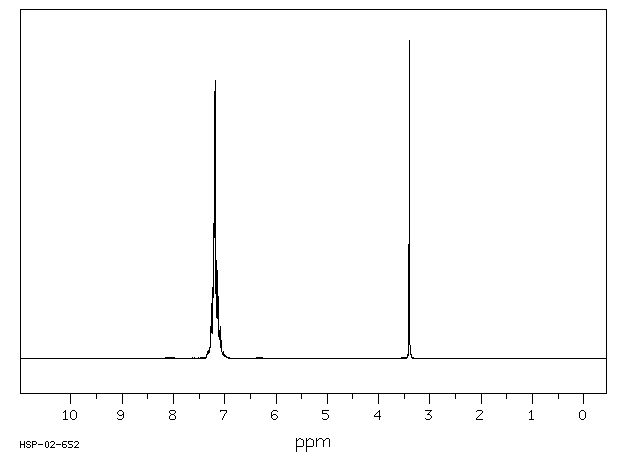
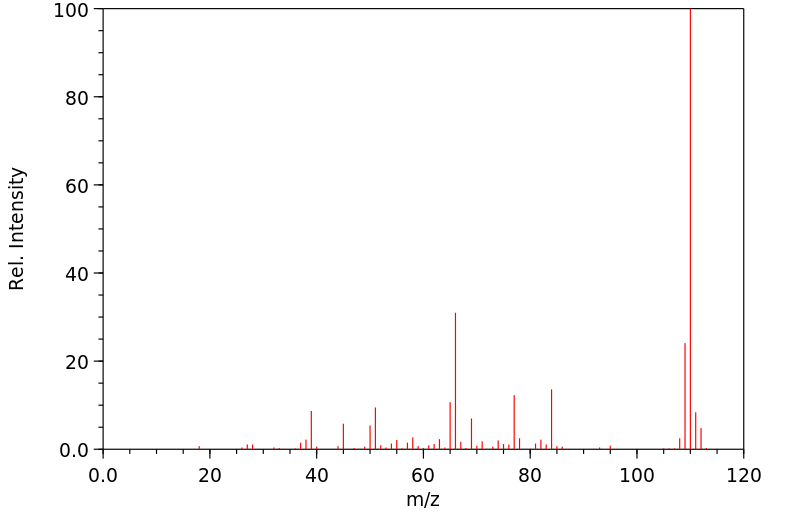
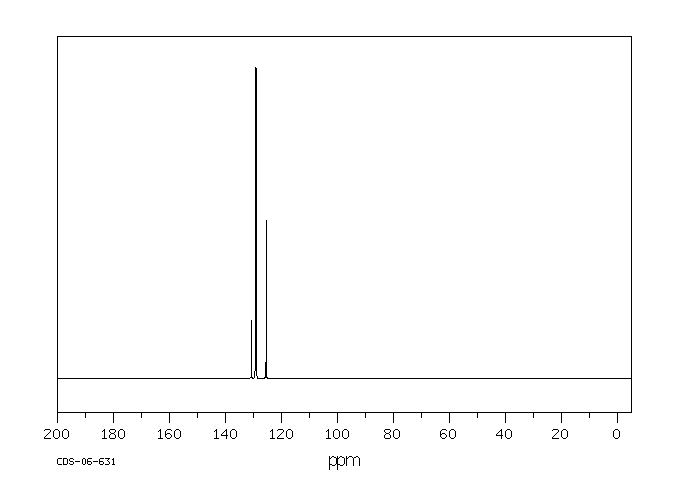
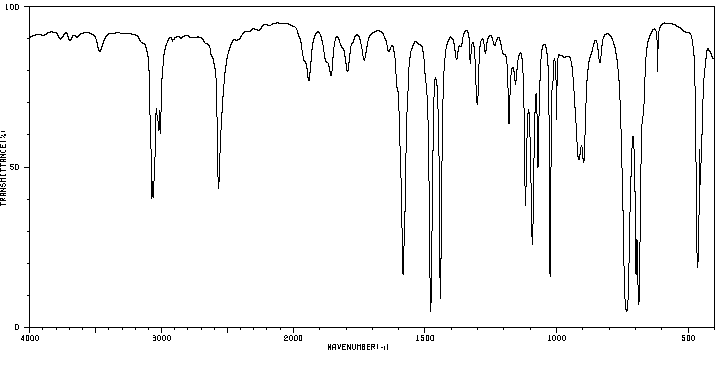
苯硫酚 | 108-98-5
中文名称
苯硫酚
中文别名
(S)-(+)-3-氯-1,2-丙二醇;硫代苯酚;硫酚;苯硫醇;4-溴-1-氯-2-氟苯;苯基硫醇;巯基苯
英文名称
thiophenol
英文别名
Benzenethiol;phenylthiol;PhSH
CAS
108-98-5
化学式
C6H6S
mdl
MFCD00004826
分子量
110.18
InChiKey
RMVRSNDYEFQCLF-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.5
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:1
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
代谢
Yields methyl phenyl thioether probably in rats; phenylthio-beta-d-glucoside in crickets & cockroaches; & phenylthio-beta-d-glucuronide in mice. /From table/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
硫嘌呤甲基转移酶(TPMT)催化硫嘌呤和硫嘧啶药物的S-甲基化。发现了几种非杂环芳香硫醇化合物,包括硫酚,是硫嘌呤甲基转移酶的底物。这些芳香硫醇化合物的一些表观Km常数在纳摩尔范围内,比以前认为的仅是硫嘌呤甲基转移酶底物的硫嘌呤和硫嘧啶低几个数量级。这些观察结果提示,芳基硫醇甲基转移酶可能是这个酶比硫嘌呤甲基转移酶更好的名称。...
Thiopurine methyltransferase (TPMT) catalyzes the S-methylation of thiopurine and thiopyrimidine drugs. Several nonheterocyclic aromatic thiol compounds, including thiophenol, were discovered to be substrates for thiopurine methyltransferase. Apparent Km constants for some of these aromatic thiol compounds were in the nanomolar range, several orders of magnitude lower than those of the thiopurines & thiopyrimidines previously thought to be the only substrates for thiopurine methyltransferase. These observations suggested that aryl thiol methyltransferase might be a better name than thiopurine methyltransferase for this enzyme. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
N-Acetylcysteine was ... elevated in the urine of smokers compared to nonsmoking humans. ... Studies with ... /a human volunteer/ with (14)C-benzene revealed the thiophenol excreted to be derived from the benzene metabolite S-phenyl-N-acetylcysteine. Human smokers also exhibited elevated urinary thiophenol levels.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在大鼠研究中,接受了已知通过谷胱甘肽结合途径代谢的外源性化学物质,结果显示尿液中总硫醇和苯酚硫醇含量增加。进一步的大鼠研究使用放射性碳(14)标记的苯,揭示了排出的苯酚硫醇来源于苯代谢物S-苯基-N-乙酰半胱氨酸。
