1,1,1,5-四氯戊烷 | 2467-10-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:97°C (estimate)
-
沸点:211.46°C (estimate)
-
密度:1.3506
-
保留指数:1220;1211;1211
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.7
-
重原子数:9
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1,1,1-trichloropentane 3922-27-8 C5H9Cl3 175.485 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,1,5-三氯戊烷 1,1,5-trichloropentane 13059-14-8 C5H9Cl3 175.485 1,1,5,5-四氯戊烷 1,1,5,5-Tetrachlor-pentan 17655-64-0 C5H8Cl4 209.931 —— 5,5,5-Trichlor-pentylmercaptan 60303-21-1 C5H9Cl3S 207.551 —— 5,5,5-trichloropentan-1-ol 4189-04-2 C5H9Cl3O 191.485 —— 5,5,5-trichloro-pentylamine 26342-07-4 C5H10Cl3N 190.5 —— 1,1-dichloropentane 30586-10-8 C5H10Cl2 141.04 —— Bis-<5,5,5-trichlor-pentyl>-sulfid 14146-66-8 C10H16Cl6S 381.021
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Joyce; Hanford; Harmon, Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1948, vol. 70, p. 2531摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Burton,T.; Bruylants,A., Bulletin des Societes Chimiques Belges, 1972, vol. 81, p. 639 - 642摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:参考文献:名称:Nessmajanow et al., Izvestiya Akademii Nauk SSSR, Seriya Khimicheskaya, 1954, p. 34,38摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
SYNTHESIS OF 1,1,2,3-TETRACHLOROPROPENE申请人:Honeywell International Inc.公开号:US20140221705A1公开(公告)日:2014-08-07The present invention provides an improved process for producing 1,1,2,3-tetrachloropropene. By using a first reactive distillation column for HCC-250fb dehydrochlorination, and a second reactive distillation column for HCC-240db dehydrochlorination/HCC-1230xf isomerization, the 1,1,2,3-tetrachloropropene manufacturing process can be greatly simplified, resulting in reduced equipment use, energy use, as well as increased productivity.
-
Halogenated hydrocarbons and method for their preparation申请人:DU PONT公开号:US02440800A1公开(公告)日:1948-05-04
Telomers are prepared by subjecting aliphatic mono-olefines and a substance YZ to elevated temperature and pressure in the presence of an ethylene polymerization catalyst. The substance YZ is defined as being free from aliphatic carbon-carbon unsaturation and capable of forming monovalent fragments Y and Z, one of which is an inorganic acid radicle and the other is either an inorganic acid radicle or a radicle containing carbon and which is (a) a halogen, e.g. chlorine, bromine and iodine; (b) a halogen containing carbon compound, e.g. chloriodoform, a -brompropionic acid, propyl trichloracetate, chloracetic anhydride, chlorpropionaldehyde, ethylene bromhydrin, glycerol a -monochlorhydrin, monochlormethyl ether, methyl chloride and chloracetyl chloride; (c) or compounds containing halogen in combination with an inorganic acid radicle, e.g. cyanogen chloride and bromide; (d) a sulphur halide, e.g. benzene sulphonyl chloride and sulphuryl chloride; (e) cyanogen; or (f) an ester of an inorganic acid, e.g. triethyl borate, tetraethyl silicate, tributyl phosphate and methyl sulphate. Suitable catalysts are oxygen, hydrogen, acetyl, benzoyl, diethyl and tetrahydronaphthalene peroxides, alkali ammonium persulphates, perborates and percarbonates, tetraethyl and tetraphenyl lead, ultra-violet light especially in the presence of photosensitizers such as mercury, alkyl iodides, benzoin and acetone, di-, tri-methylamine oxides dibenzoyl hydrazine, hydrazine hydrochloride and sebacate and hexachloroethane water solvents, e.g. isooctane, cyclohexane, benzene and dioxane, surface active agents, e.g. sodium acetoxyoctadecyl sulphate, buffers, and substances capable of forming interpolymers with olefines, e.g. vinyl compounds and unsaturated acids, esters and ketones may be present. Examples describe the telomerization of ethylene and carbon tetrachloride (1 to 5); chloroform (6 to 7); methylene chloroiodide (8); chloral hydrate (9); 1,1,1-trichloroethane (10); ethyl dichloroacetate (11); dichloroacetic acid (12); hexachloroethane (13); tetra- and pentra-chloroethylbenzenes (14); hexachlorobenzene (15); trichlorofluoromethane (16); dimethyl sulphate (17); ethyl orthosilicate (18); sulphuryl chloride (19); ethyl iodide (20); a ,a 1-dichloro-dimethyl ether (25); isobutylene and carbon tetrachloride (21); ethylene carbon tetrachloride and n-octene-1 (22), styrene (23); and vinyl chloride (24). The products may contain pure compounds, e.g. of the type Cl(CH2.CH2)nCCl3, where n is an integer. They may be used as solvents, heat transfer media, plasticisers, wax substitutes, coating materials and as additions to lubricating oils. Specifications 471,590, 497,643, 578,584 and 581,900 are referred to.
