5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-methylfuran) | 59212-75-8
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-methylfuran)
英文别名
5,5’-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-methylfuran);5,5′-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-methylfuran);2,2'-Isopropylidenebis(5-methylfuran);2-methyl-5-[2-(5-methylfuran-2-yl)propan-2-yl]furan
CAS
59212-75-8
化学式
C13H16O2
mdl
——
分子量
204.269
InChiKey
NKSPRRDOULOQCZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.7
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.38
-
拓扑面积:26.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:5,5'-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(2-methylfuran) 在 N-溴代丁二酰亚胺(NBS) 、 偶氮二异丁腈 、 水 、 potassium carbonate 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 环己烷 为溶剂, 反应 7.0h, 生成 5,5’-(propane-2,2-diyl)bis(furan-5,2-diyl)dimethanol参考文献:名称:Bisfuran dihalide, method for producing bisfuran dihalide, and method for producing bisfuran diacid, bisfuran diol or bisfuran diamine using bisfuran dihalide摘要:一种双噁呋二卤代化合物,其结构如下式(1)所示:其中R1是由—CR2R3—表示的双价碳氢基团(其中R2和R3中的每一个独立表示氢原子或一价碳氢基团,R2和R3可以共同形成一个环状结构),或者是一个羰基(—C(═O)—);每个X独立地表示一个卤素原子。公开号:US09840485B1
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:生产具有乙酰化酶和木质纤维素衍生的平台分子的液态烃燃料摘要:乙缩醛是一种源自新ABE发酵系统的新型C 4平台分子,被用作生产液体烃类燃料的生物基构件。DOI:10.1039/c5gc02414e
文献信息
-
A two-phase system for the clean and high yield synthesis of furylmethane derivatives over –SO<sub>3</sub>H functionalized ionic liquids作者:S. H. Shinde、C. V. RodeDOI:10.1039/c7gc01654a日期:——respective ionic liquids. Among the several preapered ionic liquids, strong acidic imidazolium based butylsulfonic acid (6) showed the best activity with a maximum of 84% yield of condensation product. This strategy offers significantly high yield production of condensation products of furan and furfural as compared to the traditional mineral acid route. The activity and stability of the -SO3H functionalized我们在这里报告了一种新的有效的独特的两相反应系统,用于从糠醛和呋喃中高产率生产三(糠基)甲烷。该策略包括酸性水相(水+ -SO3H官能化的IL)和呋喃相,它们显着抑制了聚合物的形成,从而提高了三(呋喃基)甲烷的收率。呋喃既用作反应物又用作萃取溶剂,以回收缩合产物。为了进行比较,制备了不同的-SO3H官能化离子液体,并评估了它们在呋喃和糠醛缩合中的性能。发现具有烷基链接头的离子液体比咪唑鎓连接的N-磺酸更有效和酸性。除此之外,咪唑/三乙胺/吡啶和-SO3H之间的碳链长度增加,增加了相应离子液体的催化活性。在几种预离子化的液体中,强酸性咪唑基丁基磺酸(6)表现出最佳的活性,缩合产物的收率最高为84%。与传统的无机酸路线相比,该策略可显着提高呋喃和糠醛缩合产物的收率。-SO3H功能化的IL的活性和稳定性通过其成功的七个循环而得到证实,而没有丧失活性。然后,成功地扩展了这一新策略,使呋喃衍生物(例
-
