硝基甲烷 | 75-52-5
分子结构分类
中文名称
硝基甲烷
中文别名
硝基甲烷(易制爆);一硝基甲烷
英文名称
nitromethane
英文别名
nitromethae;MeNO2
CAS
75-52-5
化学式
CH3NO2
mdl
MFCD00007400
分子量
61.0403
InChiKey
LYGJENNIWJXYER-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
无色油状液体,能与醇、醚、四氯化碳、二甲基甲酰胺等有机溶剂混溶。它能够溶解染料、油脂、蜡、纤维素衍生物、树脂等物质,尤其对硝酸纤维素和醋酸纤维素有良好的溶解能力。然而,它不与烷烃和环烷烃混合。这种选择性特性可用于烃类的分离及润滑油的精制。硝基甲烷及其所有的硝基烷烃都容易溶解无水三氯化铝,可制成约50%的溶液。溶解后形成的加成产物AlCl3-RNO2用于烃类的烷基化反应中,其催化作用比三氯化铝更强。其水溶液呈弱酸性。此物质易燃、易爆,在操作时需穿戴防护用具。它不吸湿,但激烈撞击时有爆炸危险。
-
化学性质:硝基甲烷的水溶液用石蕊试纸检验呈酸性,例如0.01mol/L的水溶液pH值为6.12;饱和水溶液pH值为4.01;水饱和的硝基甲烷pH值为4.82。硝基甲烷存在互变异构现象,并含有微量的酸硝式结构,在水中的互变异构常数KT=1.1×10-17。酸硝式中氧原子上的氢原子相当活泼,容易生成质子,因此显酸性,能够与强碱作用生成盐。硝基甲烷与氢氧化钠形成的钠盐有爆炸性,此钠盐能与醛类发生亲核加成反应,例如在碱性溶液中与甲醛加成得到β-硝基乙醇。β-硝基醇容易脱水变成不饱和硝基化合物,如硝基甲烷与苯甲醛生成ω-硝基苯乙烯。此外,硝基甲烷可以还原生成甲胺。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
应避免接触的条件:震动、受热
-
聚合危害:不聚合
-
分解产物:氮氧化物
-
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.1
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:45.8
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
Nitromethane is apparently metabolized by different mechanism than nitroethane and nitropropane in that negligible amt of nitrites are found in blood following iv injection of 1 mmol in rabbits.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Rabbit liver homogenate yields nitrite after incubation with nitromethane.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
使用苯巴比妥预处理的大鼠肝微粒体在还原型烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸和氧的存在下,将硝基甲烷转化为丙酮和硝酸盐。向氧化的大鼠肝微粒体悬浮液中加入硝基甲烷,产生了在437纳米处有峰值的底物结合差异光谱,这被解释为细胞色素P450亚硝基复合物的形成。与复合物形成平行,氧化的大鼠肝微粒体在还原型烟酰胺腺嘌呤二核苷酸磷酸依赖反应中催化硝基甲烷生成甲醛。
Liver microsomes from phenobarbital pretreated rats convert nitromethane to acetone and nitrate in presence of the reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate and oxygen. Addition of nitromethane to oxidized rat liver microsomal suspension gave rise to substrate binding difference spectrum with peak at 437 nm, interpreted as formation of cytochrome p450 no complex. Parallel to complex formation, oxidized rat liver microsomes catalyzed prodn of formaldehyde from nitromethane in the reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-dependent reaction.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
甲醛由硝基甲烷生成,在与Fischer 344大鼠肝脏的微粒体孵化后仅发现微量,但在与大鼠鼻腔微粒体孵化后未发现。硝基甲烷抑制了兔肝脏细胞色素P450活性,显然与一氧化碳竞争相同的铁血色蛋白结合位点。