端粒是通过将脂肪族单烯烃和一种名为YZ的物质在乙烯聚合催化剂存在下在高温高压下处理制备的。物质YZ被定义为不含脂肪族碳碳不饱和度并且能够形成一价片段Y和Z的物质,其中一个是无机酸基团,另一个是含碳的无机酸基团或含有碳的基团,其为(a) 卤素,例如氯、溴和碘;(b) 含碳卤素化合物,例如氯碘甲烷、α-溴丙酸、三氯乙酸丙酯、氯乙酸酐、氯丙醛、溴水合乙烯、甘油α-单氯水合物、单氯甲基醚、氯化甲烷和氯乙酰氯;(c) 或含有卤素与无机酸基团结合的化合物,例如氰化氯和溴化物;(d) 硫卤素,例如苯磺酰氯和亚砜氯;(e) 氰化物;或(f) 无机酸酯,例如三乙基硼酸酯、四乙基硅酸酯、三丁基磷酸酯和硫酸甲酯。适用的催化剂包括氧气、氢气、乙酰、苯甲酰、双乙基和四氢萘过氧化物、碱金属过硫酸盐、过硼酸盐和过碳酸盐、四乙基和四苯基铅、紫外光尤其在存在光敏剂如汞、烷基碘化物、苯甲醇和丙酮、二甲基胺氧化物、二苯甲酰肼、盐酸和己二酸和六氯乙烷水溶剂,例如异辛烷、环己烷、苯和二噁烷、表面活性剂,例如乙酰氧基十八烷基硫酸钠、缓冲剂和能够与烯烃形成共聚物的物质,例如乙烯化合物和不饱和酸、酯和酮可能存在。示例描述了乙烯和四氯化碳(1至5);氯仿(6至7);氯碘甲烷(8);氯乙醛(9);1,1,1-三氯乙烷(10);二氯乙酸乙酯(11);二氯乙酸(12);六氯乙烷(13);四氯和五氯乙基苯(14);六氯苯(15);三氟氯甲烷(16);硫酸二甲酯(17);正硅酸乙酯(18);亚砜氯(19);碘化乙基(20);α,α'-二氯二甲醚(25);异丁烯和四氯化碳(21);乙烯四氯化碳和正辛烯-1(22)、苯乙烯(23);和氯乙烯(24)的端粒化反应。产品可能含有纯化合物,例如Cl(CH2. )nCCl3类型的化合物,其中n是整数。它们可用作溶剂、传热介质、增塑剂、蜡替代品、涂料材料以及添加到润滑油中。规范471,590、497,643、578,584和581,900被提及。 -
Method for producing 1,1,1,3-tetrachloropropane and other haloalkanes with iron catalyst申请人:VULCAN CHEMICALS A BUSINESS GROUP OF VULCAN MATERIALS COMPANY公开号:US20040225166A1公开(公告)日:2004-11-11A continuous process is provided for the manufacture of haloalkanes by the reaction of carbon tetrachloride with olefins in the presence of iron metal, trialkylphosphate, and ferric chloride. A fraction of the catalyst and co-catalyst are separated after the reaction and recycled. In a preferred application, the olefin is ethene, and the haloalkane product is 1,1,1,3-tetrachloropropane. Two distillation steps take place in order to enhance the production of 1,1,1,3-tetrachloropropane.提供了一种连续的工艺,用于在铁金属、三烷基磷酸酯和氯化铁存在的情况下,通过四氯化碳与烯烃的反应来制备卤代烷。在反应后,催化剂和共催化剂的一部分被分离并回收。在一个首选的应用中,烯烃是乙烯,卤代烷产品是1,1,1,3-四氯丙烷。为了增强1,1,1,3-四氯丙烷的生产,进行了两个蒸馏步骤。
-
Polyhalogenated olefins申请人:DU PONT公开号:US02410541A1公开(公告)日:1946-11-05
Polychlorolefins and, in some cases, chloracetylenes are prepared by removal of hydrogen chloride from compounds of at least 5 carbon atoms and having the formula <;FORM:0581901/IV/1>; where X is H or halogen, R is a divalent hydrocarbon radical, and R1 is H or a monovalent hydrocarbon radical, by treatment with alkaline reagents, by application of heat in presence of water or sulphuric acid or a dehydrochlorination catalyst. The reaction may be effected in the vapour phase at about 200-450, preferably 250-350 DEG C., and generally at atmospheric or slightly increased pressure. A diluent, particularly water, is preferably present, generally in a molecular ratio between 1 : 1 and 20 : 1 to the trichlormethyl compound which preferably contains 5-15 carbon atoms. Heteropoly acids of which one radical contains an element of Group 5 or 6A of the Periodic Table are the preferred catalysts, for example phosphotungstic, silicotungstic, phosphomolybdic, borophosphoric, and silicovanadic acids, alone or on charcoal, silica, alumina or the like. Other catalysts are chlorides of metals of Groups 2, 3, and 8, e.g. Mg, Zn, Ba, Al and Fe. The space velocity is usually 1-5 c.c. of liquid feed per c.c. of catalyst per hour. Liquid phase reaction is preferably effected at 100-200 DEG C. with a Friedel Crafts' catalyst such as chlorides of Zn, Al, FeIII, SnIV and TiIV, and