Studies with rats receiving xenobiotics known to be metabolized via glutathione conjugation, revealed increases in urinary total thiols and thiophenol. ... Further studies with rats with (14)C benzene revealed the thiophenol excreted to be derived from the benzene metabolite S-phenyl-N-acetylcysteine. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:硫酚是一种无色透明的液体或棱柱状晶体,具有类似大蒜的刺鼻、穿透性气味,尤其是当它不纯时。它主要用作蚊幼虫杀虫剂和农药、药物以及琥珀色染料的化学中间体。人类暴露和毒性:硫酚会导致人类红细胞中的氧合血红蛋白转化为高铁血红蛋白,并引起剂量依赖性的氧化应激。动物研究:在兔眼上滴用硫酚会导致严重的刺激、中等程度的发红、结膜的水肿和3-4天的排出物。角膜出现混浊,在2-3周内逐渐加重,变得乳白色,遮盖了瞳孔和虹膜的细节。然而,在2个月内眼睛会恢复。在大鼠妊娠期间给予硫酚会增加着床后损失,减少活产仔数,降低胎儿体重/窝,高剂量组还会增加外部畸形的发生率。总之,在高剂量水平(50 mg/kg/天)观察到母体毒性,表现为母体死亡率、持续的身体重量和体重增加减少,以及治疗期间食物消耗量减少。在给药期间,所有硫酚组都观察到挖掘行为,表明对给药配方有厌恶感。挖掘行为随着剂量的增加和剂量的提前开始而呈剂量相关增加。基于妊娠第6-9天母体体重增加和食物消耗的轻微、暂时性减少,母体毒性的最低观察到有害效应水平(LOAEL)为20 mg/kg/天。在另一项Sprague Dawley大鼠的实验中,F0和F1代的肝脏和肾脏重量随着硫酚剂量的增加而增加,并与中心小叶肝细胞肥大和肾小管变性相关。在给予18和35 mg/kg的Sprague Dawley F0大鼠中观察到精子运动能力下降了5-6%。在所有处理的F1雄性中观察到精子生成抑制,但在F0雄性中没有观察到。在兔子的发育研究中,发育毒性的NOAEL为大于或等于40 mg/kg/天;母体毒性的NOAEL为10 mg/kg/天。硫酚在沙门氏菌鼠伤寒测试菌株TA100和TA98中,无论是否进行代谢激活,都显示出相对的诱变反应。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Thiophenol is a water-white liquid or prism-like crystal with a repulsive, penetrating odor similar to garlic, especially when impure. It is primarily used as a mosquito larvicide and chemical intermediate for pesticides, pharmaceuticals and amber dyes. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Thiophenols causes conversion of oxyhemoglobin to methemoglobin in human red blood cells and dose-dependent oxidative stress. ANIMAL STUDIES: Application of a drop to rabbit eyes caused severe irritation, moderate redness, chemosis of the conjunctiva with discharge for 3-4 days. Corneas developed opacities which gradually increased during 2-3 wk, becoming opalescent and obscuring details of pupil and iris. However, in 2 months the eyes recovered. Thiophenol administration in rats during gestation increased postimplantation loss, decreased the live litter size, decreased fetal body weight/litter, and increased the incidence of external malformations in the high dose group. In summary, maternal toxicity, observed as maternal mortality, a persistent decrease in body weight and weight gain, and decreased in food consumption during the treatment period occurred at the high dose level of 50 mg/kg/day. Rooting behavior was observed in all thiophenol groups during the dosing period indicating an aversion to