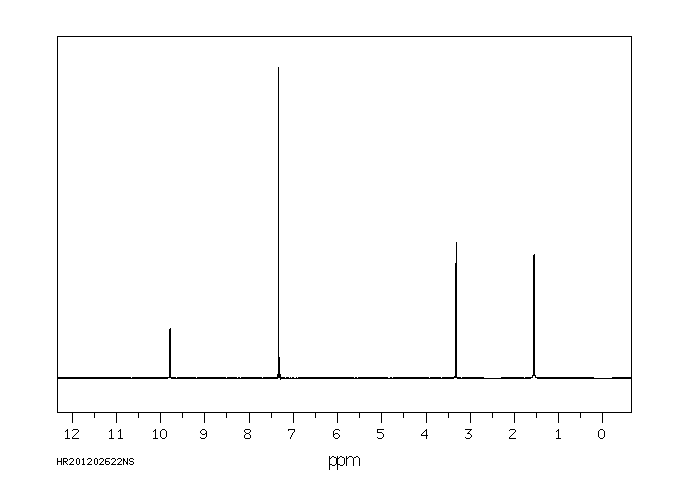
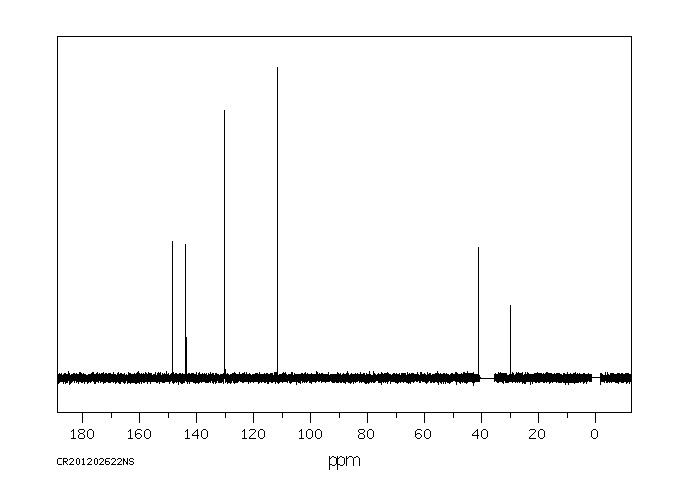
代谢
四溴双酚A(TBBPA)是一种非遗传毒性阻燃剂,会导致雌性大鼠子宫肿瘤。这些肿瘤的一个提出的机制(MoA)涉及由于TBBPA抑制雌激素硫酸转移酶(ES),即负责失活和增强雌二醇消除的酶,导致雌二醇的生物利用度增加。本研究的目的是评估TBBPA剂量和重复给药对雌性Wistar Han大鼠血浆、肝脏和子宫中TBBPA、TBBPA-葡萄糖苷酸(GA)和TBBPA-硫酸盐(S)结合物水平的影响,这些大鼠连续28天接受TBBPA(50、100、250、500或1000 mg/kg)给药。根据这一目标,TBBPA硫酸化被用作评估在高剂量TBBPA水平上雌二醇硫酸化潜力受限的替代指标。在研究第7、14和28天的4和8小时后采集血液样本,同时在28天给药后相同的时间点收集肝脏和子宫。通过LC-MS/MS分析组织样本中的TBBPA、TBBPA-GA和TBBPA-S。在血浆(第7、14和28天)以及肝脏和子宫组织(第28天)中,所有三种分析物的浓度均随剂量增加而增加,在4和8小时后给药均如此。与7天或14天给药相比,28天给药的大鼠血浆中TBBPA-GA和TBBPA-S的浓度更高,表明随着重复给药,这些结合物在系统循环中的增加。这些结合物在不同组织中的平衡也不同,高剂量时肝脏中TBBPA-S > TBBPA-GA,而在血浆和子宫中TBBPA-GA > TBBPA-S。在所有三种组织中,TBBPA-S/TBBPA-GA的比例随剂量增加呈下降趋势,表明在高TBBPA剂量水平下,TBBPA的硫酸化受到限制。这种效应在28天给药的肝脏和血浆中最明显。总的来说,这些数据表明,与诱导子宫肿瘤相关的高剂量TBBPA给药会导致结合物平衡的破坏,表现为TBBPA-S/TBBPA-GA比例的降低。TBBPA体内硫酸化的限制支持了将其定义为ES活性的抑制剂的研究数据,从而进一步支持了在Wistar Han大鼠高剂量、慢性TBBPA给药条件下提出的MoA发生的证据。鉴于在大鼠中观察到的子宫肿瘤(250-1000 mg/kg-day)仅在扰乱稳态控制的非常高的剂量下发生,考虑到目前的TBBPA暴露水平大约比这些扰乱结合途径容量的剂量低八个数量级,因此在人类中不太可能出现此类效应。
Tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA), a nongenotoxic flame retardant, causes uterine tumors in female rats. A proposed mode of action (MoA) for these tumors involves an increase in the bioavailability of estradiol as a result of TBBPA inhibiting estrogen sulfotransferases (ES), the enzymes responsible for inactivating and enhancing the elimination of estradiol. The objective of this study was to evaluate the effect of dose and repeated administration of TBBPA on the level of TBBPA, TBBPA-glucuronide (GA) and TBBPA-sulfate (S) conjugates in plasma, liver and uterus of female Wistar Han rats administered TBBPA (50, 100, 250, 500 or 1000 mg/kg) for 28 consecutive days. In accordance with this objective, TBBPA sulfation was used as a surrogate for evaluating the potential for estradiol sulfation to be limited at high dose levels of TBBPA. Blood samples were collected at 4 and 8 h post-dosing on study day 7, 14, and 28, while liver and uterus were collected at the same time points following 28 days of dosing. Tissue samples were analyzed for TBBPA, TBBPA-GA and TBBPA-S by LC-MS/MS. A dose-related increase in the concentration of all three analytes occurred in plasma (day 7, 14, and 28) as well as liver and uterus tissue (day 28) at both 4 and 8 h post dose. The plasma concentration of TBBPA-GA and TBBPA-S was higher in animals dosed for 28 days compared to those dosed for 7 or 14 days showing an increase in systemic circulation of these conjugates with repeated administration. The balance of these conjugates was also different in tissues with TBBPA-S > TBBPA-GA at high doses in the liver and TBBPA-GA > TBBPA-S in both plasma and uterus. In all three tissues the ratio of TBBPA-S/TBBPA-GA showed a decreasing trend with dose, suggesting that at high TBBPA dose levels sulfation of TBBPA becomes limited. This effect was most apparent in the liver and plasma at 28 days of administration. Together these data show that administration of high doses of TBBPA associated with the induction of uterine tumors, results in a disruption in the balance of conjugates reflected by a decrease in the TBBPA-S/TBBPA-GA ratio. A limitation in the sulfation of TBBPA in vivo supports in vitro data defining TBBPA as an inhibitor of ES activity, thus providing further support that the proposed MoA occurs under conditions of high dose, chronic TBBPA administration to Wistar Han rats. Given that the uterine tumors observed in rats (250-1000 mg/kg-day) only occur at very high doses that perturb homeostatic control, it is unlikely such effects would occur in humans given that current TBBPA exposure levels are approximately eight orders of magnitude lower than these doses that are associated with exceeding the capacity of conjugation pathways in animal studies.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)