毒草胺 | 1918-16-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:67-76°C
-
沸点:110°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.2420
-
闪点:100 °C
-
介电常数:2.8-2.9(0.0℃)
-
物理描述:Propachlor is a light tan solid. Corrosive to iron and steel. Used as an herbicide.
-
颜色/状态:Light tan solid
-
溶解度:In acetone 448, benzene 737, toluene 342, ethanol 408, xylene 239, chloroform 602, carbon tetrachloride 174, diethyl ether 219 (all in g/kg, 25 °C).
-
蒸汽压力:7.4X10-4 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
STABLE FOR AT LEAST 4 YEARS, NOT SENSITIVE TO LIGHT
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of /hydrogen chloride and nitrogen oxides/.
-
腐蚀性:No corrosion to number 316 and 304 stainless steel, aluminum, and heresite; corrosive to ordinary steel.
-
碰撞截面:142.07 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: TW]
-
保留指数:1608;1607.5;1612.1;1585.8;1585.1;1585.6
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.2
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.363
-
拓扑面积:20.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn,N
-
安全说明:S24,S37,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R22,R36,R50/53,R43
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2924299014
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2811
-
RTECS号:AE1575000
-
储存条件:请将贮藏器密封保存,并存放在阴凉、干燥处。同时,确保工作环境有良好的通风或排气设施。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 毒草安;2-氯-N-(1-甲基乙基)-N-苯基乙酰胺 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Propachlor;2-Chloro-N-isopropylacetanilide |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 1918-16-7 |
| 分子式: | C 11 H 14 ClNO |
| 分子量: | 211.71 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||||
| 化学品名称:毒草安;2-氯-N-(1-甲基乙基)-N-苯基乙酰胺 | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第6.1类 毒害品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 本品为低毒除草剂。中毒症状有头痛、头晕、恶心、呕吐、胸闷、紫绀、抽搐及昏迷等。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 立即脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及流动清水彻底冲洗污染的皮肤、头发、指甲等。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 饮足量温水,催吐。洗胃,导泄。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。其粉体与空气可形成爆炸性混合物, 当达到一定浓度时, 遇火星会发生爆炸。受高热分解放出有毒的气体。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢、氧化硫。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 泡沫、干粉、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,建议应急处理人员戴好口罩、护目镜,穿工作服。小心扫起,避免扬尘,运至废物处理场所。用水刷洗泄漏污染区,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,全面通风。防止粉尘释放到车间空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩,戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿透气型防毒服,戴防化学品手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与氧化剂接触。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。包装密封。应与氧化剂分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 生产过程密闭,全面通风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 空气中粉尘浓度较高时,建议佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿透气型防毒服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作时不得进食、饮水或吸烟。工作完毕,彻底清洗。保持良好的卫生习惯。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 淡黄褐色固体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 67~76 |
