2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯 | 33697-53-9
中文名称
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
中文别名
——
英文名称
ethyl 2-ethyl-2-methylacetoacetate
英文别名
2-ethyl-2-methyl-acetoacetic acid ethyl ester;2-Aethyl-2-methyl-acetessigsaeure-aethylester;Ethyl 2-ethyl-2-methyl-3-oxobutanoate
CAS
33697-53-9
化学式
C9H16O3
mdl
MFCD00191433
分子量
172.224
InChiKey
NWMTWESXONQJPU-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:199 °C
-
密度:0,98 g/cm3
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.6
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.777
-
拓扑面积:43.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2918300090
SDS
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Ethyl 2-Ethyl-2-methylacetoacetate
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第4级
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 警告
危险描述 可燃液体
防范说明
[预防] 远离明火/热表面。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
百分比: >93.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 33697-53-9
俗名: 2-Ethyl-2-methylacetoacetic Acid Ethyl Ester
分子式: C9H16O3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离明火和热表面。
采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 使用封闭系统,通风。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 液体
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 199 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.98
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
模块 9. 理化特性
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 明火
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Ethyl 2-Ethyl-2-methylacetoacetate
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害
易燃液体 第4级
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 警告
危险描述 可燃液体
防范说明
[预防] 远离明火/热表面。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[储存] 存放于通风良好处。保持凉爽。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
百分比: >93.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 33697-53-9
俗名: 2-Ethyl-2-methylacetoacetic Acid Ethyl Ester
分子式: C9H16O3
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,二氧化碳
不适用的灭火剂: 水(有可能扩大灾情。)
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。确保足够通风。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 用合适的吸收剂(如:旧布,干砂,土,锯屑)吸收泄漏物。一旦大量泄漏,筑堤控
制。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的法律法规废弃处置。
副危险性的防护措施 移除所有火源。一旦发生火灾应该准备灭火器。使用防火花工具和防爆设备。
7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止烟雾产生。远离明火和热表面。
采取措施防止静电积累。使用防爆设备。处理后彻底清洗双手和脸。
注意事项: 使用封闭系统,通风。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗、通风良好处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防毒面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 液体
外观: 透明
颜色: 无色-黄色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 199 °C
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 0.98
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
模块 9. 理化特性
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
避免接触的条件: 明火
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守
国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯 2-acetylpropanoic acid ethyl ester 609-14-3 C7H12O3 144.17
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯 在 溴 作用下, 生成 2-ethyl-4-bromo-2-methyl-acetoacetic acid ethyl ester参考文献:名称:Method for Synthesis of 2,5-Dioxane-1,4-Diones摘要:本发明涉及一种合成2,5-二氧杂环戊二酮(式(I))的新方法,包括氧化具有式(II)的环状化合物的酮基,其中R1、R2、R3和R4独立地表示氢原子、卤素、(C2-C6)烯基、(C3-C7)环烷基、环己烯基和具有式-(CH2)m-V-W的基团。公开号:US20080004453A1
-
作为产物:描述:2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯 在 sodium hydride 作用下, 生成 2-乙基-2-甲基乙酰乙酸乙酯参考文献:名称:Method for Synthesis of 2,5-Dioxane-1,4-Diones摘要:本发明涉及一种合成2,5-二氧杂环戊二酮(式(I))的新方法,包括氧化具有式(II)的环状化合物的酮基,其中R1、R2、R3和R4独立地表示氢原子、卤素、(C2-C6)烯基、(C3-C7)环烷基、环己烯基和具有式-(CH2)m-V-W的基团。公开号:US20080004453A1
文献信息
-
Experimental and Computational Studies of Palladium-Catalyzed Spirocyclization via a Narasaka–Heck/C(sp<sup>3</sup> or sp<sup>2</sup>)–H Activation Cascade Reaction作者:Wan-Xu Wei、Yuke Li、Ya-Ting Wen、Ming Li、Xue-Song Li、Cui-Tian Wang、Hong-Chao Liu、Yu Xia、Bo-Sheng Zhang、Rui-Qiang Jiao、Yong-Min LiangDOI:10.1021/jacs.1c04114日期:2021.5.26es via a palladium-catalyzed tandem Narasaka–Heck/C(sp3 or sp2)–H activation reaction is reported here. The key step in this transformation is the activation of a δ-C–H bond via an in situ generated σ-alkyl-Pd(II) species to form a five-membered spiro-palladacycle intermediate. The concerted metalation-deprotonation (CMD) process, rate-determining step, and energy barrier of the entire reaction were
-
Rhenium(I)-Catalyzed Cyclization of Silyl Enol Ethers Containing a Propargyl Carboxylate Moiety: Versatile Access to Highly Substituted Phenols作者:Kodai Saito、Yuji Onizawa、Hiroyuki Kusama、Nobuharu IwasawaDOI:10.1002/chem.200903586日期:2010.4.26containing an acyloxy substituent at the propargylic position gave highly substituted phenols in good yields (see scheme). Depending on the structure of the silyl enol ether, either nucleophilic addition of this moiety or 1,2‐acyloxy migration occurs to give two kinds of synthetically useful, substituted phenols.