Formaldehyde generated from nitromethane was found only in trace amounts after incubation with microsomes from from Fischer 344 rat liver, but none was found after incubation with rat nasal microsomes. Nitromethane inhibited rabbit liver cytochrome P450 activity, apparently competing for the same ferrohaemochrome- binding sites as carbon monoxide.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:硝基甲烷是一种无色油性液体。它被用作纤维素化合物、聚合物、蜡、脂肪的溶剂;化学合成;模型火箭燃料;汽油添加剂。人类暴露和毒性:吸入的症状包括咳嗽、嗜睡、头痛、恶心、喉咙痛、昏迷和呕吐。有文献记录,4名同事在处理含有硝基甲烷的粘合剂溶剂后出现了过敏性接触手皮炎。这4个病例通过贴片测试得到证实,并在避免过敏原后得到解决。已经报道了一例人类中毒的案例。在那个案例中,一名杂务工暴露于高浓度的硝化纤维和硝基甲烷,导致他的血红蛋白67%转化为高铁血红蛋白和硫化血红蛋白。经过高压氧治疗、输血、腹膜透析然后是6次血液透析后得以恢复。硝基甲烷被确认为动物致癌物,但对人类的相关性未知。动物研究:急性动物研究中最常见的毒性迹象是中枢神经系统(CNS)的抑制和呼吸道轻微刺激。组织病理学变化主要发生在肝脏和肾脏,其中肝脏显示出最明显的损伤,即包膜下损伤、局部坏死、脂肪浸润、充血和水肿。在给小鼠单次或三次腹腔注射类似药物后,研究了硫化血红蛋白血症和高铁血红蛋白血症的形成活性。单次给药后,硝基甲烷没有产生高铁血红蛋白血症。只有在连续给药三次后,硝基甲烷才产生了硫化血红蛋白血症。根据NTP进行的2年吸入研究的条件,没有证据表明硝基甲烷在大鼠中具有致癌活性。基于乳腺纤维腺瘤和癌的增加发生率,有明确证据表明硝基甲烷在大鼠中具有致癌活性。基于哈德氏腺腺瘤和癌的增加发生率,有明确证据表明硝基甲烷在雄性小鼠中具有致癌活性。基于肝脏肿瘤(主要是腺瘤)和哈德氏腺腺瘤和癌的增加发生率,有明确证据表明硝基甲烷在雌性小鼠中具有致癌活性。在暴露于硝基甲烷的雄性和雌性小鼠中,肺泡/支气管腺瘤和癌的增加发生率也被认为是与化学给药有关的。在雌性大鼠中调查了生殖效应。在处理组和对照组大鼠之间,成功交配的百分比、窝大小、幼崽死亡率、出生体重或母性行为没有发现差异。在迷宫学习装置中对2.5个月大的幼崽进行了测试;与对照组相比,处理组大鼠的后代显示出迷宫学习能力受损。在另一项发育研究中,雄性大鼠的尾、附睾和睾丸重量以及精子计数降低。附睾精子活动力呈现剂量反应性下降。雌性小鼠的平均动情周期长度表现出剂量相关的增加。硝基甲烷在含有和不含有活化的鼠伤寒沙门氏菌TA 98和TA 100菌株中不具有诱变性。硝基甲烷进一步使用沙门氏菌试验、果蝇黑腹菌和体内微核试验进行了诱变性测试。硝基甲烷在这三个诱变测试系统中都是不活跃的。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Nitromethane is a colorless oily liquid. It is used as solvent for cellulosic compounds, polymers, waxes, fats; chemical synthesis; model rocket fuel; gasoline additive. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: Symptoms of inhalation include cough, drowsiness, headache, nausea, sore throat, unconsciousness, and vomiting. Allergic contact hand dermatitis was documented in 4 coworkers who similarly handled an adhesive solvent containing nitromethane. All 4 cases were confirmed by patch testing and resolved after allergen avoidance. One case of human poisoning has been reported. In that case, a handyman was exposed to high concentrations of nitrocellulose and nitromethane resulting in a 67% conversion of his hemoglobin to methemoglobin and sulfhemoglobin. Treatment with hyperbaric oxygen, transfusion, peritoneal dialysis and then 6 sessions of hemodialysis resulted in recovery. Nitromethane is confirmed animal carcinogen with unknown relevance to humans. ANIMAL STUDIES: The most common signs of toxicity in acute animal studies were central nervous system (CNS) depression and slight irritation of the respiratory tract. Histopathologic changes were mainly in the liver and kidneys with the liver showing the most prominent injury, ie subcapsular damage, focal necrosis, fatty infiltration, congestion, and edema. The sulfhemoglobinemia and methemoglobinemia formation activities of similar drugs were