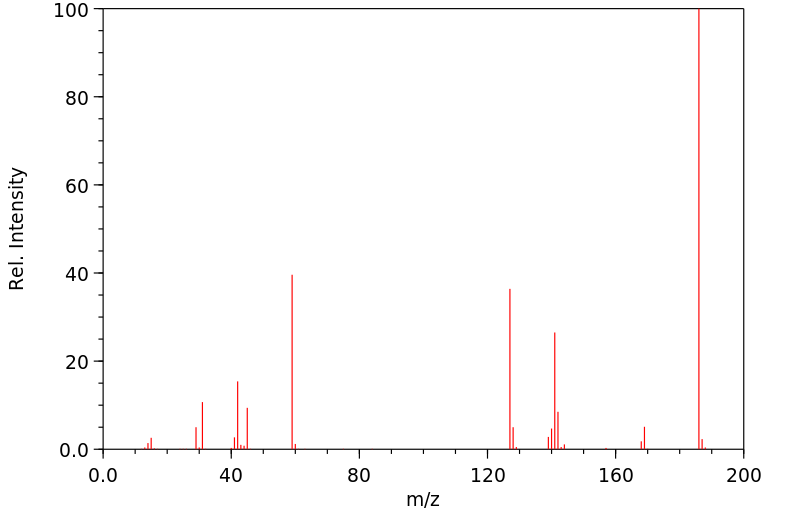
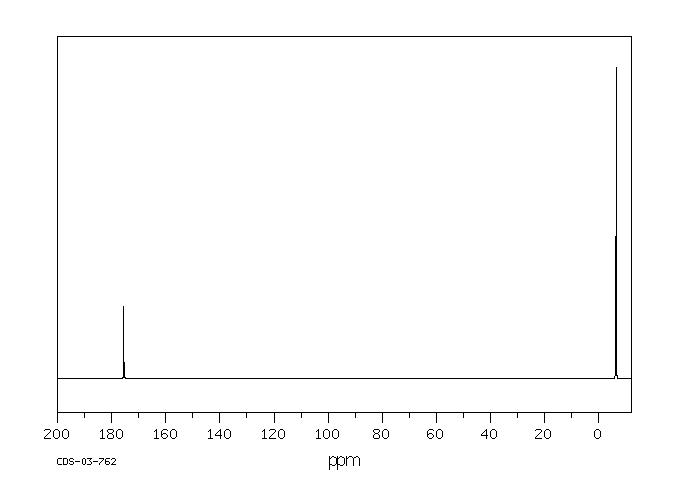
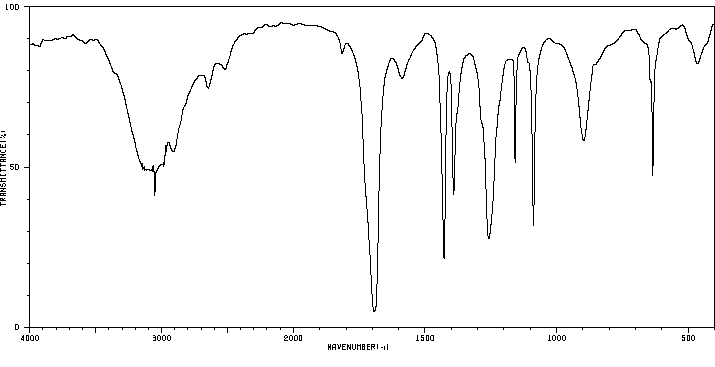
毒理性
识别和使用:碘乙酸是一种固体。它被用作试剂。人体研究:碘乙酸对眼睛几乎所有部位都有毒性,无论是直接应用还是系统给药。碘乙酸盐已被证明对角膜、虹膜、晶状体、睫状体和视网膜有毒。碘乙酸并没有显著增加二核TK6细胞中微核的频率。稳定染色体畸变(易位)是由碘乙酸钠在人类细胞中诱导的。动物研究:在兔或猫中静脉注射碘乙酸盐会几乎立即导致视网膜电动作电位的下降,这是由于视觉细胞的损伤。它还导致蛋白和细胞出现在房水中,并在五天内诱导细胞渗出进入玻璃体。在角膜内皮和睫状上皮中可以观察到组织学变化。当应用于去除角膜上皮的眼睛,或当注射到角膜基质中时,从0.001 M到0.1 M的溶液会造成严重到毁灭性的损伤。将碘乙酸盐添加到房水中会导致角膜水肿。前房注射对角膜和虹膜造成了严重损害,并导致白内障。几位研究者已经证明,碘乙酸盐可以直接毒害离体或孤立的兔视网膜,消除ERG并导致在低浓度下选择性破坏杆细胞。碘乙酸盐对杆细胞的损害比锥细胞更严重。在大鼠膝关节的关节腔内注射碘乙酸盐,使关节软骨发生了类似骨关节炎的变化。碘乙酸在细胞转化试验中转化了NIH3T3细胞,导致注射到小鼠后形成了侵袭性纤维肉瘤。碘乙酸对S. typhimurium具有显著的基因毒性。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Iodoacetic acid is a solid. It is used as a reagent. HUMAN STUDIES: Iodoacetic acid is toxic to essentially all parts of the eye, when either applied directly or administered systemically. Iodoacetate has been shown to be toxic to the cornea, iris, lens, ciliary body, and retina. Iodoacetic acid did not increase significantly the frequency of micronucleus in binucleated TK6 cells. Stable chromosome aberrations (translocations) were induced in human cells by sodium iodoacetate. ANIMAL STUDIES: Iodoacetate injected intravenously in rabbits or cats causes almost immediate drop in the electric action potentials of the retina, owing to injury of the visual cells. It also causes proteins and cells to appear in the aqueous humor and induces cellular exudation into the vitreous body in five days. Histologic changes are observable in the corneal endothelium and ciliary epithelium. When applied to eyes from which the corneal epithelium has been removed, or when injected into the corneal stroma, solutions from 0.001 M to 0.1 M cause severe to devastating injury. Addition of iodoacetate to the aqueous humor causes corneal edema. Injection into the anterior chamber caused severe damage to the cornea and iris as well as cataract. Excised or isolated rabbit retina has been shown by several investigators to be directly poisoned by iodoacetate, abolishing the ERG and causing selective destruction of rod cells at low concentrations. Iodoacetate is selectively more injurious to rods than cones. The intra-articular injection of iodoacetate into the knee joint of rats produced changes in the articular cartilage which resembled those of osteoarthritis. Iodoacetic acid transformed NIH3T3 cells in a cell-transformation assay that resulted in aggressive fibrosarcomas after injection into mice. Iodoacetic acid was significantly genotoxic to S. typhimurium.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)