the dosing formulation. Rooting behavior showed a dose-related increase and an earlier onset with increasing dose. The lowest observed-adverse-effect-level (LOAEL) was 20 mg/kg/day for maternal toxicity based upon minor, transient decreases in maternal weight gain & food consumption on gestation day 6-9. In another experiment in Sprague Dawley rats, F0 and F1 liver and kidney weights increased with increasing dose of thiophenol and were associated with centrilobular hepatocellular hypertrophy and renal tubule degeneration. Decreased (5-6%) sperm motility was observed in Sprague Dawley F0 rats administered 18 and 35 mg/kg. Inhibited spermiation was observed in all treated F1 males but not the F0 males. In developmental study in rabbits NOAEL for developmental toxicity was > or = 40 mg/kg/day; The NOAEL for maternal toxicity was 10 mg/kg/day. Thiophenol, in Salmonella typhimurium tester strains TA100 and TA98, showed relative mutagenic response with and without metabolic activation.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
这种物质可以通过吸入、皮肤接触和摄入被身体吸收。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation, through the skin and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,皮肤吸收,吞食,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
眼睛、皮肤、呼吸系统刺激;皮炎;发绀;咳嗽、喘息、呼吸困难(呼吸困难)、肺水肿、肺炎;头痛、眩晕、中枢神经系统抑制;恶心、呕吐;肾脏、肝脏、脾脏损伤
irritation eyes, skin, respiratory system; dermatitis; cyanosis; cough, wheezing, dyspnea (breathing difficulty), pulmonary edema, pneumonitis; headache, dizziness, central nervous system depression; nausea, vomiting; kidney, liver, spleen damage
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
毒理性
咳嗽。头痛。恶心。喉咙痛。
Cough. Headache. Nausea. Sore throat.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
制备方法与用途
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— antimony triphenylsulphide —— C18H15S3Sb 449.265 苯硫醇 3-mercaptothiophenol 626-04-0 C6H6S2 142.246 —— phenylsulfenyl bromide 28074-23-9 C6H5BrS 189.076 —— benzenesulfenic acid 27610-20-4 C6H6OS 126.179 茴香硫醚 methyl-phenyl-thioether 100-68-5 C7H8S 124.207 苯次磺酰氯 benzenesulfenyl chloride 931-59-9 C6H5ClS 144.625 4-甲苯硫酚 para-thiocresol 106-45-6 C7H8S 124.207 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— antimony triphenylsulphide —— C18H15S3Sb 449.265 