studied in mice after administration of one or three ip doses. After administration of a single dose, nitromethane did not produce methemoglobinemia. Nitromethane produced sulfhemoglobinemia only after administration of three consecutive doses. Under the conditions of 2 yr inhalation studies conducted by NTP, there was no evidence of carcinogenic activity of nitromethane in male rats. There was clear evidence of carcinogenic activity of nitromethane in female rats based on increased incidences of mammary gland fibroadenomas and carcinomas. There was clear evidence of carcinogenic activity of nitromethane in male mice based on increased incidences of harderian gland adenomas and carcinomas. There was clear evidence of carcinogenic activity in female mice, based on increased incidences of liver neoplasms (primarily adenomas) and harderian gland adenomas and carcinomas. Increased incidences of alveolar/bronchiolar adenomas and carcinomas in male and female mice exposed to nitromethane were also considered to be related to chemical administration. Reproductive effects were investigated in female rats. No differences were found between treated and control rats in percentages of successful matings, litter size, pup mortality, birth weight, or maternal behavior. Pups were tested at 2.5 months of age in a maze-learning apparatus; the offspring of treated rats showed impaired maze learning when compared to controls. In another developmental study male rats had decreased caudal, epididymal, and testicular weights and decreased sperm counts. There was a dose-response decrease in epididymal sperm motility. Female mice showed a dose-related increase in the average estrous cycle length. Nitromethane was not mutagenic in Salmonella typhimurium strains TA 98 and TA 100 with and without activation. Nitromethane was further tested for mutagenicity of using the Salmonella assay, Drosophila melanogaster and an in vivo micronucleus test. Nitromethane was inactive in each of the three mutagenic test systems.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A3; 已确认的动物致癌物,对人类的相关性未知。
A3; Confirmed animal carcinogen with unknown relevance to humans.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:硝基甲烷
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:Nitromethane
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:2B组:可能对人类致癌
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 2B: Possibly carcinogenic to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构专著:第77卷:(2000年)一些工业化学品
IARC Monographs:Volume 77: (2000) Some Industrial Chemicals
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