| 沸点(℃): | 110/0.004kPa |
| 相对密度(水=1): | |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 0.004/110℃ |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 11 H 14 ClNO |
| 分子量: | 211.71 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 微溶于水,易溶于苯、丙酮、乙醇、甲苯、四氯化碳等。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作农用除草剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氯化氢、氧化硫。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:710 mg/kg(大鼠经口);290 mg/kg(小鼠经口);380 mg/kg(兔经皮);392 mg/kg(兔经口)? LC50:无资料 |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 用安全掩埋法处置。在规定场所掩埋空容器。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61900 |
| UN编号: | 2769 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | 塑料袋或二层牛皮纸袋外全开口或中开口钢桶;两层塑料袋或一层塑料袋外麻袋、塑料编织袋、乳胶布袋;塑料袋外复合塑料编织袋(聚丙烯三合一袋、聚乙烯三合一袋、聚丙烯二合一袋、聚乙烯二合一袋);塑料袋或二层牛皮纸袋外普通木箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶、复合塑料瓶或铝瓶外普通木箱;塑料瓶、两层塑料袋或两层牛皮纸袋(内或外套以塑料袋)外瓦楞纸箱。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 铁路运输时包装所用的麻袋、塑料编织袋、复合塑料编织袋的强度应符合国家标准要求。运输前应先检查包装容器是否完整、密封,运输过程中要确保容器不泄漏、不倒塌、不坠落、不损坏。严禁与酸类、氧化剂、食品及食品添加剂混运。运输时运输车辆应配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。运输途中应防曝晒、雨淋,防高温。公路运输时要按规定路线行驶,勿在居民区和人口稠密区停留。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定;常用危险化学品的分类及标志 (GB 13690-92)将该物质划为第6.1 类毒害品。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 5 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
毒草安又称为“杀草安”、“扑草安”或“毒草胺”,是一种酰胺类除草剂。其工业产品为淡褐色固体,微溶于水,易溶于一般有机溶剂。毒草安具有低毒性,但对眼睛有刺激作用。常见剂型包括10%、20%可湿性粉剂及30%乳油,适用于土壤施用,能有效抑制杂草根或幼苗生长,从而防止一年生单子叶和部分双子叶杂草如稗、狗尾草、苋菜的生长;对马齿苋、马唐、蓼等的效果较差。
适用范围毒草安可有效防除一年生禾本科杂草及某些阔叶杂草,例如稗、马唐、狗尾草、早熟禾、看麦娘、藜、苋、龙葵和马齿苋等。然而对红蓼、苍耳的效果差,对多年生杂草无效,在稻田中对稗草具有显著的防治效果,并且使用安全,不易引发药害。毒草安在土壤中的残留期约为30天。
毒性65%可湿性粉剂对大鼠急性经口LD50为1200毫克/千克;10.4%水悬液对家兔急性经皮LD50380毫克/千克。对眼睛有刺激作用,鲶鱼LC50为1.3毫克/升。
化学性质毒草安的原药为淡黄褐色固体,熔点67~76℃。其蒸气压在110℃时为4帕斯卡。20℃下溶解度分别为:苯50%、丙酮30.9%、乙醇29%、甲苯25.5%、四氯化碳14.8%,水700毫克/升。常温下稳定,但在酸碱条件下受热易分解。
用途毒草安是一种酰胺类选择性芽前除草剂,适用于水稻、棉花、玉米、花生、甘蔗、油菜和豆类作物的田间管理,用于防除一年生禾本科杂草及某些阔叶杂草,如稗草、马唐、狗尾草、野燕麦、苋、藜、马齿苋和牛毛草等。其应用剂量为35~50克/平方米,在此剂量下,药剂在土壤中的持效期约为4~6周。
生产方法毒草安的生产采用苯胺与2-氯丙烷于130-140℃、约1MPa压力下反应4小时制得N-异丙基苯胺;随后降温至95℃,泄压后缓慢滴加氯乙酰氯,在100℃条件下反应3小时即得毒草胺。原料消耗定额为:苯胺530公斤/吨、丙烯410公斤/吨、盐酸520公斤/吨、氯乙酰氯740公斤/吨、氯化钙200公斤/吨。
类别与性质毒草安属于农药,归类于高毒性物质。急性毒性表现为:口服-大鼠LD50: 710毫克/千克;口服-小鼠LD50: 290毫克/千克。
燃烧危险性燃烧时会产生有毒的氮氧化物和氯化物气体。
储运特性应存放在通风干燥、低温处,并与食品原料分开储运。
灭火剂可使用干粉、泡沫或砂土灭火。
