霜脲氰 | 57966-95-7
中文名称
霜脲氰
中文别名
1-(2-氰基-2-甲氧基亚氨基乙酰基)-3-乙基脲;酰脲氰;氰基-N-[(乙胺基)羧基]-2-(甲氧亚胺基)乙酰胺;清菌脲;2-氰基-N-[(乙胺基)羰基]-2-(甲氧基亚胺基)乙酰胺;菌疫清;克露;1-氰基-N-[(乙胺基)羰基]-2-(甲氧基亚氨基)乙酰胺;2-氰基-N-[(乙胺基)羰基]-2-(甲氰基亚胺基)乙酰胺
英文名称
cymoxanil
英文别名
2-cyano-N-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-2-(methoxyimino)acetamide;2-(ethylcarbamoylamino)-N-methoxy-2-oxoethanimidoyl cyanide
CAS
57966-95-7
化学式
C7H10N4O3
mdl
——
分子量
198.181
InChiKey
XERJKGMBORTKEO-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:160-161°
-
沸点:335.48°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.3841 (rough estimate)
-
闪点:100 °C
-
溶解度:二甲基亚砜:100 mg/mL(504.59 mM)
-
LogP:0.590
-
颜色/状态:Colorless crystals
-
气味:Odorless
-
蒸汽压力:1.13X10-6 mm Hg at 20 °C
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 9.7 (decomposes)
-
稳定性/保质期:
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.7
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.43
-
拓扑面积:104
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
代谢
在粪便中完整地检测到了(14)C-cymoxanil(小于1%)和IN W3595,但大部分放射性物质是(14)C-glycine(大约9-13%)。根据数据,代谢途径涉及将cymoxanil水解为IN W3595,然后IN W3595进一步降解为glycine,glycine进而被并入天然成分或进一步代谢。
... In feces intact (14)C-cymoxanil (< 1%) and IN W3595 was detected, but the majority of radioactivity was (14)C-glycine (about 9 - 13%). Based on the data, the metabolic pathway involves hydrolysis of cymoxanil to IN W3595, which is then degraded to glycine, which in turn is incorporated into natural constituents or further metabolized.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
IN-U3204(1-乙基-5,6-二-2,4(1H,3H)吡啶二酮)在接受了120毫克/千克DPX-3217处理的动物的两性混合0-48小时尿样中被检测到,以及在正在进行的低剂量胆管瘘研究中,接受了2.5毫克/千克处理的动物的两性混合0-24小时尿样中也被检测到。后一组被包括进来是为了确保IN-U3204的存在不是储存过程中的伪迹;尽管在两组中检测到的IN-U3204水平看似较低,但它确实在两组中都被检测到了。
... IN-U3204 (1-ethyl-5,6-di-2,4(1H,3H) pyridinedione) was detected in pooled 0-48 hr urine samples, both sexes, from animals treated with 120 mg/kg DPX-3217 and in pooled 0-24 hr samples, both sexes, from animals treated with 2.5 mg/kg in an ongoing low dose biliary fistula study. The latter group was included to ensure that the presence of IN-U3204 was not an artifact of storage; IN-U3204 was detected in both groups, though at apparently low levels.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
