1,3-二硝基咪唑烷-2-酮 | 2536-18-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:307.66°C (rough estimate)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.2
-
重原子数:12
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.67
-
拓扑面积:115
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:5
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1-硝基-2-咪唑烷酮 1-nitroimidazolidin-2-one 77084-61-8 C3H5N3O3 131.091
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Bis(hydrazinium) N,N'-Dinitroethylenediaminate(2 –)摘要:The title compound, 2N(2)H(5)(+).C2H2N4O42-, is an inherently insensitive high-energy material. The anion has C-i symmetry and is almost planar. The nitrate groups are asymmetric, with a mean nitrate N-O distance longer than that found in N,N'-dinitroethylenediamine and an N1-N2 distance close to a double-bond value.DOI:10.1107/s0108270196002521
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:MacKenzie et al., Canadian Journal of Research, Section B: Chemical Sciences, 1948, vol. 26, p. 138,150摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Electrophilic tetraalkylammonium nitrate nitration. I. Convenient new anhydrous nitronium triflate synthesis and in-situ heterocyclic N-nitration作者:Christopher M. Adams、Clay M. Sharts、Scott A. ShackelfordDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(00)61671-4日期:1993.10Reaction of tetra-n-butylammonium nitrate and triflic anhydride, CF3SO2OSO2CF3 (Tf2O), in dichloromethane (CH2Cl2) solvent at 0 degrees C, produces anhydrous nitronium nitrate, NO2OSO2CF3 (NO2OTf). Subsequent introduction of various heterocycles and their N-acetylated analogs yield N-nitrated products in 20–76% yield with an overall one-pot procedure.
-
A Convenient Method For<i>N</i>-Nitration Using Ammonium Nitrate/Trifluoroacetic Anhydride作者:Suresh Chander Suri、Robert D. ChapmanDOI:10.1055/s-1988-27696日期:——A mixture of ammonium nitrate and trifluoroacetic anhydride is found to be a convenient reagent for N-nitration in the synthesis of nitramines, nitramides, and nitrimides. Yields are comparable to those from conventional, but less convenient or safe, nitrating reagents.
-
Investigation of Ethylenedinitramine as a Versatile Building Block in Energetic Salts, Cocrystals, and Coordination Compounds作者:Michael S. Gruhne、Marcus Lommel、Maximilian H. H. Wurzenberger、Thomas M. Klapötke、Jörg StierstorferDOI:10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c03752日期:2021.4.5subsequent hydrolysis in water at 100 °C. The versatility of 1 allows its application as starting material for a broad range of different materials. It was used for the preparation of both various salts and cocrystalline materials incorporating varying amounts of the TATOT moiety. Furthermore, H2EDN was successfully applied in the concept of energetic coordination compounds (ECCs) resulting in five copper(II)以简单的方式制备乙二胺(H 2 EDN,1),方法是在0°C下使用100%HNO 3直接硝化2-咪唑啉酮,然后在100°C的水中水解,从而以较高的总产率制备乙二胺。