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— N-isopropyl-N-phenyl-acetamide 5461-51-8 C11H15NO 177.246 —— 2-Chloro-N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(propan-2-yl)acetamide 88036-35-5 C11H14ClNO2 227.69 —— N1-isopropyl-N1-phenylglycinamide 75945-59-4 C11H16N2O 192.261 —— 2-bromo-N-isopropyl-N-phenyl-acetamide 161455-97-6 C11H14BrNO 256.142 扑草胺-2-羟基 hydroxy-N-isopropyl-N-phenyl-acetamide 42404-06-8 C11H15NO2 193.246 —— 2-formamido-N-isopropylacetanilide 68420-09-7 C12H16N2O2 220.271 —— N-phenyl-2-piperazin-1-yl-N-propan-2-ylacetamide 1097811-66-9 C15H23N3O 261.367 2-氯乙酰苯胺 N-chloroacetyl-aniline 587-65-5 C8H8ClNO 169.611
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Martinetz, Dieter; Wenzel, Klaus-Dieter, Zeitschrift fur Chemie, 1985, vol. 25, # 9, p. 331 - 332摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Thioimidazoline based compounds reverse glucocorticoid resistance in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia xenografts摘要:糖皮质激素是小儿急性淋巴细胞白血病化疗方案的重要组成部分,对糖皮质激素治疗的初次反应不佳预示着较差的预后。DOI:10.1039/c5ob00779h
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE AND 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO))MÉTHYL]-N-(TÉTRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE ET DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO)MÉTHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'HERBICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG公开号:WO2021013969A1公开(公告)日:2021-01-28The present invention related to compounds of Formula (I): or an agronomically acceptable salt thereof, wherein Q, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are as described herein. The invention further relates to compositions comprising said compounds, to methods of controlling weeds using said compositions, and to the use of compounds of Formula (I) as a herbicide.本发明涉及以下式(I)的化合物或其农业上可接受的盐,其中Q、R2、R3、R4、R5和R6如本文所述。该发明还涉及包含所述化合物的组合物,使用这些组合物控制杂草的方法,以及将式(I)的化合物用作除草剂的用途。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
[EN] HERBICIDALLY ACTIVE HETEROARYL-S?BSTIT?TED CYCLIC DIONES OR DERIVATIVES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DIONES CYCLIQUES SUBSTITUÉES PAR HÉTÉROARYLE À ACTIVITÉ HERBICIDE OU DÉRIVÉS DE CELLES-CI申请人:SYNGENTA LTD公开号:WO2011012862A1公开(公告)日:2011-02-03The invention relates to a compound of formula (I), which is suitable for use as a herbicide wherein G is hydrogen or an agriculturally acceptable metal, sulfonium, ammonium or latentiating group; Q is a unsubstituted or substituted C3-C8 saturated or mono-unsaturated heterocyclyl containing at least one heteroatom selected from O, N and S, or Q is heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; m is 1, 2 or 3; and Het is an optionally substituted monocyclic or bicyclic heteroaromatic ring; and wherein the compound is optionally an agronomically acceptable salt thereof.
-
TRIAZOLE ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
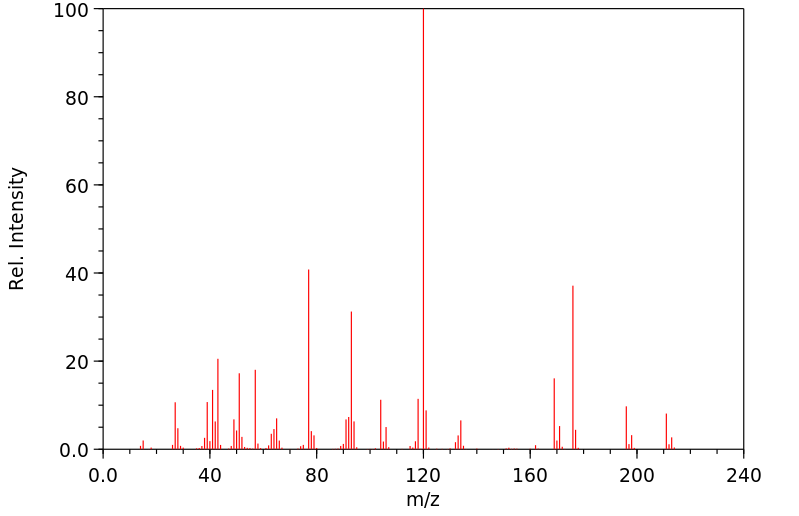
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
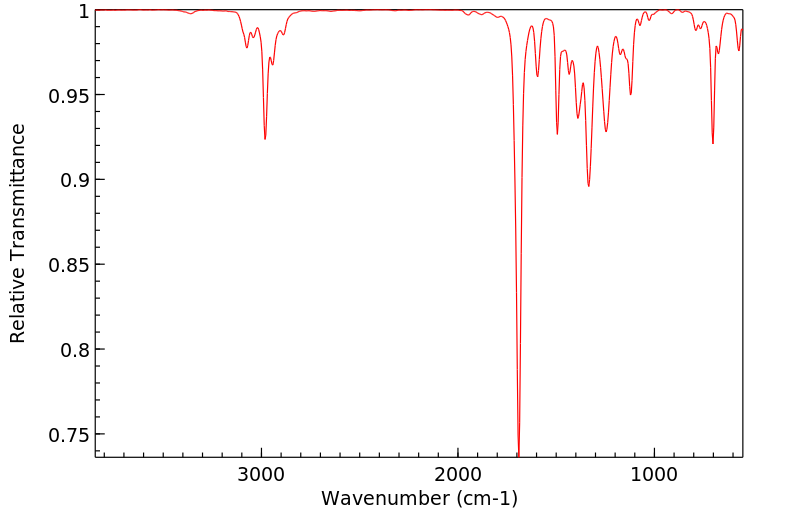
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息