/2-(14)C-DPX-T3217/ 以玉米油形式给予大鼠单次剂量组:2.5 & 120 mg/kg,0.5 & 2 mL/只动物(约10 & 约20 uCi/只动物,分别为D组和E组),以及多次剂量组:每天2.5 mg/kg,连续给药14天后给予标记剂量2.5 mg/kg(F组)。在5/性别/剂量的方案下,通过HPLC和TLC检测排泄物中的主要代谢物是IN-W3595(2-氰基-2-甲氧基亚氨基乙酸)和极性成分(甘氨酸和其他氨基酸结合物);在D组雄性大鼠中,24小时内:58%的/给药剂量(AD)/出现在尿液中(8.6%为IN-W3595,46.5%为极性成分),21.9%出现在粪便中(14%可提取,<1% IN-W3595,13.1%极性成分)。在D组雌性大鼠中,64.2%的AD出现在尿液中(16.1% IN-W3595,45.2%极性成分),16.3%出现在粪便中(10.1%可提取,<1% IN-W3595,8.7%极性成分)。在E组雄性大鼠中,70.3%的AD出现在尿液中(26.3% IN-W3595,40.3%极性成分),16.1%出现在粪便中(11.3%可提取,<1% IN-W3595,8.6%极性成分)。在E组雌性大鼠中,73%的AD出现在尿液中(33% IN-W3595,36.7%极性成分),17.1%出现在粪便中(11.5%可提取,<1% IN-W3595,8.5%极性成分)。在F组雄性大鼠中,66.2%的AD出现在尿液中(6.5% IN-W3595,55%极性成分),14.5%出现在粪便中(9%可提取,<1% IN-W3595,8.9%极性成分)。在F组雌性大鼠中,63.1%的AD出现在尿液中(11.1% IN-W3595,46.6%极性成分),19.4%出现在粪便中(12.3%可提取,<1% IN-W3595,12.2%极性成分)。/IN-W3595代谢物/
/2-(14)C-DPX-T3217/ was administered /to rats/ in corn oil to/ single dose groups: 2.5 & 120 mg/kg, 0.5 & 2 mL/animal (~10 & ~20 uCi/animal, groups D & E, respectively) and a multiple dose group: daily administration at 2.5 mg/kg for 14 days followed by labeled dose at 2.5 mg/kg (group F). /In a/ 5/sex/dose regimen, the primary metabolites detected by HPLC and TLC in excreta were IN-W3595 (2-cyano-2-methoxyimino acetic acid) and polar components (glycine and other amino acid conjugates); In group D males, 24 hr: 58% of /administered dose (AD)/ in urine (8.6% as IN-W3595, 46.5% as polars), 21.9% in feces (14% extractable, <1% IN-W3595, 13.1% polars). In /group D/ females, 64.2% of AD /appeared/ in urine (16.1% IN-W3595, 45.2% polars), 16.3% in feces (10.1% extractable, <1% IN-W3595, 8.7% polars). In group E males, 70.3% of AD /appeared/ in urine (26.3% IN-W3595, 40.3% polars), 16.1% in feces (11.3% extractable, <1% IN-W3595, 8.6% polars). /In group E/ females, 73% of AD in urine (33% IN-W3595, 36.7% polars), 17.1% in feces (11.5% extractable, <1% IN-W3595, 8.5% polars). In group F males, 66.2% of AD /appeared/ in urine (6.5% IN-W3595, 55% polars), 14.5% in feces (9% extractable, <1% IN-W3595, 8.9% polars). In group F females, 63.1% of AD /appeared/ in urine (11.1% IN-W3595, 46.6% polars), 19.4% in feces (12.3% extractable, <1% IN-W3595, 12.2% polars). /IN-W3595 metabolite/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
癌症分类:不太可能对人类致癌
Cancer Classification: Not Likely to be Carcinogenic to Humans
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
皮肤致敏剂 - 一种可以诱导皮肤产生过敏反应的制剂。
Skin Sensitizer - An agent that can induce an allergic reaction in the skin.
