氟乙酸 | 144-49-0
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:35.2 °C
-
沸点:165 °C
-
密度:1.3693 g/cm3(Temp: 36 °C)
-
物理描述:Fluoroacetic acid appears as a colorless crystalline solid. May be toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals.
-
颜色/状态:Needles
-
溶解度:Miscible with water (1.0X10+6 mg/L) at 25 °C
-
蒸汽压力:1.27 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.24e-08 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 稳定性:稳定。
- 禁配物:强氧化剂、碱类。
- 避免接触的条件:受热。
- 聚合危害:不聚合。
- 分解产物:氟化氢。
-
分解:When heated to decomposition, it emits highly toxic fumes of /hydrogen fluoride and sodium oxides/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 2.59
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.2
-
重原子数:5
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:37.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1
-
危险品标志:T+,N
-
安全说明:S20,S22,S26,S36/37/39,S45,S61
-
危险类别码:R20/21/22
-
海关编码:2915900090
-
包装等级:I
-
危险类别:6.1(a)
-
危险品运输编号:2642
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61099 |
| CAS: | 144-49-0 |
| 中文名称: | 氟乙酸 |
| 英文名称: | fluoroacetic |
| 别 名: | 氟醋酸 |
| 分子式: | C 2 H 3 FO 2 ;CH 3 COOF |
| 分子量: | 78.04 |
| 熔 点: | 33℃ |
| 密 度: | |
| 蒸汽压: | |
| 溶解性: | 溶于水、乙醇 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 无色或白色结晶固体 |
| 危险标记: | 13(剧毒品) |
| 用 途: | 用于制造农药、杀鼠药 |
2.对环境的影响: 一、健康危害 侵入途径: 吸入、食入、经皮吸收。 健康危害:急性中毒以中枢神经系统和心脏损害为主。口服中毒时先有呕吐、大量流泻、麻木感、上腹痛、精神恍惚、恐惧感、肌肉震颤、视力障碍、后出现癫痫发作、呼吸抑制、心率紊乱和心搏骤停。患者可因心搏骤停、抽搐发作时窒息或呼吸衰竭而死亡。 二、毒理学资料及环境行为 毒性:高毒类。 急性毒性:LD504.6mg/Kg(大鼠经口);0.28mg/Kg(大鼠经皮);人口服2~10mg/kg,致死量。 危险特性:遇明火、高热可燃。受热分解放出有毒的氟化氢。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氟化氢。 3.现场应急监测方法: 4.实验室监测方法: 城市废物焚化炉烟道气体中卤代有机酸的鉴定[刊,英]/Mowrer J.;Nordin J.//Chemosphere.-1987,16(6).-1181~1192 《分析化学文摘》1989.3 5.环境标准: 6.应急处理处置方法: 一、泄漏应急处理 隔离泄漏污染区,限制出入。建议应急处理人员戴自给正压式呼吸器,穿防毒服。不要直接接触泄漏物。小量泄漏:避免扬尘,用洁净的铲子收集于干燥、洁净、有盖的容器中。大量泄漏:用塑料布、帆布覆盖,减少飞散。然后收集、回收或运至废物处理场所处置。 二、防护措施 呼吸系统防护:可能接触其蒸气时,必须佩戴自吸过滤式防毒面具(全面罩)。可能接触其粉尘时,建议佩戴头罩型电动送风过滤式防尘呼吸器。 眼睛防护:呼吸系统防护中已作防护。 身体防护:穿连衣式胶布防毒衣。 手防护:戴橡胶耐酸碱手套。 其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作毕,彻底清洗。工作服不准带至非作业场所。单独存放被毒物污染的衣服,洗后备用。保持良好的卫生习惯。 三、急救措施 皮肤接触:脱去被污染的衣着,用肥皂水和清水彻底冲洗皮肤,就医。 眼睛接触:提起眼睑,用流动清水或生理盐水冲洗,就医。 吸入:迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。保持呼吸道通畅。如呼吸困难,给输氧。如呼吸停止,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 食入:催吐。洗胃给饮牛奶或蛋清。就医。 灭火方法:消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服。灭火剂:雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、二氧化碳、砂土。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:[EN] IMIDAZOPYRROLIDINONE DERIVATIVES AND THEIR USE IN THE TREATMENT OF DISEASE
