戊-2-烯二酸 | 505-36-2
中文名称
戊-2-烯二酸
中文别名
——
英文名称
(Z)-glutaconic acid
英文别名
itaconic acid;cis-glutaconic acid;cis-Glutaconsaeure;pentene-1,5-dioic acid;cis-Glutaconsaeure-dimethylester;cis-Pentenedioic acid;(Z)-pent-2-enedioic acid
CAS
505-36-2
化学式
C5H6O4
mdl
——
分子量
130.1
InChiKey
XVOUMQNXTGKGMA-UPHRSURJSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:136 °C
-
沸点:413.8±28.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.384±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.3
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.2
-
拓扑面积:74.6
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:4
安全信息
-
海关编码:2917190090
SDS
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 反-戊烯二酸 glutaconic acid 628-48-8 C5H6O4 130.1
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Malachowski, Chemische Berichte, 1929, vol. 62, p. 1325摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Malachowski, Chemische Berichte, 1929, vol. 62, p. 1325摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Mechanism‐Based Inactivation of Coenzyme B <sub>12</sub> ‐Dependent 2‐Methyleneglutarate Mutase by ( <i>Z</i> )‐Glutaconate and Buta‐1,3‐diene‐2,3‐dicarboxylate作者:Wolfgang Buckel、Antonio J. Pierik、Sandra Plett、Ashraf Alhapel、Diana Suarez、Shang‐min Tu、Bernard T. GoldingDOI:10.1002/ejic.200600405日期:2006.9(E)-glutaconate, each induced homolysis of the Co–C bond of coenzyme B12 to afford cob(II)alamin and the 5′-deoxyadenosyl radical. The latter probably added to the double bond in (Z)-glutaconate and one of the double bonds in buta-1,3-diene-2,3-dicarboxylate to afford a corresponding “radical adduct”. The formation of new radicals and cob(II)alamin was diagnosed by UV/Visible and EPR spectroscopy. (Z)-Glutaconate在全 2-亚甲基戊二酸变位酶存在下,buta-1,3-diene-2,3-dicarboxylate 和 (Z)-glutaconate [(Z)-pent-2-ene-1,5-dicarboxylate],但不存在 ( E)-戊二酸,各自诱导辅酶 B12 的 Co-C 键的均裂,以提供 cob(II) 氨基丙酸和 5'-脱氧腺苷自由基。后者可能添加到 (Z)-戊二酸中的双键和 buta-1,3-diene-2,3-dicarboxylate 中的双键之一,以提供相应的“自由基加合物”。通过紫外/可见光和 EPR 光谱诊断新自由基和 cob (II) alamin 的形成。(Z)-Glutaconate 迅速灭活变位酶,形成 aquocobalamin,这可能是通过电子从 cob(II)alamin 转移到自由基加合物而获得的。相比之下,buta-1,3-diene-2,3-dicarboxylate