-
A convenient synthesis of tetrazole, precursors of α-dialkylated α-amino acids, by reaction of trimethylsilyl azide with α-dialkylated β-ketoesters作者:Henri-Jean Cristau、Xavier Marat、Jean-Pierre Vors、Jean-Luc PiratDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(03)00444-1日期:2003.4The Schmidt rearrangement using trimethylsilyl azide with various α-dialkylated β-keto esters affords a convenient synthesis of tetrazole, precursors of α-dialkylated α-amino acids.
-
Components and Catalysis for the Polymerization of Olefins申请人:Gulevich Yuri公开号:US20070208150A1公开(公告)日:2007-09-06The present invention relates to a solid catalyst component for the polymerization of olefins CH 2 =CHR in which R is hydrogen or a hydrocarbon radical with 1-12 carbon atoms, comprising Mg, Ti, halogen and an electron donor selected from β-keto-ester derivatives of a particular formula. Said catalyst components when used in the polymerization of olefins, and in particular of propylene, are capable to give polymers in high yields and with high isotactic index expressed in terms of high xylene insolubility.
-
Ink composition and image forming method申请人:Fujifilm Corporation公开号:EP2626390A2公开(公告)日:2013-08-14An inkjet ink composition includes: (a) particles of a polymer compound having at least one reactive functional group selected from the group consisting of an epoxy