[FR] DÉRIVÉS IMIDAZOPYRROLIDINONE ET LEUR UTILISATION DANS LE TRAITEMENT DE MALADIES摘要:本发明提供了化合物(I)或其药学上可接受的盐;制造本发明化合物的方法及其治疗用途。本发明还提供了药理活性剂的组合和药物组合物。公开号:WO2014191894A1 -
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:银催化杂芳烃与α-氟代羧酸的单氟烷基化:溶剂效应的洞察摘要:已经开发了一种温和有效的方法,用于用易于获得且廉价的 α-氟羧酸直接 C-H 单氟烷基化杂芳烃。这种银催化的反应在温和条件下以良好的收率提供单和双单氟烷基化杂芳烃,并详细讨论了溶剂对单氟烷基化反应的影响。DOI:10.1039/d1cc06466e
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:一种合成2-氯吡啶的方法摘要:本发明公开了一种合成2-氯吡啶的方法。该方法的步骤为将吡啶和溶剂加入到500mL的容器中,压力控制在常压条件,搅拌10-20min,然后滴加醋酸氟,控制温度不超过30℃;将反应混合物移至500mL容器中,升温至50℃-70℃,真空度0.07-0.09MPa的条件下进行减压蒸馏,等到没有液体蒸出之后,剩余的物料即为2-氯吡啶。本发明方法的氯化并不需要氯气、三氯化磷、五氯化磷、三氯氧磷和光气等剧毒物质作为氯代试剂,而是用了二氯甲烷作为氯代试剂,工艺生产安全可靠;反应在常温常压下进行,2-氯吡啶的产率达到80%。公开号:CN105669534A
文献信息
-
[EN] METHODS OF TREATMENT OF AMYLOIDOSIS USING ASPARTYL-PROTEASE INIHIBITORS<br/>[FR] PROCEDES DE TRAITEMENT D'AMYLOIDOSE UTILISANT DES INHIBITEURS DE PROTEASE ASPARTYLE申请人:ELAN PHARM INC公开号:WO2005070407A1公开(公告)日:2005-08-04The invention relates to acetyl 2-hydroxy-1,3-diaminospirocyclohexanes and derivatives thereof that are useful in treating diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with amyloidosis. Amyloidosis refers to a collection of diseases, disorders, and conditions associated with abnormal deposition of A-beta protein.
-
Synthetic Routes towards Fluorine-Containing Amino Sugars: Synthesis of Fluorinated Analogues of Tomosamine and 4-Amino-4-deoxyarabinose作者:Christopher Albler、Walther SchmidDOI:10.1002/ejoc.201301614日期:2014.4Fluorinated analogues of bioactive amino sugars are of high interest in medicinal chemistry. We developed a straightforward synthetic route towards this class of carbohydrates by applying a titanium-mediated aldol addition. Thus, two-carbon chain elongations of serine- and threonine-derived aldehydes with a chiral fluoroacetyl-oxazolidinone could be achieved in good yields and excellent diastereoselectivities
-
Organocatalytic Enantioselective Synthesis of α-Fluoro-β-amino Acid Derivatives作者:Matthew R. Straub、Vladimir B. BirmanDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.8b03297日期:2018.12.7catalyst HBTM-2 generates 3-fluoro-β-lactams with high enantio- and diastereoselectivity. These reactive compounds are opened with alcohols or amines to produce the corresponding α-fluoro-β-amino acid derivatives in moderate yields.