苯硫醇酸三甲基锡烷鎓 (phenylthio)trimethylstannane 1007-27-8 C9H14SSn 272.986 —— (Et)3tin(phenylthiolate) 1012-56-2 C12H20SSn 315.067 1,2-苯二硫醇 1,2-Benzenedithiol 17534-15-5 C6H6S2 142.246 —— phenylsulfenyl bromide 28074-23-9 C6H5BrS 189.076 茴香硫醚 methyl-phenyl-thioether 100-68-5 C7H8S 124.207 苯次磺酰氯 benzenesulfenyl chloride 931-59-9 C6H5ClS 144.625 苯基汞 benzenethiolato(phenyl)mercury(II) 5980-94-9 C12H10HgS 386.867 甲基-<sup>13</sup>C苯基硫醚 [13C]methyl phenyl sulfide 91597-65-8 C7H8S 125.196 —— Phenylmercaptoboran 6178-50-3 C6H7BS 121.999 —— Phenyl-germyl-sulfid 21737-95-1 C6H8GeS 184.786 —— d-thiophenol 15570-03-3 C6H6S 111.172 —— phenyl disulphide 31819-07-5 C6H6S2 142.246 4-甲苯硫酚 para-thiocresol 106-45-6 C7H8S 124.207 - 1
- 2
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:使用氯胺-T从硫醇一锅法合成磺酰胺和磺酰叠氮摘要:描述了由硫醇方便地合成磺酰胺和磺酰叠氮化物。通过用氯胺-T(= N-氯代甲苯磺酰胺= N-氯--4-甲基苯磺酰胺),四丁基氯化铵(Bu 4 NCl)和H 2 O氧化,可以完成从硫醇中磺酰氯的原位制备。在同一锅中与过量的胺或NaN 3反应。DOI:10.1002/hlca.201200648
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Dual Pathways in the Solvolyses of Phenyl Chlorothioformate摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo970657b
-
作为试剂:描述:tert-butyl (S)-(3-(isoquinolin-6-ylamino)-3-oxo-2-phenylpropyl)(2-((2-nitrophenyl)sulfonyl)-5,8,11-trioxa-2-azatridecan-13-yl)carbamate 在 potassium carbonate 、 苯硫酚 、 potassium iodide 作用下, 以 二氯甲烷 、 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 20.0h, 生成 tert-butyl (2R,5R)-4-(2-(6-(4-fluorobenzyl)-5-(14-((S)-3-(isoquinolin-6-ylamino)-3-oxo-2-phenylpropyl)-2,17,17-trimethyl-15-oxo-5,8,11,16-tetraoxa-2,14-diazaoctadecyl)-3,3-dimethyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyridin-1-yl)-2-oxoethyl)-5-(methoxymethyl)-2-methylpiperazine-1-carboxylate参考文献:名称:WO2024071371A1摘要:公开号:
文献信息
-
Copper-Mediated Direct Sulfenylation of 4-Hydroxyquinolinones and 4-Hydroxypyridones with Aryl Thiols via a C−H Functionalization Process作者:Tao Guo、Hongyan WangDOI:10.1055/s-0036-1588829日期:2017.9
An efficient approach for the direct sulfanylation of 4-hydroxyquinolinones and 4-hydroxypyridones with aryl thiols in the presence of CuI/DMSO has been developed. The substrate scope is broad, allowing facile synthesis of a range of structurally diverse 3-sulfanyl-4-hydroxyquinolinones and 3-sulfanyl-4-hydroxypyridones in good efficiency.
