2,2-双[(4-三甲基硅氧基)苯基]丙烷 | 4387-16-0
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:179°C 1,5mm
-
密度:0.981 g/cm3
-
保留指数:2203
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):6.44
-
重原子数:25
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.43
-
拓扑面积:18.5
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
TSCA:No
-
海关编码:2931900090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 双酚A BPA 80-05-7 C15H16O2 228.291 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2,2-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl) propane monotrimethylsilyl ether —— C18H24O2Si 300.473 双酚A BPA 80-05-7 C15H16O2 228.291 —— bisphenol A bis(methyl carbonate) 4824-74-2 C19H20O6 344.364 —— Carbonic acid, 4-[1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-methylethyl]phenyl methyl ester 122890-41-9 C17H18O4 286.328
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:2,2-双[(4-三甲基硅氧基)苯基]丙烷 在 nano magnetic sulfated zirconia (Fe3O4 at ZrO2/SO42-) 作用下, 以 neat (no solvent) 为溶剂, 反应 0.75h, 以72%的产率得到双酚A参考文献:名称:Nano Fe3O4@ZrO2/SO42−:一种在无溶剂条件下使用HMDS对羟基进行保护和脱保护的高效催化剂摘要:图形摘要在这项工作中,我们介绍了在纳米磁性硫酸化氧化锆(Fe3O4@ZrO2/SO42−)作为固体酸催化剂存在下,HMDS 保护和脱保护各种醇类和酚类的新方法。温和无溶剂条件。这种方法具有有趣的优点,如反应时间短和后处理过程简单。考虑到这种新型多相催化剂的一些突出优点,如优异的收率、催化剂的可重复使用性和易热稳定性、高酸性、强和优异的磁性能,该方法在绿色化学原理方面非常有趣。DOI:10.1080/10426507.2016.1236104
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Nano Fe3O4@ZrO2/SO42−:一种在无溶剂条件下使用HMDS对羟基进行保护和脱保护的高效催化剂摘要:图形摘要在这项工作中,我们介绍了在纳米磁性硫酸化氧化锆(Fe3O4@ZrO2/SO42−)作为固体酸催化剂存在下,HMDS 保护和脱保护各种醇类和酚类的新方法。温和无溶剂条件。这种方法具有有趣的优点,如反应时间短和后处理过程简单。考虑到这种新型多相催化剂的一些突出优点,如优异的收率、催化剂的可重复使用性和易热稳定性、高酸性、强和优异的磁性能,该方法在绿色化学原理方面非常有趣。DOI:10.1080/10426507.2016.1236104
文献信息
-
Sulfur(VI) fluoride compounds and methods for the preparation thereof申请人:The Scripps Research Institute公开号:US10117840B2公开(公告)日:2018-11-06This application describes a compound represented by Formula (I): (I) wherein: Y is a biologically active organic core group comprising one or more of an aryl group, a heteroaryl aryl group, a nonaromatic hydrocarbyl group, and a nonaromatic heterocyclic group, to which Z is covalently bonded; n is 1, 2, 3, 4 or 5; m is 1 or 2; Z is O, NR, or N; X1 is a covalent bond or —CH2CH2—, X2 is O or NR; and R comprises H or a substituted or unsubstituted group selected from an aryl group, a heteroaryl aryl group, a nonaromatic hydrocarbyl group, and a nonaromatic heterocyclic group. Methods of preparing the compounds, methods of using the compounds, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds are described as well.