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
毒理性
LCLo(大鼠)= 4,980 毫克/立方米/4小时
LCLo (rat) = 4,980 mg/m3/4h
来源:Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases
毒理性
/SRP:/ 立即急救:确保已经进行了充分的中和。如果患者停止呼吸,请开始人工呼吸,最好使用需求阀复苏器、气囊面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练操作。如有必要,执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果患者呕吐,让患者向前倾或将其置于左侧(如果可能的话,头部向下)以保持呼吸道畅通,防止吸入。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗帮助。 /毒物A和B/
/SRP:/ Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR if necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on the left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 基本治疗:建立专利气道(如有需要,使用口咽或鼻咽气道)。如有必要,进行吸痰。观察呼吸不足的迹象,如有需要,协助通气。通过非循环呼吸面罩以10至15升/分钟的速度给予氧气。监测肺水肿,如有必要,进行治疗……。监测休克,如有必要,进行治疗……。预期癫痫发作,如有必要,进行治疗……。对于眼睛污染,立即用水冲洗眼睛。在运输过程中,用0.9%的生理盐水(NS)持续冲洗每只眼睛……。不要使用催吐剂。对于摄入,如果患者能够吞咽、有强烈的干呕反射且不流口水,则用温水冲洗口腔,并给予5毫升/千克,最多200毫升的水进行稀释……。在去污后,用干燥的无菌敷料覆盖皮肤烧伤……。/毒药A和B/
/SRP:/ Basic treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if needed. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 mL/kg up to 200 mL of water for dilution if the patient can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
赛默昔尼尔(Cymoxanil)能够迅速被吸收,服药后4小时内血液和血浆中的浓度达到最高。在48小时内,观察到服用放射性剂量后在尿液和粪便中快速且几乎完全消除。排泄主要通过尿液(64 - 75%)、粪便(16 - 24%)和呼出气体(小于5%)完成。在性别、剂量水平或单次或多次给药之间,残留物剖面或消除率没有显著差异。没有检测到生物积累的证据。DPX-T3217被广泛代谢,尿液中仅检测到微量的服用(14)C-赛默昔尼尔。
Cymoxanil is rapidly absorbed and maximum concentrations in the blood and plasma is reached within 4 hours after dosing. Rapid and almost complete elimination of the administered radioactive dose was observed in urine and feces within 48 hours. Excretion is primarily by urine (64 - 75%), fecal (16 - 24%) and expired air (< 5%) of the administered dose. There is no significant difference in residue profiles or elimination rates between sexes, dose levels, or single or multiple dosing. No evidence of bioaccumulation was detected. DPX-T3217 is metabolized extensively and only trace level of the administered (14)C-cymoxanil was detected in the urine and feces. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
五只胆管插管的SD大鼠/性别口服给予2.5毫克/千克的(14)C-Cymoxanil(放射性纯度= 98%; 14.09 uCi/mg)作为玉米油悬浮液。在48小时的时间内收集尿液、粪便和胆汁,然后将动物处死并收集全血、肝脏、肾脏和残留尸体以测量放射性标记物。在48小时内,超过85%的测试化合物通过尿液(大约65%)、粪便(大约14%)和胆汁(大约7%)排出,大部分排出发生在前24小时内;极性氨基酸结合物是尿液中(大约45-50%)和胆汁中(大约4-6%)发现的主要代谢物类别;代谢物A(未知)和IN-W3595/(2-氰基-2-甲氧亚氨基乙酸)/在尿液中的浓度较低(< 10%)。IN-W3595在雌性(7.7%)尿液中的浓度高于雄性(2.8%);代谢物A在胆汁中未发现。
Five SD rats/sex with cannulated bile ducts were dosed orally with 2.5 mg/kg of (14)C-Cymoxanil (radiochemical purity = 98%; 14.09 uCi/mg) as a corn oil suspension. Urine, feces, and bile were collected over a 48 h period, after which the animals were terminated and whole blood, liver, kidneys, and residual carcass were collected for measurement of radiolabel. ...More than 85% of the test compound was eliminated in urine ( approximately 65%), feces (approximately 14%), and bile (approximately 7%) within 48 hr in both sexes, with most elimination occurring with the first 24 hr; polar amino acid conjugates comprised the major class of metabolites found in both urine (approximately 45-50%) and bile (approximately 4-6%); Metabolite A (unknown) and IN-W3595 /(2-cyano-2-methoxyimino acetic acid)/ were found at much lower concentrations (< 10%) in urine. IN-W3595 was found at higher concentrations in the urine of females (7.7%) as compared to males (2.8%); Metabolite A was not found in bile.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