-
Synthesis of Sulfonylhydrazine-1,2-dicarboxylates from Thiols and Dialkyl Azodicarboxylates作者:Jiaxi Xu、Bingnan Zhou、Xiao YangDOI:10.1055/s-0036-1588108日期:——thiols/thiophenols to dialkyl azodicarboxylates and subsequent oxidation with MCPBA. The protocol represents the first application of sulfenylhydrazines as precursors to sulfonylhydrazine derivatives, leading to a novel and effective method for the synthesis of sulfonylhydrazines. 1-Sulfonylhydrazine-1,2-dicarboxylates are efficiently prepared via nucleophilic addition of thiols/thiophenols to dialkyl azodicarboxylates
-
[EN] BENZAMIDE OR BENZAMINE COMPOUNDS USEFUL AS ANTICANCER AGENTS FOR THE TREATMENT OF HUMAN CANCERS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS BENZAMIDE OU BENZAMINE À UTILISER EN TANT QU'ANTICANCÉREUX POUR LE TRAITEMENT DE CANCERS HUMAINS申请人:UNIV TEXAS公开号:WO2017007634A1公开(公告)日:2017-01-12The described invention provides small molecule anti-cancer compounds for treating tumors that respond to cholesterol biosynthesis inhibition. The compounds selectively inhibit the cholesterol biosynthetic pathway in tumor-derived cancer cells, but do not affect normally dividing cells.
-
Expanding the Scope of Hypervalent Iodine Reagents for Perfluoroalkylation: From Trifluoromethyl to Functionalized Perfluoroethyl作者:Václav Matoušek、Jiří Václavík、Peter Hájek、Julie Charpentier、Zsófia E. Blastik、Ewa Pietrasiak、Alena Budinská、Antonio Togni、Petr BeierDOI:10.1002/chem.201503531日期:2016.1.4A series of new hypervalent iodine reagents based on the 1,3‐dihydro‐3,3‐dimethyl‐1,2‐benziodoxole and 1,2‐benziodoxol‐3‐(1H)‐one scaffolds, which contain a functionalized tetrafluoroethyl group, have been prepared, characterized, and used in synthetic applications. Their corresponding electrophilic fluoroalkylation reactions with various sulfur, oxygen, phosphorus, and carbon‐centered nucleophiles
-
[EN] HYPERVALENT IODINE CF2CF2X REAGENTS AND THEIR USE<br/>[FR] RÉACTIFS CF2CF2X À BASE D'IODE HYPERVALENT ET LEUR UTILISATION申请人:ETH ZUERICH公开号:WO2016019475A1公开(公告)日:2016-02-11A hypervalent iodine of formula (I) or formula (II) wherein R is a nucleophile and a method for their production is described. Such compounds can be used for fluoroethylation of compounds carrying a reactive group. A preferred compound carrying a reactive group is cystein in any environment such as peptide targets.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
邻氯苯硫酚
邻巯基苯乙酮肟
苯硫醇,4-氨基-2,5-二氟-
苯硫醇,2-[(丙基硫代)甲基]-
苯硫醇,2-(氨基甲基)-6-氟-
苯硫醇
苯硫酚钾
苯硫酚钠
苯硫酚
苯六硫酚
甲苯-3,4-二硫酚
烯丙基(邻巯基苯基)甲基硫醚
戊甲基苯硫醇
对氟苯硫酚
对叔丁基硫酚
对-(三甲基甲硅烷)苯硫酚
四巯基苯
五氯苯硫酚锌盐
五氯苯硫酚
五氟苯硫酚
三(巯基苯基)(甲基)硅烷
S-(2-溴-2-氯-1,1-二氟乙基)半胱氨酸
6-氨基-2-氟-3-甲基苯硫醇
6-氨基-2,3-二氟苯硫醇
5-溴-1,3-苯基二硫醇
5-氯-2-甲基苯硫酚
5-氯-2-(甲硫基)苯硫酚
5-氨基-2-氯-4-氟苯硫醇
5-氟-2-甲氧基苯硫醇
5-氟-2-甲基硫代苯酚
5-氟-2-巯基苄醇
4H-吡喃-4-酮,2,3-二氢-2-甲基-,(2R)-(9CI)
4-辛氧基苯硫醇
4-羟基苯硫醇钠
4-羟基苯硫酚
4-羟-3-甲基苯硫酚
4-碘代苯-1-硫醇
4-甲苯硫酚
4-甲硫基苯硫醇
4-甲氧基苯硫酚
4-甲氧基-3-<(2-甲氧基吡啶-5-基)甲基>苯硫酚
4-甲氧基-2-硫基苯甲醛
4-甲氧基-2-甲基硫代苯酚
4-甲基苯硫醇铅
4-甲基磺酰氧基苯硫酚
4-甲基-2-硫基苯甲醛
4-甲基-2,3,5,6-四氟苯硫酚
4-环戊基苯硫醇
4-环己基-苯硫酚
4-环丙基苯硫醇