多功能性1使其可用作各种不同材料的起始材料。它用于制备各种盐和结合了不同量TATOT部分的共晶材料。此外,H 2EDN已成功地应用于高能配位化合物(ECCs)的概念中,产生了五种铜(II)和两种银(I)配合物。给出了直接沉淀或缓慢结晶17种不同盐类(包括几种碱金属,碱土金属,银和富氮样品)的反应路径。通过低温单晶X射线衍射,元素分析(EA),红外光谱,差热分析(DTA)和热重分析(TGA)对这些物质进行了广泛表征,证明了它们的高热稳定性,尤其是碱盐。此外,1和所有盐的特征在于1 H,13 C和14 N NMR,而1还使用了有益的1 H- 15 N HMBC NMR光谱进行了研究。使用BAM 1-out-6方法确定了根据BAM
-
Energetic propane-1,3-diaminium and butane-1,4-diaminium salts of <i>N</i>,<i>N</i>′-dinitroethylenediazanide: syntheses, crystal structures and thermal properties作者:Gerhard T. Roodt、Bhawna Uprety、Demetrius C. Levendis、Charmaine ArderneDOI:10.1107/s2053229618017588日期:2019.1.1
The acidity of the amine H atoms and the consequent salt formation ability of ethylenedinitramine (EDNA) were analyzed in an attempt to improve the thermal stability of EDNA. Two short-chain alkanediamine bases, namely propane-1,3-diamine and butane-1,4-diamine, were chosen for this purpose. The resulting salts, namely propane-1,3-diaminium
N ,N ′-dinitroethylenediazanide, C3H12N2 2+·C2H4N4O4 2−, and butane-1,4-diaminiumN ,N ′-dinitroethylenediazanide, C4H14N2 2+·C2H4N4O4 2−, crystallize in the orthorhombic space groupPbca and the monoclinic space groupP 21/n , respectively. The resulting salts display extensive hydrogen-bonding networks because of the presence of ammonium and diazenide ions in the crystal lattice. This results in an enhanced thermal stability and raises the thermal decomposition temperatures to 202 and 221 °C compared to 180 °C for EDNA. The extensive hydrogen bonding present also plays a crucial role in lowering the sensitivity to impact of these energetic salts.为了提高乙二胺四乙酸(EDNA)的热稳定性,我们分析了胺 H 原子的酸性以及由此产生的成盐能力。为此选择了两种短链烷二胺碱,即丙烷-1,3-二胺和丁烷-1,4-二胺。由此产生的盐,即丙烷-1,3-二氨基 N,N′-二硝基乙二氮杂烷,C3H12N2 2+-C2H4N4O4 2-,以及丁烷-1,4-二氨基 N,N′-二硝基乙撑二氮杂烷,C4H14N2 2+- 2- 分别在正交空间群 Pbca 和单斜空间群 P21/n 中结晶。由于铵离子和重氮离子存在于晶格中,因此生成的盐显示出广泛的氢键网络。这就增强了热稳定性,并将热分解温度提高到 202 和 221 °C,而 EDNA 的温度仅为 180 °C。存在的大量氢键在降低这些高能盐对冲击的敏感性方面也发挥了重要作用。 -
Nitration of carbonic, sulfuric and oxalic acid-derived amides in liquid carbon dioxide作者:Ilya V. Kuchurov、Igor V. Fomenkov、Sergei G. Zlotin、Vladimir A. TartakovskyDOI:10.1016/j.mencom.2013.03.008日期:2013.3N-Nitro- and N,N'-dinitroamides of carbonic, sulfuric and oxalic acids have been prepared in 76-99% yield by the nitration of the corresponding amides with dinitrogen pentoxide in liquid carbon dioxide.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
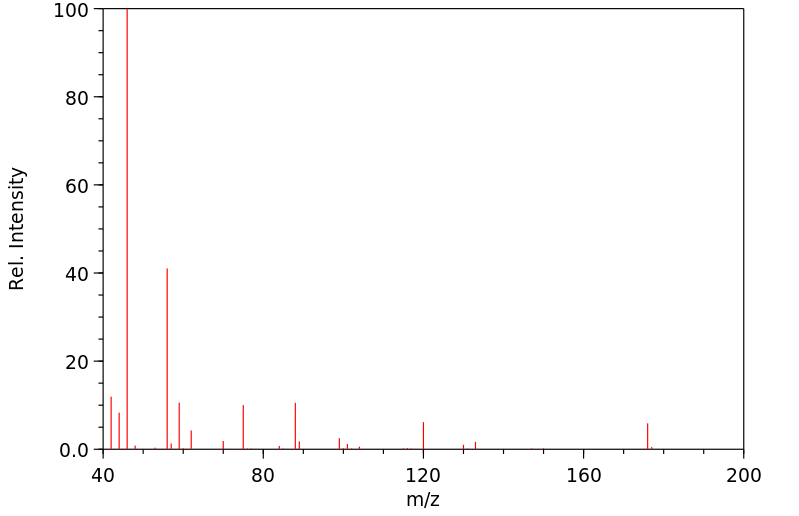
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息