a hydroxylic promoter which reacts with the catalyst to produce hydrogen chloride, e.g. water and aliphatic acids. Alkaline substances may alternatively be used, e.g. oxides, hydroxides, and carbonates of alkali and alkaline-earth metals, tertiary amines such as pyridine, quinoline, and triethylamine, and aliphatic amides such as formamide, and acetamide, alone or in a suitable solvent. Such substances may, however, remove more than one molecule of HCl from a compound containing the group -CH2-CCl3 to form a chloracetylene. Compounds of the formula Cl-R-CH2-CCl3 with alcoholic solutions of alkali may yield alcoholysis products of the chlorolefins or -acetylenes. Dehydrochlorination can also be effected by heating under pressure to 200 DEG C. with water or dilute sulphuric acid. The initial trichlormethyl compounds may be prepared as described in Specification 581,899 by reaction of mono-olefins with carbon tetrachloride, chloroform or trichlorbrom (iodo or fluor) methane. Thus ethylene with carbon tetrachloride or chloroform gives compounds of the formula Cl(CH2CH2)nCCl3 or H(CH2CH2)n CCl3, where n is an integer greater than 1. Dehydrochlorination gives compounds Cl(CH2 CH2)n1CH2CH=CCl2 or H(CH2CH2)n-1CH2 CH=CCl2. Initial materials specified include 1,1,1-trichlor derivatives of pentane, nonane, 2,4-dimethylpentane, tridecane, 3,3,5,5-tetramethylpentane, 5-brompentane, 7-iodoheptane, and 5-fluorpentane, and 1,1,1,15-tetrachlorpentadecane. The hydrocarbon radicals R and R1 may also be aryl or aralkyl. The reactors may be of glass, stainless steels or Ni-Fe-Mo alloys. The chlor-olefins produced are stored in contact with an oxidation inhibitor, such as hydroquinone, pyrogallol or an aliphatic tertiary amine, or in an oxygen-free atmosphere. They are used as solvents in coating composition, cleaning fluids, and metal degreasing solvents. They can be hydrolyzed to carboxylic acids as described in Specification 591,900. In examples: (1) a vertical tube heated to 300-310 DEG C. is packed in its lower part with phosphotungstic acid on silica gel, the upper part, serving as a vaporizer, containing small glass tubing. 1,1,1,5-Tetrachlorpentane and water are fed in at the top, the products leaving at the base being extracted with carbon tetrachloride and worked up to give 1,1,5-trichlorpentene-1; (2) granular borophosphoric acid at 255 DEG C. is used similarly or zinc chloride on alumina, the latter giving also what appears to be a di-dehydrochlorination product; (3) 1,1,1,5-tetrachlorpentane, zinc chloride and acetic acid are heated at 110-120 DEG to give 1,1,5-trichlorpentene-1; (4) 1,1,1,7-tetrachlorheptane, zinc chloride, and acetic acid heated at 140-160 DEG C. give 1,1,7-trichlorheptene-1. Similarly, 1,1,1,9-tetrachlornonane yields 1,1,9-trichlornonene-1; (5) 1,1,1,1-trichlornonane is refluxed with formamide to give 1,1-dichlornonene-1; (6) 1,1,1,5-tetrachlorpentane is added to alcoholic potash while refluxing, the products being alcoholysis products of chlor-olefin and chloracetylene of the formul C2H5O(CH2)3 CCCl and C2H5O(CH2)3CH=CCl2.