硝基石蜡通过肺部吸收,也可通过胃肠道吸收。皮肤应用没有足够的证据表明会被吸收到足以导致全身性伤害的程度。
Nitroparaffins are absorbed through lung and from GI tract. Applications to skin give no evidence of sufficient absorption to result in systemic injury. /nitroparaffins/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
制备方法与用途
根据提供的信息,以下是硝基甲烷的主要用途:
-
溶剂:
-
制造炸药和火箭燃料:
- 硝基甲烷可用来制取炸药,如某些类型的烈性炸药。
- 作为火箭推进剂的一部分或直接用作燃料。
-
医药和农药领域:
- 可用于生产药物、杀虫剂及杀菌剂等产品。
- 在制药工业中可用作合成中间体或其他反应试剂。
-
稳定剂与表面活性剂:
- 有时会添加到某些稳定剂或表面活性剂配方中,以提高其性能特性。
-
汽油添加剂:
- 可作为改善燃料品质的添加剂使用,在一定程度上可以提升燃烧效率和减少排放。
-
其他用途:
- 在有机合成领域也有应用价值。
- 作为一种气雾推进剂(虽然这种用途较为少见)。
值得注意的是,尽管硝基甲烷具有上述多种应用潜力,但由于其强烈的爆炸性和毒性特征,在使用过程中必须严格遵守安全规范,并在专业人员指导下进行操作。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 溴代硝基甲烷 bromonitromethane 563-70-2 CH2BrNO2 139.936 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— nitromethyl free radical 16787-85-2 CH2NO2 60.0324 溴代硝基甲烷 bromonitromethane 563-70-2 CH2BrNO2 139.936 硝基乙烷 Nitroethane 79-24-3 C2H5NO2 75.0672 —— deuterio-nitro-methane 23171-70-2 CH3NO2 62.0324 硝基甲醇 Hydroxynitromethan 25731-06-0 CH3NO3 77.0397 碘硝基甲烷 trifluoroiodomethane 25538-43-6 CH2INO2 186.937 硝基乙烯 1-nitroethylene 3638-64-0 C2H3NO2 73.0513 氯硝甲烷 monochloronitromethane 1794-84-9 CH2ClNO2 95.4854
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Kandel, R. J., Journal of Chemical Physics, 1955, vol. 23, p. 84 - 87摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:硫酸二甲酯 在 sodium carbonate 、 sodium nitrite 作用下, 以 水 为溶剂, 35.0~110.0 ℃ 、150.0 kPa 条件下, 以87.34 %的产率得到硝基甲烷参考文献:名称:一种硝基甲烷的连续流合成方法摘要:本发明公开了一种硝基甲烷的连续流合成方法。该方法包括将硫酸二甲酯、亚硝酸盐、催化剂、水混合得到混合物,将所得混合物连续进料到第一反应器中,在第一温度下反应得到第一反应液;将第一反应液连续进料到第二反应器中,在第二温度下反应得到第二反应液;将第二反应液连续进料到蒸馏塔,得到硝基甲烷粗品,再经精馏得到硝基甲烷产品;其中,第一反应器和第二反应器均为平推流反应器,且第一温度小于第二温度。该方法反应条件更为温和,反应过程易于控制,并通过细化并精确控制两个反应阶段的反应温度,减少了副产物的生成和能耗成本,避免了反应过程中起泡剧烈冲料带来的安全隐患,工艺安全性和效率均得到大幅度提高。公开号:CN117466740A
-
作为试剂:描述:5-己烯酸 在 二(氰基苯)二氯化钯 、 silver(I) nitrite 、 copper(II) choride dihydrate 、 硝基甲烷 、 氧气 、 叔丁醇 作用下, 20.0 ℃ 、101.33 kPa 条件下, 反应 6.0h, 以51%的产率得到6-氧代己酸参考文献:名称:亚硝酸盐助催化剂对无偏烯烃的醛选择性瓦克型氧化摘要:违反规则:使用亚硝酸盐助催化剂逆转了Wacker型氧化的高Markovnikov选择性。可以高收率和醛选择性地氧化无偏的脂肪族烯烃,并且可以容忍多个官能团。18 O标记实验表明,醛O原子源自亚硝酸盐。DOI:10.1002/anie.201306756
文献信息
-
[EN] PYRAZOLE DERIVATIVES USEFUL AS INHIBITORS OF FAAH<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE PYRAZOLE UTILES COMME INHIBITEURS DE FAAH申请人:MERCK & CO INC公开号:WO2009151991A1公开(公告)日:2009-12-17The present invention is directed to certain imidazole derivatives which are useful as inhibitors of Fatty Acid Amide Hydrolase (FAAH). The invention is also concerned with pharmaceutical formulations comprising these compounds as active ingredients and the use of the compounds and their formulations in the treatment of certain disorders, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic neuropathy, postherpetic neuralgia, skeletomuscular pain, and fibromyalgia, as well as acute pain, migraine, sleep disorder, Alzheimer disease, and Parkinson's disease
