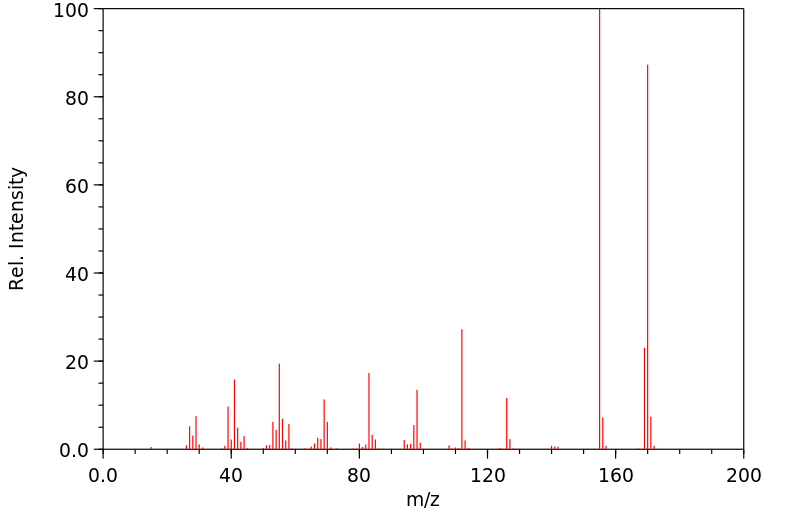
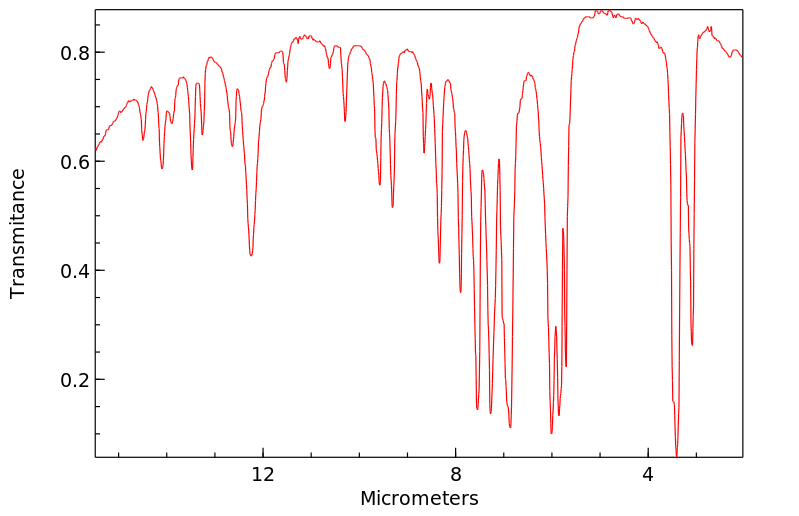
毒理性
Metharbital 结合在一个与 GABAA 受体上的 Cl- 离子通道相关联的独特结合位点,增加了 Cl- 离子通道开启的时间长度。因此,GABA 在丘脑中的突触后抑制效应被延长。所有这些效应都与 GABA 敏感神经元钙离子电导率 (gCa) 显著降低相关。巴比妥类药物作用的净结果是急性增强抑制性的 GABAergic 调控。巴比妥类药物还通过强大(尽管不太明确)且直接抑制兴奋性 AMPA 型谷氨酸受体发挥作用,导致谷氨酸能神经传递的深刻抑制。
Metharbital binds at a distinct binding site associated with a Cl<sup>-</sup> ionopore at the GABA<sub>A</sub> receptor, increasing the duration of time for which the Cl<sup>-</sup> ionopore is open. The post-synaptic inhibitory effect of GABA in the thalamus is, therefore, prolonged. All of these effects are associated with marked decreases in GABA-sensitive neuronal calcium conductance (gCa). The net result of barbiturate action is acute potentiation of inhibitory GABAergic tone. Barbiturates also act through potent (if less well characterized) and direct inhibition of excitatory AMPA-type glutamate receptors, resulting in a profound suppression of glutamatergic neurotransmission.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)