfortunately, the multiple secondary structures that RNA can adopt have caused difficulty in the development of a general paradigm for RNA-small molecule binding. In particular, the standard RNA-binding compounds such as
-
Homodimeric Bis-Quaternary Heterocyclic Ammonium Salts as Potent Acetyl- and Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors: A Systematic Investigation of the Influence of Linker and Cationic Heads over Affinity and Selectivity作者:Ana Conejo-García、Leonardo Pisani、Maria del Carmen Núñez、Marco Catto、Orazio Nicolotti、Francesco Leonetti、Joaquín M. Campos、Miguel A. Gallo、Antonio Espinosa、Angelo CarottiDOI:10.1021/jm101299d日期:2011.4.28A molecular library of quaternary ammonium salts (QASs), mainly composed of symmetrical bis-quaternary heterocyclic bromides exhibiting choline kinase (ChoK) inhibitory activity, were evaluated for their ability to inhibit acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase (AChE and BChE, respectively). The molecular framework of QASs consisted of two positively charged heteroaromatic (pyridinium or quinolinium) or
-
A Simple Synthetic Method of [2.2]Cyclophanes by Lanthanoid-Mediated Coupling of Bis(bromomethyl)benzenes
-
Design, synthesis and characterization of self-assembled As2L3 and Sb2L3 cryptands作者:Sean A. Fontenot、Virginia M. Cangelosi、Melanie A. W. Pitt、Aaron C. Sather、Lev N. Zakharov、Orion B. Berryman、Darren W. JohnsonDOI:10.1039/c1dt10817d日期:——The syntheses and X-ray crystal structures of six new self-assembled supramolecular As and Sb-containing cryptands are described. Analysis in the context of previously reported As2L3 and Sb2L3 cryptands reveals that small differences in ligand geometries result in significant differences in the helicity of the complexes and the stereochemistry of the metal coordination within the assembled complexes
表征谱图
-
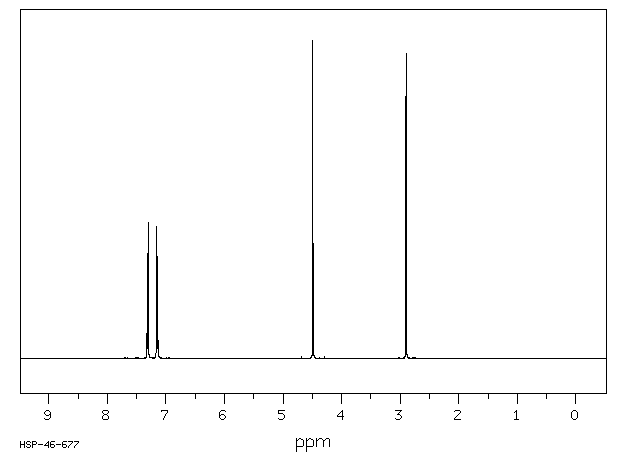
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
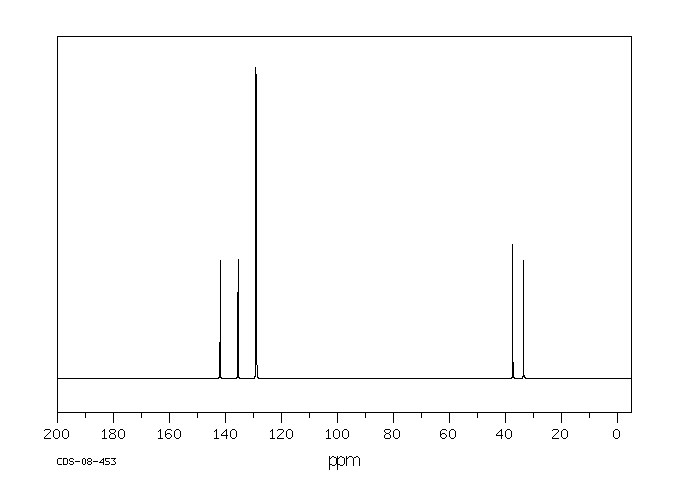
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(E,Z)-他莫昔芬N-β-D-葡糖醛酸
(E/Z)-他莫昔芬-d5
(4S,5R)-4,5-二苯基-1,2,3-恶噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S,5R,5''R)-2,2''-(1-甲基亚乙基)双[4,5-二氢-4,5-二苯基恶唑]
(4R,5S)-4,5-二苯基-1,2,3-恶噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4R,4''R,5S,5''S)-2,2''-(1-甲基亚乙基)双[4,5-二氢-4,5-二苯基恶唑]
(1R,2R)-2-(二苯基膦基)-1,2-二苯基乙胺
鼓槌石斛素
黄子囊素
高黄绿酸
顺式白藜芦醇三甲醚
顺式白藜芦醇
顺式己烯雌酚
顺式-白藜芦醇3-O-beta-D-葡糖苷酸
顺式-桑皮苷A
顺式-曲札芪苷
顺式-二苯乙烯
顺式-beta-羟基他莫昔芬
顺式-a-羟基他莫昔芬
顺式-3,4',5-三甲氧基-3'-羟基二苯乙烯
顺式-1-(3-甲基-2-萘基)-2-(2-萘基)乙烯
顺式-1,2-双(三甲基硅氧基)-1,2-双(4-溴苯基)环丙烷
顺式-1,2-二苯基环丁烷
顺-均二苯乙烯硼酸二乙醇胺酯
顺-4-硝基二苯乙烯
顺-1-异丙基-2,3-二苯基氮丙啶
非洲李(PRUNUSAFRICANA)树皮提取物
阿非昔芬
阿里可拉唑
阿那曲唑二聚体
阿托伐他汀环氧四氢呋喃
阿托伐他汀环氧乙烷杂质
阿托伐他汀环(氟苯基)钠盐杂质
阿托伐他汀环(氟苯基)烯丙基酯
阿托伐他汀杂质D
阿托伐他汀杂质94
阿托伐他汀杂质7
阿托伐他汀杂质5
阿托伐他汀内酰胺钠盐杂质
阿托伐他汀中间体M4
阿奈库碘铵
锌(II)(苯甲醛)(四苯基卟啉)
银松素
铜酸盐(5-),[m-[2-[2-[1-[4-[2-[4-[[4-[[4-[2-[4-[4-[2-[2-(羧基-kO)苯基]二氮烯基-kN1]-4,5-二氢-3-甲基-5-(羰基-kO)-1H-吡唑-1-基]-2-硫代苯基]乙烯基]-3-硫代苯基]氨基]-6-(苯基氨基)-1,3,5-三嗪-2-基]氨基]-2-硫代苯基]乙烯基]-3-硫代
铒(III) 离子载体 I
铀,二(二苯基甲酮)四碘-
钾钠2,2'-[(E)-1,2-乙烯二基]二[5-({4-苯胺基-6-[(2-羟基乙基)氨基]-1,3,5-三嗪-2-基}氨基)苯磺酸酯](1:1:1)
钠{4-[氧代(苯基)乙酰基]苯基}甲烷磺酸酯
钠;[2-甲氧基-5-[2-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯基)乙基]苯基]硫酸盐
钠4-氨基二苯乙烯-2-磺酸酯