为了研究2-(14)C-DPX-T3217在大鼠体内的吸收、分布、代谢和排泄,以玉米油为溶剂,给大鼠分别以2.5毫克/千克和120毫克/千克的剂量给药,每只动物的给药体积分别为0.5毫升和2毫升。给药的放射性活度分别约为10微居里和20微居里。高剂量是根据预期轻微毒性来设定的。通过单次灌胃给药:每剂量组每性别3只动物用于血液药代动力学研究,5只用于排泄/分布研究,8只用于组织分布研究;多次给药(在2.5毫克/千克的冷剂量下连续给药14天,然后给予标记剂量):每性别5只动物;血液/血浆和组织残留物轮廓在各组之间没有显著差异。最大血药浓度在4小时内达到;在高剂量(两个性别)和多次低剂量(仅限雄性)时,相对粪便排泄量可能略有减少。在比较性别、剂量或单次与多次给药方案时,排泄时间或途径没有显著差异。包括所有剂量组,24小时内57-65%的给药剂量(AD)在尿液中回收,5-17%在粪便中;96小时内63-75%在尿液中,16-24%在粪便中;在96小时时,组织中剩余的AD少于1%(肾脏、肝脏和皮肤中的含量最高)。
/To study the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of 2-(14)C-DPX-T3217 in rats, doses of/ 2.5 & 120 mg/kg in corn oil /at/ 0.5 & 2 mL/animal, /were administered. Radioactivity amounted to/ ~10 & ~20 uCi/animal, respectively. /High dose/ set by expectation of slight toxicity. /With/ single gavage administration: 3/sex/dose - blood pharmacokinetics, 5/sex/dose - elimination/distribution, 8/sex/dose - tissue distribution; multiple administration (cold dosing at 2.5 mg/kg for 14 days followed by labeled dose): 5/sex; no significant differences between groups in blood/plasma and tissue residue profiles. Max. blood concentrations were attained by 4 hr; with the possible exception of a somewhat decreased relative fecal excretion at the high dose (both sexes) and at the multiple low dose (males only). No significant differences in excretion time or route were seen when comparing sexes, doses, or single vs. multiple dosing regimens. Including all dose groups, 57-65% of the administered dose (AD) recovered in urine & 5-17% in feces by 24 hr, 63-75% in urine & 16-24% in feces by 96 hr; at 96 hr <1% of AD remained in tissues (highest levels found in kidney, liver, & skin).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
(14)C-Cymoxanil施用到番茄植株的根系或叶面上,通过放射自显影、燃烧和薄层色谱分析水或甲醇提取物来跟踪其吸收、传输和降解情况。Cymoxanil在1小时内被根系吸收,并在16小时内传输到子叶、茎和叶片。该化合物在16-44小时内主要降解为甘氨酸,在根系和所有地上部分。当将(14)C-cymoxanil施用到五叶植物的叶2表面时,与单独施用(14)C-cymoxanil的植物相比,使用氧化噁菌灵和(14)C-cymoxanil混合物处理的植物显示出增强的吸收、传输和降解(主要转化为甘氨酸)现象。根系施用的数据确认了cymoxanil在番茄植株中是一种具有短暂持效的系统化合物。叶面施用的数据表明,cymoxanil、氧化噁菌灵和代森锰锌之间在控制由霜霉目引起的植物病害方面已知的协同作用,并不是由于其他杀菌剂存在时cymoxanil降解延迟所致;协同作用的机制尚未阐明。
(14)C-Cymoxanil was applied to either the root system or to the foliage of tomato plants and its uptake, translocation and degradation was followed using autoradiography, combustion and thin-layer chromatographic analyses of water or methanolic extracts. Cymoxanil was taken up by the root system within 1 hr and translocated to cotyledons, stem and leaves within 16 hr. The compound was degraded, mostly to glycine, within 16-44 h, in the root and all parts of the shoot. When applied to the surface of leaf 2 of five-leaf plants, enhanced uptake, translocation and degradation (mainly to glycine) of (14)C-cymoxanil was observed in plants treated with a mixture of oxadixyl and (14)C-cymoxanil, compared with plants treated with (14)C-cymoxanil alone. Root application data confirm that cymoxanil is a systemic compound with a short persistence in tomato plants. Foliage application data suggest that the well-documented synergistic interaction between cymoxanil, oxadixyl and mancozeb in controlling plant diseases caused by Peronosporales does not result from a delayed degradation of cymoxanil in the presence of the other fungicides; the mechanism of synergism has not yet been elucidated.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险等级:9