group, an acetoacetoxy group, a halomethyl group, a carboxylic acid anhydride, an amino group, a hydroxyl group, a phenolic hydroxyl group, and a carboxy group;(b) a reactive compound having a functional group that reacts with the reactive functional group of the (a) particles of the polymer compound by energy application; (c) a coloring agent; and (d) a water-soluble organic solvent.
表征谱图
-
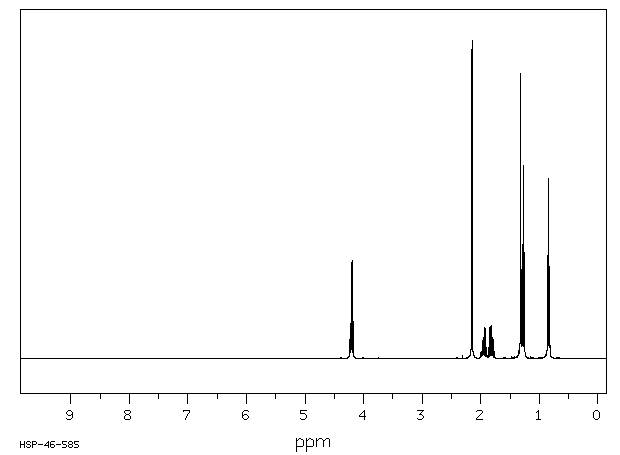
氢谱1HNMR
-
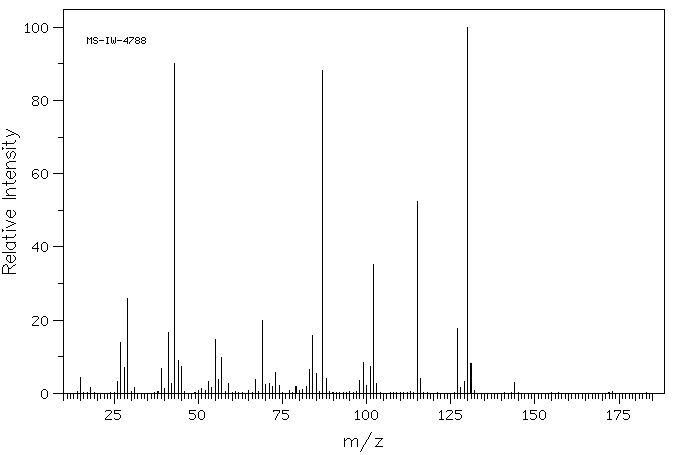
质谱MS
-
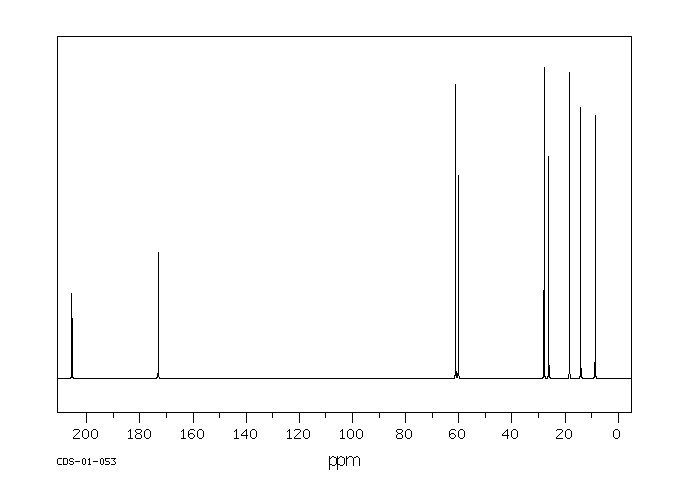
碳谱13CNMR
-
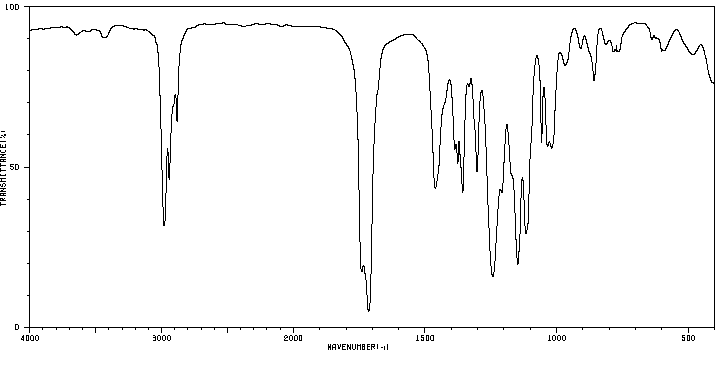
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
马来酰基乙酸
顺-3-己烯-1-丙酮酸
青霉酸
钠氟草酰乙酸二乙酯
醚化物
酮霉素
辛酸,2,4-二羰基-,乙基酯
草酸乙酯钠盐
草酰乙酸二乙酯钠盐
草酰乙酸二乙酯
草酰乙酸
草酰丙酸二乙酯
苯乙酰丙二酸二乙酯
苯丁酸,b-羰基-,2-丙烯基酯
聚氧化乙烯
羟基-(3-羟基-2,3-二氧代丙基)-氧代鏻
磷酸二氢2-{(E)-2-[4-(二乙胺基)-2-甲基苯基]乙烯基}-1,3,3-三甲基-3H-吲哚正离子
碘化镝
硬脂酰乙酸乙酯
甲氧基乙酸乙酯
甲氧基乙酰乙酸酯
甲基氧代琥珀酸二甲盐
甲基4-环己基-3-氧代丁酸酯
甲基4-氯-3-氧代戊酸酯
甲基4-氧代癸酸酯
甲基4-氧代月桂酸酯
甲基4-(甲氧基-甲基磷酰)-2,2,4-三甲基-3-氧代戊酸酯
甲基3-羰基-2-丙酰戊酸酯
甲基3-氧代十五烷酸酯
甲基2-氟-3-氧戊酯
甲基2-氟-3-氧代己酸酯
甲基2-氟-3-氧代丁酸酯
甲基2-乙酰基环丙烷羧酸酯
甲基2-乙酰基-4-甲基-4-戊烯酸酯
甲基2-乙酰基-2-丙-2-烯基戊-4-烯酸酯
甲基2,5-二氟-3-氧代戊酸酯
甲基2,4-二氟-3-氧代戊酸酯
甲基2,4-二氟-3-氧代丁酸酯
甲基1-异丁酰基环戊烷羧酸酯
甲基1-乙酰基环戊烷羧酸酯
甲基1-乙酰基环丙烷羧酸酯
甲基1-乙酰基-2-乙基环丙烷羧酸酯
甲基(2Z,4E,6E)-2-乙酰基-7-(二甲基氨基)-2,4,6-庚三烯酸酯
甲基(2S)-2-甲基-4-氧代戊酸酯
甲基(1S,2R)-2-乙酰基环丙烷羧酸酯
甲基(1R,2R)-2-乙酰基环丙烷羧酸酯
瑞舒伐他汀杂质
瑞舒伐他汀杂质
环氧乙烷基甲基乙酰乙酸酯
环戊戊烯酸,Β-氧代,乙酯