Activation of Mononuclear Arene Ruthenium Complexes for Catalytic Propargylation Directly with Propargyl Alcohols作者:Emilio Bustelo、Pierre H. DixneufDOI:10.1002/adsc.200600512日期:2007.4.2ligand. The in situ generated catalyst has been applied to catalytic transformations of alkynes and propargylic alcohols: propargylation of furans, propargyl ether synthesis from internal and terminal propargylic alcohols with propargyl, homopropargyl and allyl alcohols, selective dimerization of phenylacetylene into E-enyne, and propargyl alcohol rearrangement into α,β-unsaturated aldehydes and ketones[(对伞花基)RuX(CO)(PR 3)] [OTf](R = Ph,Cy; X = Cl,OTf)类型的单核络合物促进呋喃与炔丙醇的直接催化炔丙基化。这些前体是通过活化炔丙醇从[(对-cymene)RuCl(OTf)(PR 3)]原位产生的,导致经由亚烯基和烯基-羟基卡宾中间体形成羰基配体。催化活性物质的产生需要短的初始热活化以诱导对-异丙基配体的去配位。在原位生成的催化剂已用于炔烃和炔丙醇的催化转化:呋喃的炔丙基化,内部和末端炔丙醇与炔丙基,高炔丙基和烯丙基醇的炔丙基醚合成,苯乙炔的选择性二聚为E-烯炔和炔丙醇重排为α ,β-不饱和醛和酮通过Meyer-Schuster重排。含有内部CC键的炔丙醇的炔丙基化表明通过Nicholas型中间体(金属稳定的炔丙基阳离子)的活化。
-
Poly(vinylsulfonic acid)-grafted solid catalysts: new materials for acid-catalysed organic synthetic reactions作者:Teruyuki Okayasu、Kei Saito、Hiroyuki Nishide、Milton T. W. HearnDOI:10.1039/c0gc00241k日期:——The synthesis, characterisation and application of novel high-density poly(vinylsulfonic acid)-grafted solid acid catalysts are described. A graft, radical polymerization procedure was employed, allowing the immobilisation of the acid form of vinylsulfonic acid monomer onto various carrier materials, such as polystyrene, silica or polysaccharide-based gels. The highest acid-exchange capacity (as determined by acid–base titration methods) achieved with these new materials was 5.2 mmol H+ g−1. The properties of these PVS-grafted materials as solid state acid catalysts have been examined from several perspectives, including their fundamental properties as materials with extremely high acid dissociation characteristics, their structural features as revealed from IR and solid-state NMR measurements, their thermal stability properties, and their surface morphologies, humidity dependencies and functionality. Compared to many other types of acid catalysts, these high-density poly(vinylsulfonic acid)-grafted materials demonstrated superior catalytic performance in esterification, Friedel–Crafts acylation, and condensation reactions. Moreover, these novel materials show high stability, significant anticorrosion capability and can be easily recycled.本文描述了新型高密度聚乙烯磺酸(PVS)接枝固体酸催化剂的合成、表征和应用。采用接枝自由基聚合方法,将乙烯磺酸单体的酸态固定在各种载体材料上,如聚苯乙烯、硅胶或基于多糖的凝胶等。通过酸碱滴定法测定,这些新材料的最大酸交换容量达到5.2毫摩尔H+/克。从多个角度考察了这些PVS接枝材料作为固体酸催化剂的性能,包括它们作为具有极高酸性解离特性的材料的基态性质、通过红外光谱和固体核磁共振测量揭示的结构特征、热稳定性、表面形貌、湿度和功能性等方面的影响。与许多其他类型的酸催化剂相比,这些高密度聚乙烯磺酸接枝材料在酯化、Friedel-Crafts酰基化、缩合反应等方面表现出更优异的催化性能。此外,这些新材料表现出高度的稳定性、显著的防腐能力和易于回收的特点。