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S36/37,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R22,R50/53,R43
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2926909038
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3077
-
RTECS号:AB5957000
-
储存条件:0-6°C
SDS
制备方法与用途
毒性
原药对大鼠急性经口LD50为1196毫克/公斤,豚鼠为1096毫克/公斤。兔急性经皮LD50大于3000毫克/公斤。该物质对眼睛有轻度刺激,但无皮肤刺激作用。Ames试验呈阴性,表明其无致突变作用。
虹鳟鱼LC50为18.7毫克/升(96小时),野鸭和鹌鹑的LC50分别为大于10000毫克/公斤饲料和2847毫克/公斤饲料。该物质无积累毒性。
化学性质霜脲氰是一种白色结晶体,熔点为160~161℃,相对密度1.31(25℃),蒸气压约8×10-5帕斯卡(25℃)。在25℃时的溶解度分别为:丙酮10.5%,二甲基甲酰胺18.5%,氯仿10.3%,甲醇4.1%,苯0.2%,己烷0.1%,水0.1%。正常贮存条件下稳定。
用途霜脲氰是一种高效杀菌剂,具有内吸作用,与保护性杀菌剂混用能提高残留活性。它对霜霉目真菌(包括疫霉属、霜霉属和单轴霉属)有效。推荐剂量为0.9~1.2克/100平方米,用于防治马铃薯晚疫病和葡萄霜霉病。
此外,霜脲氰还适用于防治番茄、黄瓜等作物的霜霉病和晚疫病,以及黄瓜霜霉病。
生产方法-
N-氰乙酰基-N-乙基脲 的制备:将98克N-乙基脲、94克氰乙酸和200克乙酸酐混合,升温至60℃并保持3小时。冷却后减压脱去乙酸,并用水处理结晶,最终得白色细针状结晶,熔点173℃。
-
2-氰基-2-肟基乙酰胺 的制备:在氮气氛围下将甲醇、水与N-氰乙酰基-N-乙基脲混合,在40℃反应1小时后加入6摩尔/升盐酸,继续反应2小时。调节pH值至7~8。
-
霜脲氰 的合成:缓加硫酸二甲酯,并用50% NaOH溶液维持pH值在7~8之间,在40℃下反应2小时后冷却至5℃,抽滤、水洗并干燥,再于无水乙醇中重结晶。
- 农药
- 毒性分级:中毒
- 急性毒性:
- 口服-大鼠 LD50:1100毫克/公斤;
- 腹腔注射-大鼠 LD50:166毫克/公斤
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-氰基-N-[(乙基氨基)羰基]-2-(羟基亚胺)-乙酰胺 1-(2-cyano-2-hydroxyiminoacetyl)-3-ethylurea 41078-09-5 C6H8N4O3 184.155
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:通过识别色谱 19F NMR 检测和鉴定腈化合物摘要:腈类化合物在医药、农用化学品、染料和功能材料等不同领域的应用激增,需要开发快速有效的检测和识别方法。在这项研究中,我们引入了一种采用新型19 F 标记探针的化学传感策略,有助于快速、准确地分析多种含腈分析物。该方法利用19 F 标记探针与分析物之间的可逆相互作用来产生类似色谱图的输出,确保精确识别复杂基质中的各种药物和农药。此外,该动态系统提供了一个多功能平台来研究空间19 F- 19 F 相互作用,展示了其在机械研究中未来应用的潜力。DOI:10.1021/acs.analchem.3c04909
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:一种改进的霜脲氰合成方法摘要:本发明公开了一种改进的霜脲氰合成方法,该工艺废水实现了循环套用,大大降低了环保压力。所以该改进后的霜脲氰工艺不仅收率高,质量好,而且环保安全,更加适合工业化生产。公开号:CN106588700B
文献信息
-
FR2274611申请人:——公开号:——公开(公告)日:——
-
Characterization of Metabolites of Fungicidal Cymoxanil in a Sensitive Strain of Botrytis cinerea作者:Frederique Tellier、Rene Fritz、Lucien Kerhoas、Paul-Henri Ducrot、Jacques Einhorn、Abel Carlin-Sinclair、Pierre LerouxDOI:10.1021/jf8010917日期:2008.9.10The metabolism of cymoxanil [1-(2-cyano-2-methoxyiminoacetyl)-3-ethyl urea] by a very sensitive strain of Botrytis cinerea toward this fungicide was studied by using [2-(14)C]-cymoxanil. Labeled cymoxanil was added either in a culture of this strain or in its enzymatic extract. The main metabolites, detected in biological samples, were isolated and identified by mass and NMR spectrometry. Their identification allowed us to show that this strain quickly metabolized cymoxanil according to at least three enzymatic pathways: (i) cyclization leading, after hydrolysis, to ethyl parabanic acid, (ii) reduction giving demethoxylated cymoxanil, and (iii) hydrolysis and reduction followed by acetylation leading to N-acetylcyanoglycine. In a cell-free extract of the same strain, only the first and the second enzymatic reactions, quoted above, occurred. Biological tests showed that, among all the metabolites, only N-acetylcyanoglycine is fungitoxic toward this sensitive strain.