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
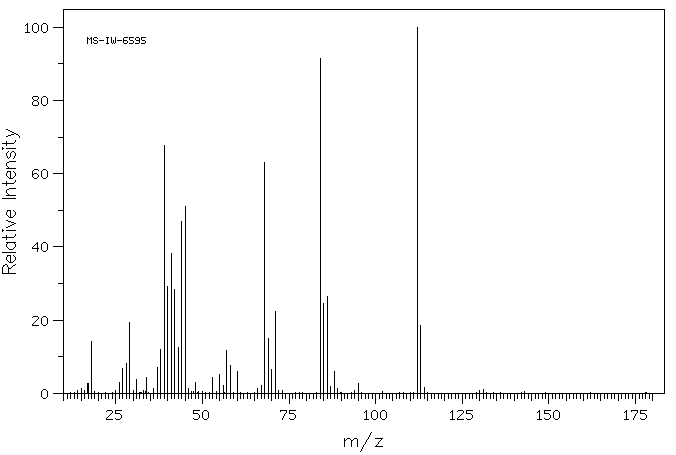
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
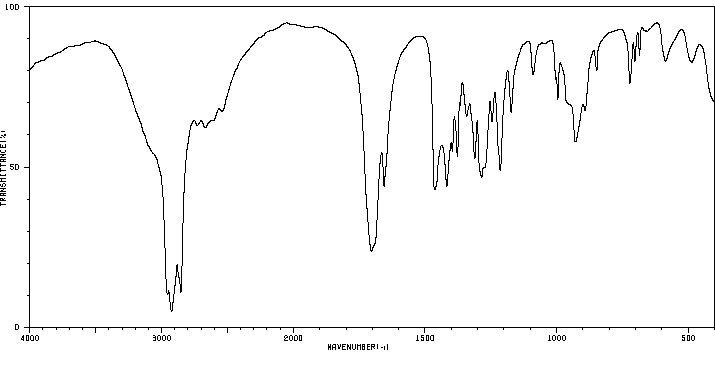
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(甲基3-(二甲基氨基)-2-苯基-2H-azirene-2-羧酸乙酯)
(±)-盐酸氯吡格雷
(±)-丙酰肉碱氯化物
(d(CH2)51,Tyr(Me)2,Arg8)-血管加压素
(S)-(+)-α-氨基-4-羧基-2-甲基苯乙酸
(S)-阿拉考特盐酸盐
(S)-赖诺普利-d5钠
(S)-2-氨基-5-氧代己酸,氢溴酸盐
(S)-2-[[[(1R,2R)-2-[[[3,5-双(叔丁基)-2-羟基苯基]亚甲基]氨基]环己基]硫脲基]-N-苄基-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(S)-2-[3-[(1R,2R)-2-(二丙基氨基)环己基]硫脲基]-N-异丙基-3,3-二甲基丁酰胺
(S)-1-(4-氨基氧基乙酰胺基苄基)乙二胺四乙酸
(S)-1-[N-[3-苯基-1-[(苯基甲氧基)羰基]丙基]-L-丙氨酰基]-L-脯氨酸
(R)-乙基N-甲酰基-N-(1-苯乙基)甘氨酸
(R)-丙酰肉碱-d3氯化物
(R)-4-N-Cbz-哌嗪-2-甲酸甲酯
(R)-3-氨基-2-苄基丙酸盐酸盐
(R)-1-(3-溴-2-甲基-1-氧丙基)-L-脯氨酸
(N-[(苄氧基)羰基]丙氨酰-N〜5〜-(diaminomethylidene)鸟氨酸)
(6-氯-2-吲哚基甲基)乙酰氨基丙二酸二乙酯
(4R)-N-亚硝基噻唑烷-4-羧酸
(3R)-1-噻-4-氮杂螺[4.4]壬烷-3-羧酸
(3-硝基-1H-1,2,4-三唑-1-基)乙酸乙酯
(2S,4R)-Boc-4-环己基-吡咯烷-2-羧酸
(2S,3S,5S)-2-氨基-3-羟基-1,6-二苯己烷-5-N-氨基甲酰基-L-缬氨酸
(2S,3S)-3-((S)-1-((1-(4-氟苯基)-1H-1,2,3-三唑-4-基)-甲基氨基)-1-氧-3-(噻唑-4-基)丙-2-基氨基甲酰基)-环氧乙烷-2-羧酸
(2S)-2,6-二氨基-N-[4-(5-氟-1,3-苯并噻唑-2-基)-2-甲基苯基]己酰胺二盐酸盐
(2S)-2-氨基-N,3,3-三甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3-甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯基甲基)丁酰胺,
(2S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-2-吡啶基丁酰胺
(2S,4R)-1-((S)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基丁酰基)-4-羟基-N-(4-(4-甲基噻唑-5-基)苄基)吡咯烷-2-甲酰胺盐酸盐
(2R,3'S)苯那普利叔丁基酯d5
(2R)-2-氨基-3,3-二甲基-N-(苯甲基)丁酰胺
(2-氯丙烯基)草酰氯
(1S,3S,5S)-2-Boc-2-氮杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-3-羧酸
(1R,5R,6R)-5-(1-乙基丙氧基)-7-氧杂双环[4.1.0]庚-3-烯-3-羧酸乙基酯
(1R,4R,5S,6R)-4-氨基-2-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己烷-4,6-二羧酸
齐特巴坦
齐德巴坦钠盐
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,苯基甲基酯,(2a,3a)-
齐墩果-12-烯-28-酸,2,3-二羟基-,羧基甲基酯,(2a,3b)-(9CI)
黄酮-8-乙酸二甲氨基乙基酯
黄荧菌素
黄体生成激素释放激素(1-6)
黄体生成激素释放激素 (1-5) 酰肼
黄体瑞林
麦醇溶蛋白
麦角硫因
麦芽聚糖六乙酸酯
麦根酸