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] SUBSTITUTED BENZYLAMINE COMPOUNDS, THEIR USE IN MEDICINE, AND IN PARTICULAR THE TREATMENT OF HEPATITIS C VIRUS (HCV) INFECTION<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS DE BENZYLAMINE SUBSTITUÉS, LEUR UTILISATION EN MÉDECINE, EN PARTICULIER DANS LE TRAITEMENT D'UNE INFECTION PAR LE VIRUS DE L'HÉPATITE C (VHC)申请人:ASTEX THERAPEUTICS LTD公开号:WO2013064538A1公开(公告)日:2013-05-10The invention provides compounds of the formula (I): or a salt, N-oxide or tautomer thereof, wherein A is CH, CF or nitrogen; E is CH, CF or nitrogen; and R0 is hydrogen or C1-2 alkyl; R1a is selected from CONH2; CO2H; an optionally substituted acyclic C1-8 hydrocarbon group; and an optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic group of 3 to 7 ring members, of which 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4 are heteroatom ring members selected from O, N and S; R2 is selected from hydrogen and a group R2a; R2a is selected from an optionally substituted acyclic d-8 hydrocarbon group; an optionally substituted monocyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic group of 3 to 7 ring members, of which 0, 1 or 2 ring members are heteroatom ring members selected from O, N and S; and an optionally substituted bicyclic heterocyclic group of 9 or 10 ring members, of which 1 or 2 ring members are nitrogen atoms; wherein at least one of R1 and R2 is other than hydrogen; R3 is an optionally substituted 3- to 10-membered monocyclic or bicyclic carbocyclic or heterocyclic ring containing 0, 1, 2 or 3 heteroatom ring members selected from N, O and S; R4a is selected from halogen; cyano; C1-4 alkyl optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; C1-4 alkoxy optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; hydroxy-C1-4 alkyl; and C1-2 alkoxy-C1-4 alkyl; R5 is selected from hydrogen and a substituent R5a; and R5a is selected from C1-2 alkyl optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; C1-3 alkoxy optionally substituted with one or more fluorine atoms; halogen; cyclopropyl; cyano; and amino, The compounds have activity against hepatitis C virus and can be used in the prevention or treatment of hepatitis C viral infections.