表征谱图
-
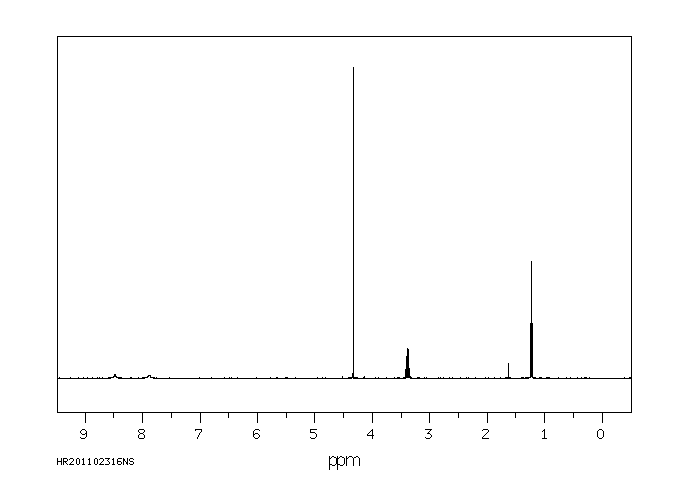
氢谱1HNMR
-
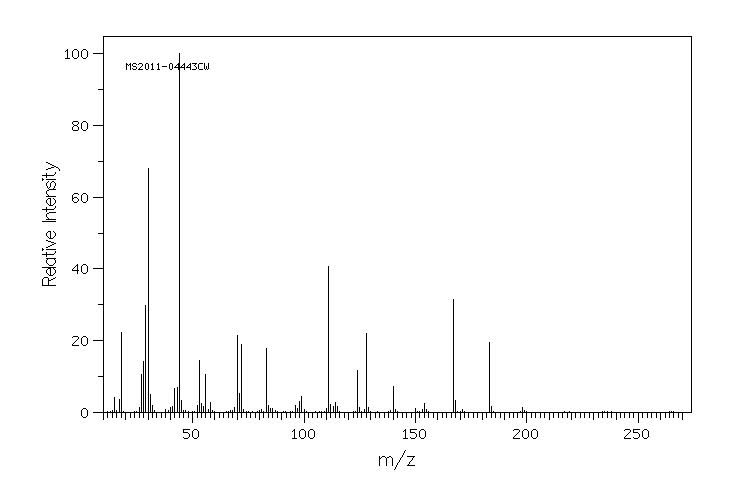
质谱MS
-
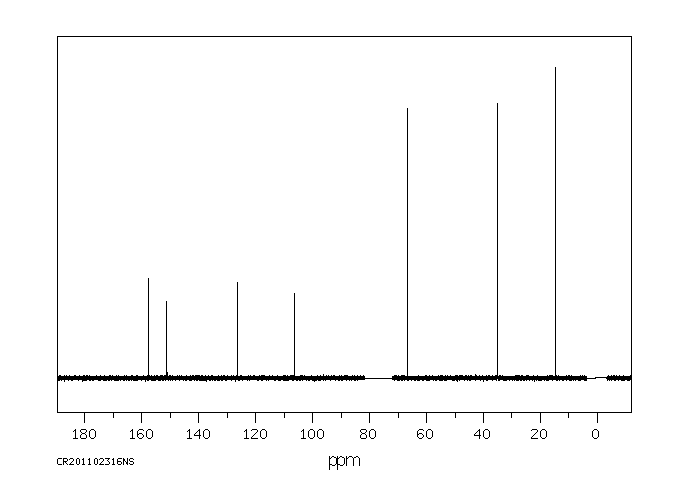
碳谱13CNMR
-
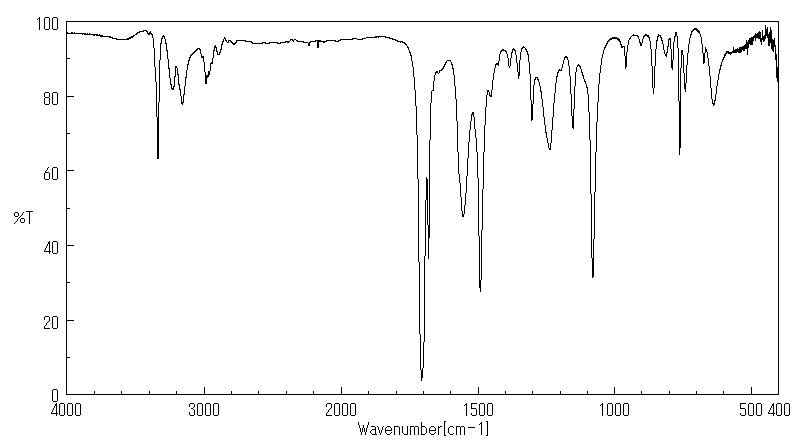
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(乙腈)二氯镍(II)
(R)-(-)-α-甲基组胺二氢溴化物
(N-(2-甲基丙-2-烯-1-基)乙烷-1,2-二胺)
(4-(苄氧基)-2-(哌啶-1-基)吡啶咪丁-5-基)硼酸
(11-巯基十一烷基)-,,-三甲基溴化铵
鼠立死
鹿花菌素
鲸蜡醇硫酸酯DEA盐
鲸蜡硬脂基二甲基氯化铵
鲸蜡基胺氢氟酸盐
鲸蜡基二甲胺盐酸盐
高苯丙氨醇
高箱鲀毒素
高氯酸5-(二甲氨基)-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-2-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-氯-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-6-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-(丙烯酰基氧基)-N,N,N-三甲基乙铵