-
Hapten Design and Monoclonal Antibody to Fluoroacetamide, a Small and Highly Toxic Chemical作者:Ling Yang、Xiya Zhang、Dongshuai Shen、Xuezhi Yu、Yuan Li、Kai Wen、Jianzhong Shen、Zhanhui WangDOI:10.3390/biom10070986日期:——Fluoroacetamide (FAM) is a small (77 Da) and highly toxic chemical, formerly used as a rodenticide and potentially as a poison by terrorists. Poisoning with FAM has occurred in humans, but few reliably rapid detection methods and antidotes have been reported. Therefore, producing a specific antibody to FAM is not only critical for the development of a fast diagnostic but also a potential treatment氟乙酰胺(FAM)是一种小型(77 Da)的剧毒化学品,以前用作杀鼠剂,并有可能被恐怖分子用作毒药。FAM中毒已在人类中发生,但几乎没有可靠的快速检测方法和解毒剂的报道。因此,产生针对FAM的特异性抗体不仅对快速诊断的发展至关重要,而且对潜在治疗也至关重要。但是,实现这一目标是一个巨大的挑战,主要是由于FAM的分子量非常低。在这里,我们首次设计了两组FAM半抗原,借助线性脂肪族或苯基间隔基臂最大限度地暴露了氟或氨基。有趣的是,在半抗原末端带有氟的半抗原并未诱导针对FAM的抗体反应,在远端带有氨基的半抗原和含苯基的间隔臂触发了明显的特异性抗体反应。最后,使用IC成功获得了名为5D11的单克隆抗体(mAb)50的值为97μgmL -1,与其他9个功能和结构类似物的交叉反应性可忽略不计。
-
Synthetic Methods and Reactions. Part 106. Suppression of anchimerically assisted rearrangement products in the synthesis of ?-fluorocarboxylic acids from ?-amino acids with 48:52 (w/w) hydrogen fluoride/pyridine [1]作者:George A. Olah、G. K. Surya Prakash、Yah Li ChaoDOI:10.1002/hlca.19810640806日期:1981.12.16Anchimerically assisted rearrangement, observed in the fluorination of some α-amino acids with 70 : 30 (w/w) hydrogen fluoride/pyridine (by weight) in the presence of NaNO2, is substantially or fully suppressed by using the less acidic reagent 48 : 52 (w/w) hydrogen fluoride/pyridine.
表征谱图
-
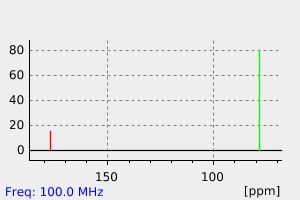
氢谱1HNMR
-
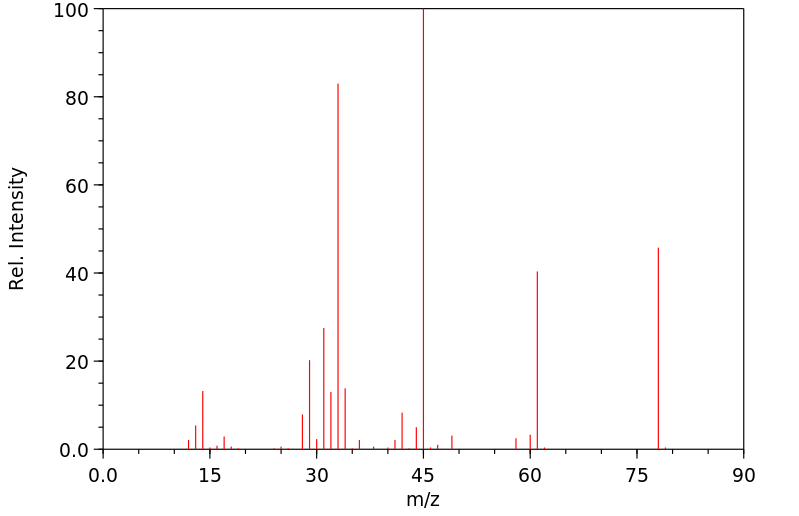
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息