该发明提供了以下式(I)的化合物,或其盐、N-氧化物或互变异构体,其中A为CH、CF或氮;E为CH、CF或氮;R0为氢或C1-2烷基;R1a选自CONH2;CO2H;一个可选择取代的非环状C1-8碳氢化合物基团;以及一个可选择取代的含有3至7个环成员的单环碳环或杂环基团,其中0、1、2、3或4个是从O、N和S中选择的杂原子环成员;R2选自氢和一个基团R2a;R2a选自一个可选择取代的非环状d-8碳氢化合物基团;一个可选择取代的含有3至7个环成员的单环碳环或杂环基团,其中0、1或2个环成员是从O、N和S中选择的杂原子环成员;以及一个可选择取代的含有9或10个环成员的双环杂环基团,其中1或2个环成员是氮原子;其中R1和R2中至少一个不是氢;R3选自一个可选择取代的含有0、1、2或3个从N、O和S中选择的杂原子环成员的3至10个成员的单环或双环碳环或杂环环;R4a选自卤素;氰基;C1-4烷基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;C1-4烷氧基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;羟基-C1-4烷基;和C1-2烷氧基-C1-4烷基;R5选自氢和一个取代基R5a;R5a选自C1-2烷基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;C1-3烷氧基,可选择取代一个或多个氟原子;卤素;环丙基;氰基;和氨基。这些化合物对丙型肝炎病毒具有活性,并可用于预防或治疗丙型肝炎病毒感染。
-
Cs2CO3-promoted carbon–sulfur bond construction via cross dehydrogenative coupling of thiophenols with acetonitrile作者:Qian Chen、Yulin Huang、Xiaofeng Wang、Chunxiao Wen、Xinxing Yan、Jiekun ZengDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.08.067日期:2017.10construction of carbon–sulfur bonds has been achieved via halogen-free Cs2CO3-promoted cross dehydrogenative coupling (CDC) of thiophenols with acetonitrile. This transformation provides a straightforward route to the synthesis of sulfenylated acetonitriles in up to 80% yield.
-
Synthesis of [3-<sup>13</sup>C]-, [4-<sup>13</sup>C]- and [11-<sup>13</sup>C]-porphobilinogen作者:Prativa B. S. Dawadi、Els A. M. Schulten、Johan LugtenburgDOI:10.1002/jlcr.1602日期:2009.7[4-13C]-porphobilinogen 1a, [3-13C]-porphobilinogen 1b and [11-13C]-porphobilinogen 1c are prepared from [1-13C]-3-(tetrahydropyran-2′-yloxy)-propionaldehyde 2a, methyl [4-13C]-4-nitrobutyrate 3b and [1-13C]-isocyanoacetonitrile 5c, respectively. The building blocks 2, 3 and 5 can be prepared efficiently in any isotopomeric form. Via base-catalyzed condensation of these building blocks porphobilinogen can be enriched with 13C and 15N stable isotopes at any position and combination of positions. Copyright © 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
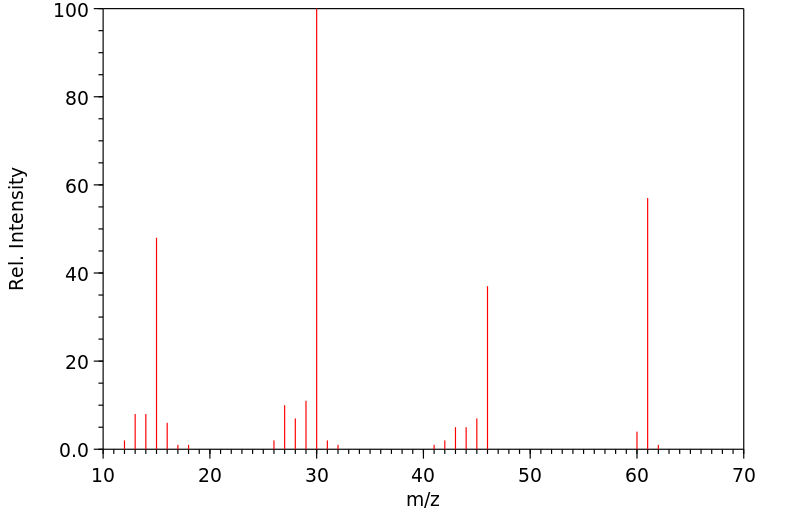
质谱MS
-
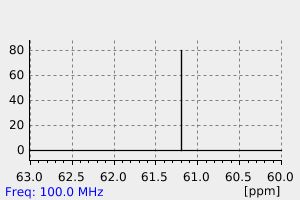
碳谱13CNMR
-
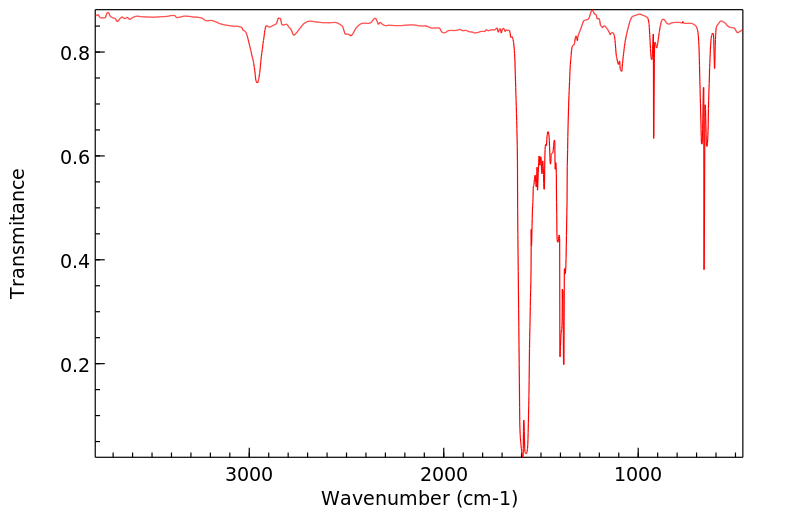
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-2-硝基环己基乙酸酯
顺式-2-硝基-6-甲基环己酮
雷尼替丁杂质18
铝硝基甲烷三氯化物
钾离子载体III
重氮(硝基)甲烷
醛基-七聚乙二醇-叠氮
过氧亚甲基
辛腈,4-氟-4-硝基-7-羰基-
辛烷,1,2-二氯-1-硝基-
赤霉素A4+7(GA4:GA7=65:35)
苄哒唑
羟胺-四聚乙二醇-叠氮
羟胺-三乙二醇-叠氮
米索硝唑
磷酸十二醇酯
碘硝基甲烷
碘化e1,1-二甲基-4-羰基-3,5-二(3-苯基-2-亚丙烯基)哌啶正离子
硝酰胺
硝基脲银(I)复合物
硝基甲醇
硝基甲烷-d3
硝基甲烷-13C,d3
硝基甲烷-13C
硝基甲烷-(15)N
硝基甲烷
硝基甲基甲醇胺
硝基环辛烷
硝基环戊烷
硝基环戊基阴离子
硝基环庚烷
硝基环己烷锂盐
硝基环己烷钾盐
硝基环己烷
硝基环丁烷
硝基氨基甲酸
硝基新戊烷
硝基二乙醇胺
硝基乙醛缩二甲醇
硝基乙醛缩二乙醇
硝基乙腈
硝基乙烷-D5
硝基乙烷-1,1-d2
硝基乙烷
硝基乙烯
硝基丙烷
硝基丙二醛(E,E)-二肟
硝基丙二腈
硝基-(3-硝基-[4]吡啶基)-胺
硝乙醛肟