-
Preparation of a novel poly(vinylsulfonic acid)-grafted solid phase acid catalyst and its use in esterification reactions作者:Teruyuki Okayasu、Kei Saito、Hiroyuki Nishide、Milton T. W. HearnDOI:10.1039/b823177j日期:——A high-density sulfonic acid polymer, grafted onto a carrier surface, was synthesized from the acid form of vinylsulfonic acid monomer, and its catalytic activity as a new class of heterogeneous acid catalyst demonstrated in esterification reactions.
-
Hydrodeoxygenation of Furylmethane Oxygenates to Jet and Diesel Range Fuels: Probing the Reaction Network with Supported Palladium Catalyst and Hafnium Triflate Promoter作者:Saikat Dutta、Basudeb SahaDOI:10.1021/acscatal.7b00986日期:2017.8.4Catalytic hydrodeoxygenation of furylmethane oxygenates to high carbon branched chain jet and diesel fuel range alkanes under mild reaction conditions is a promising strategy for energy-efficient production of fuels with minimal C–C cracking to undesired products. Here, we report that a strong Lewis acidic promoter can overcome the energy barrier for furylmethane hydrodeoxygenation at lower temperature在温和的反应条件下,将呋喃甲烷含氧化合物催化加氢脱氧成高碳支链喷气发动机和柴油燃料系列烷烃是一种有前景的策略,可实现高能效生产,并且对不希望有的产品进行最低程度的C-C裂解。在这里,我们报告说,强路易斯酸性助催化剂可以克服呋喃甲烷加氢脱氧在较低温度下的能垒。呋喃甲烷的呋喃环首先通过加氢催化剂加氢成完全饱和的环醚,然后使其容易地开环并通过促进剂进行脱氧。在开环步骤中,在助催化剂的三氟甲磺酸酯配体的协助下,在醚基O和路易斯酸性金属中心之间形成了一个环状中间体。用对称的单个呋喃环替代分子探测反应路径表明,启动子对于开环是必需的。单个呋喃环代用品比多个呋喃环呋喃基甲烷更快地发生开环含氧化合物的脱氧。最高97%的喷气燃料范围烷烃在C中的选择性为93%在最佳条件下由C 15-呋喃甲烷获得15 H 32和C 14 H 30。具有所需碳原子数的烷烃的收率和选择性可以使用具有定制碳链,呋喃原子数和最小化C-C裂解的碳中心的呋喃甲烷进行调整。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
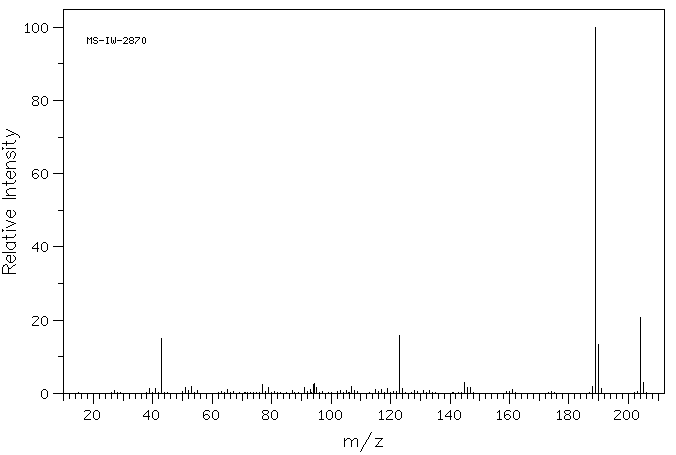
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
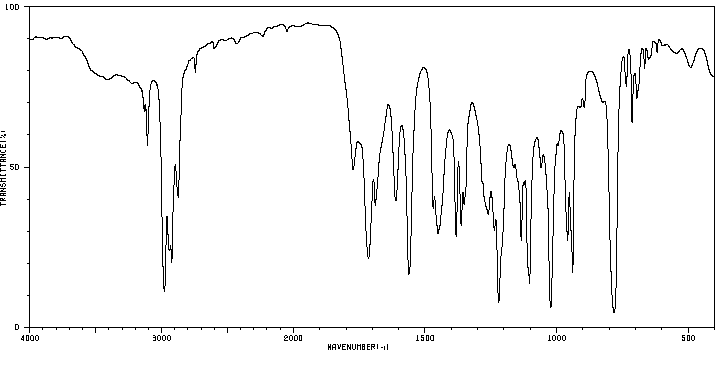
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
香薷二醇
顺式-1-(2-呋喃基)-1-戊烯
顺-1,2-二氰基-1,2-双(2,4,5-三甲基-3-噻吩基)乙烯
顺-1,2-(2-噻嗯基)二乙烯
雷尼替丁-N,S-二氧化物
雷尼替丁-N-氧化物
钴(II)双[(2-吡啶基甲基)(叔丁基二甲基甲硅烷基)酰胺]
西拉诺德
螺[环氧乙烷-2,3'-吡咯并[1,2-a]吡嗪]
萘并[2,1,8-def]喹啉
苯硫基溴化镁
苯甲酸,2-[[[7-[[(3.β.)-3-羟基-28-羰基羽扇-20(29)-烯-28-基]amino]庚基]氨基]羰基]
苍术素
羟胺,O-[4-(2-呋喃基)丁基]-
缩水甘油糠醚
紫苏烯
糠醛肟
糠醛氰醇的1-乙氧基乙基醚
糠醇-d2
糠醇
糠基硫醇-d2
糠基硫醇
糠基甲基硫醚
糠基氯
糠基氨基甲酸异丙酯
糠基丙基醚
糠基丙基二硫醚
糠基3-巯基-2-甲基丙酸酯
糠基-异戊基醚
糠基-异丁基醚
糠基 2-甲基-3-呋喃基二硫醚
磷杂茂
碘化N,N,N-三甲基丁烷-1-铵
硫酸异丙基糠酯
硫代磷酸O-糠基O-甲基S-(2-丙炔基)酯
硫代磷酸O-乙基O-糠基S-(2-丙炔基)酯
硫代甲酸S-糠酯
硫代噻吩甲酰基三氟丙酮
硫代乙酸糠酯
硫代丙酸糠酯
硒吩-3-羧酸酰肼
硅烷,三(1-甲基乙基)[(3-甲基-2-呋喃基)氧代]-
硅烷,[2-(3-呋喃基)乙烯基]三甲基-,(E)-
硅烷,(1,1-二甲基乙基)(2-呋喃基甲氧基)二甲基-
砷杂苯
甲酸糠酯
甲氧亚胺基呋喃乙酸铵盐
甲基糠基醚
甲基糠基二硫
甲基呋喃-2-基甲基氨基甲酸酯