多氯烯和在某些情况下氯乙炔是通过从至少有5个碳原子的化合物中去除氯化氢来制备的,其化学式为<;FORM:0581901/IV/1>;其中X为H或卤素,R为二价碳氢基团,R1为H或一价碳氢基团,通过与碱性试剂处理,通过在水或硫酸或脱氯催化剂存在的情况下施加热量。 反应可以在大约200-450°C的蒸汽相中进行,最好在250-350°C,并通常在大气或稍微增加的压力下进行。 最好存在稀释剂,特别是水,通常在1:1至20:1的分子比与三氯甲基化合物之间,该化合物最好含有5-15个碳原子。 偏钨酸盐是首选催化剂,其中一个基团含有周期表5或6A族元素,例如偏钨酸盐、硅偏钨酸盐、磷钼酸盐、硼磷酸盐和硅钒酸盐,单独或与木炭、二氧化硅、氧化铝等混合使用。 其他催化剂是2、3和8族金属的氯化物,例如镁、锌、钡、铝和铁。 空速通常为每小时1-5毫升液体进料与每毫升催化剂。 液相反应最好在100-200°C下进行,使用弗里德尔克拉夫特催化剂,例如锌、铝、FeIII、SnIV和TiIV的氯化物,以及与催化剂反应产生氯化氢的羟基促进剂,例如水和脂肪酸。 也可以使用碱性物质,例如碱金属和碱土金属的氧化物、氢氧化物和碳酸盐,三级胺,例如吡啶、喹啉和三乙胺,以及脂肪酰胺,例如甲酰胺和乙酰胺,单独或在适当的溶剂中使用。 但是,这些物质可能从含有-CH2-CCl3基团的化合物中去除多于一个氯化氢分子以形成氯乙炔。 包含醇溶液的化合物Cl-R- - 可能产生氯烯或-乙炔的醇解产物。 脱氯反应也可以通过在200°C下加热压力来实现,使用水或稀硫酸。 初始的三氯甲基化合物可以按照规范581,899中描述的方法制备,通过单烯与四氯化碳、氯仿或三氯溴(碘或氟)甲烷的反应。 因此,乙烯与四氯化碳或氯仿反应产生化合物的化学式为Cl( )n 或H( )n ,其中n是大于1的整数。 脱氯反应产生化合物Cl( )n1 CH=CCl2或H( )n-1 CH= 。 指定的初始材料包括戊烷、壬烷、2,4-二甲基戊烷、十三烷、3,3,5,5-四甲基戊烷、5-溴戊烷、7-碘庚烷和5-氟戊烷的1,1,1-三氯衍生物,以及1,1,1,15-四氯十五烷。 碳氢基团R和R1也可以是芳香族或芳基。 反应器可以是玻璃、不锈钢或镍-铁-钼合金。 生成的氯烯类化合物与氧化抑制剂(例如羟基喹啉、间羟基苯酚或脂肪三级胺)接触存储,或在无氧气氛中存储。 它们用作涂料配方、清洁液和金属脱脂剂中的溶剂。 它们可以按照规范591,900中描述的方法水解为羧酸。 在示例中:(1)加热至300-310°C的垂直管的下部填充有硅胶上的偏钨酸,上部作为蒸发器,含有小玻璃管。 1,1,1,5-四氯戊烷和水从顶部加入,底部离开的产物用四氯化碳提取并处理得到1,1,5-三氯戊烯-1;(2)在255°C下使用颗粒状硼磷酸盐类似地使用或氧化铝上的氯化锌,后者还产生似乎是二脱氯产物;(3)1,1,1,5-四氯戊烷、氯化锌和乙酸在110-120°C下加热得到1,1,5-三氯戊烯-1;(4)1,1,1,7-四氯庚烷、氯化锌和乙酸在140-160°C下加热得到1,1,7-三氯庚烯-1。 同样,1,1,1,9-四氯辛烷产生1,1,9-三氯辛烯-1;(5)1,1,1,1-三氯辛烷与甲酰胺回流反应得到1,1-二氯辛烯-1;(6)1,1,1,5-四氯戊烷加入酒精钾回流时,产物为氯烯和氯乙炔的醇解产物,化学式为C2H5O( )3 CCCl和 ( )3CH= 。 -