-
Multicyclic Poly(ether ketone)s Obtained by Polycondensation of 2,6,4‘-Trifluorobenzophenone with Various Diphenols作者:Hans R. Kricheldorf、Radka Hobzova、Lali Vakhtangishvili、Gert SchwarzDOI:10.1021/ma050037+日期:2005.5.12,6,4‘-Trifluorobenzophenone (TFB) was polycondensed with silylated 4,4‘-dihydroxybiphenyl (DHBP) or silylated bisphenol A in N-methylpyrrolidone by means of K2CO3 as catalyst and HF acceptor. At constant concentration (0.08 mol/L) the feed ratio was varied from 1.0/1.0 to 1.0/1.5. For polycondensations of DHBP cross-linking was observed for feed ratios above 1.0/1.1, whereas no gelation occurred with通过K 2 CO 3将2,6,4'-三氟二苯甲酮(TFB)与甲硅烷基化的4,4'-二羟基联苯(DHBP)或甲硅烷基化的双酚A在N-甲基吡咯烷酮中进行缩聚。作为催化剂和HF受体。在恒定浓度(0.08 mol / L)下,进料比从1.0 / 1.0变化至1.0 / 1.5。对于DHBP的缩聚,在进料比高于1.0 / 1.1时观察到交联,而与双酚A无关,无论进料比如何都没有发生凝胶化。MALDI-TOF质谱法在所有情况下均证明了环状,双环和多环低聚物和聚合物的形成。在进料比为1.00 / 1.48的情况下,没有官能团(末端)的多环化合物是唯一的反应产物。然而,只有当TFB的初始浓度降低到0.04 mol / L时才避免凝胶化。在这些优化的条件下,又将三双类似双酚A的二酚与TBP缩聚,并再次获得了不含官能团的多环作为主要反应产物。6 -10 9达。
-
Assessment of Exposure to Di-(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate (DEHP) Metabolites and Bisphenol A (BPA) and Its Importance for the Prevention of Cardiometabolic Diseases作者:Fabrizia Carli、Demetrio Ciociaro、Amalia GastaldelliDOI:10.3390/metabo12020167日期:——
Exposomics analyses have highlighted the importance of biomonitoring of human exposure to pollutants, even non-persistent, for the prevention of non-communicable diseases such as obesity, diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular diseases. Phthalates and bisphenol A (BPA) are endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) widely used in industry and in a large range of daily life products that increase the risk of endocrine and cardiometabolic diseases especially if the exposure starts during childhood. Thus, biomonitoring of exposure to these compounds is important not only in adulthood but also in childhood. This was the goal of the LIFE-PERSUADED project that measured the exposure to phthalates (DEHP metabolites, MEHP, MEHHP, MEOHP) and BPA in Italian mother–children couples of different ages. In this paper we describe the method that was set up for the LIFE PERSUADED project and validated during the proficiency test (ICI/EQUAS) showing that accurate determination of urinary phthalates and BPA can be achieved starting from small sample size (0.5 mL) using two MS techniques applied in cascade on the same deconjugated matrix.
曝露组学分析凸显了生物监测人类暴露于污染物的重要性,即使是非持久性的,以预防非传染性疾病,如肥胖症、糖尿病、非酒精性脂肪肝、动脉硬化和心血管疾病。邻苯二甲酸酯和双酚A(BPA)是一种广泛用于工业和日常生活产品中的内分泌干扰物质(EDC),如果暴露始于儿童期,会增加内分泌和心血管代谢疾病的风险。因此,这些化合物的暴露生物监测不仅在成年人中重要,而且在儿童中也很重要。这是LIFE-PERSUADED项目的目标,该项目测量了不同年龄的意大利母亲-儿童夫妇对邻苯二甲酸酯(DEHP代谢物,MEHP,MEHHP,MEOHP)和BPA的暴露。在本文中,我们描述了为LIFE PERSUADED项目设立并在ICI/EQUAS的熟练度测试中进行验证的方法,表明可以从小样本量(0.5 mL)开始使用两种串联的质谱技术在相同的脱共轭矩阵上实现准确测定尿中邻苯二甲酸酯和BPA。 -
Synthesis of 4-hydroxyarylene ethers by the equilibration of phenols with poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene ether)作者:Dwain M. WhiteDOI:10.1021/jo01254a010日期:1969.2
-
Niederpruem,H. et al., Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1973, p. 20 - 32作者:Niederpruem,H. et al.DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
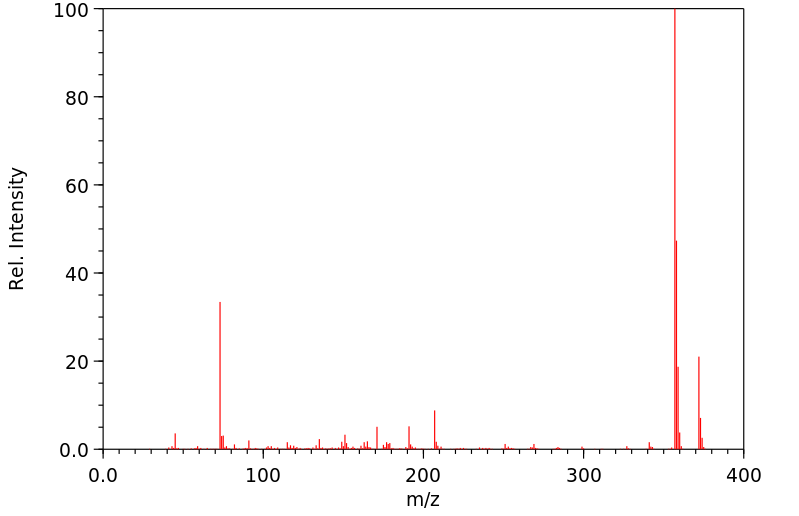
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息