马诺地尔
马来酸氢十八烷酯
马来酸噻吗洛尔EP杂质C
马来酸噻吗洛尔
马来酸倍他司汀
顺式环己烷-1,3-二胺盐酸盐
顺式氯化锆二乙腈
顺式吡咯烷-3,4-二醇盐酸盐
顺式双(3-甲氧基丙腈)二氯铂(II)
顺式3,4-二氟吡咯烷盐酸盐
顺式1-甲基环丙烷1,2-二腈
顺式-二氯-反式-二乙酸-氨-环己胺合铂
顺式-二抗坏血酸(外消旋-1,2-二氨基环己烷)铂(II)水合物
顺式-N,2-二甲基环己胺
顺式-4-甲氧基-环己胺盐酸盐
顺式-4-环己烯-1.2-二胺
顺式-4-氨基-2,2,2-三氟乙酸环己酯
顺式-3-氨基环丁烷甲腈盐酸盐
顺式-2-羟基甲基-1-甲基-1-环己胺
顺式-2-甲基环己胺
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(氨基甲基)-1-苯基环丙烷羧酸盐酸盐
顺式-1,3-二氨基环戊烷
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺二盐酸盐
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺
顺式-1,2-环丁腈
顺式-1,2-双氨甲基环己烷
顺式--N,N'-二甲基-1,2-环己二胺
顺式-(R,S)-1,2-二氨基环己烷铂硫酸盐
顺式-(2-氨基-环戊基)-甲醇
顺-2-戊烯腈
顺-1,3-环己烷二胺
顺-1,3-双(氨甲基)环己烷