The inhibition effect of inorganic compounds on the corrosion of the 3003 aluminium alloy in the presence of sodium chloride作者:L. Bazzi、R. Salghi、A. Bouchtart、Z. El Alami、S. KertitDOI:10.1051/metal:2002192日期:2002.2This study concerns the inhibition of the corrosion of the aluminium alloy 3003 in a solution of 3% NaCl by Li+, Mg2+, MoO42-, NO2- and CrO42- ions. The methods used are the determination of the polarization curves and the metallographic examination of the surface condition. The results obtained show that the tested ions inhibit the corrosion process.The comparative study of the effect of these ions shows that the Mg2+ ions are the most efficient ones in the temperature range from 25 to 65°C. The inhibition efficiency increases with the concentration of these ions and reaches a maximum value of 86% for 5 × 10-2 alloy. As a consequence, the gap between pitting and corrosion potentials becomes larger. At 75°C, Mg2+ ions tend to stimulate corrosion of alloy 3003 in the chloride solution considered.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
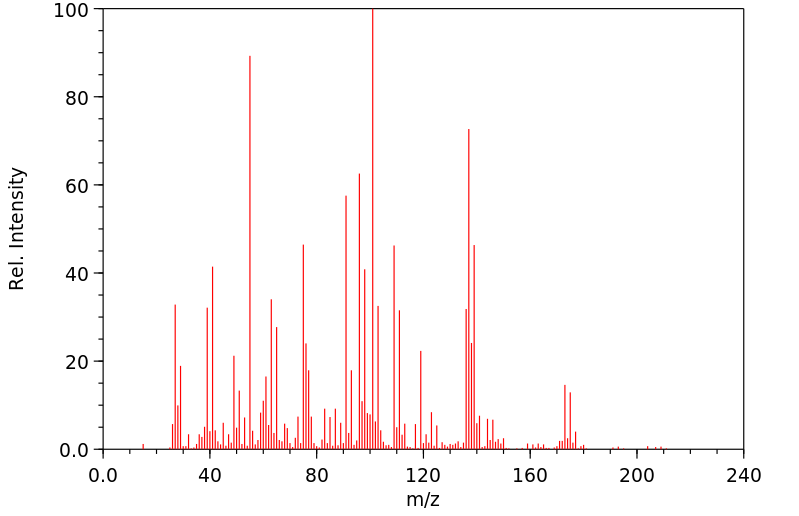
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
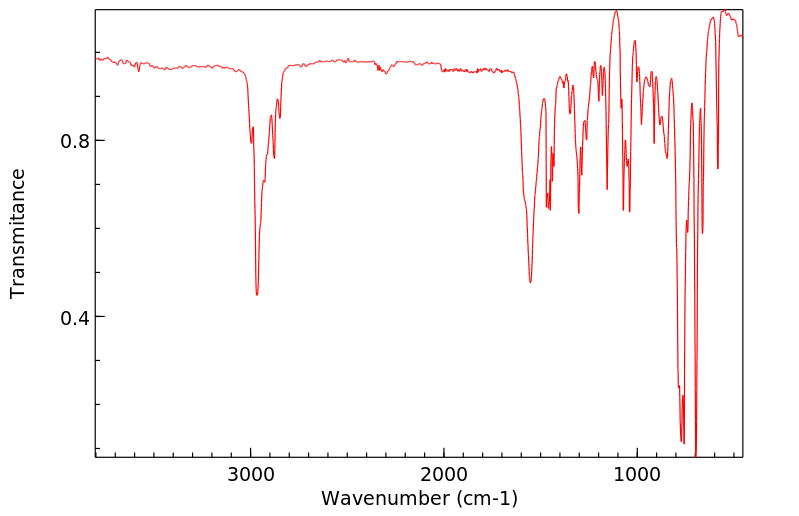
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息