2-(二甲基苯基硅烷基)苄醇 | 853955-69-8
中文名称
2-(二甲基苯基硅烷基)苄醇
中文别名
——
英文名称
[2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]dimethyl(phenyl)silane
英文别名
[2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]phenyldimethylsilane;2-(Dimethylphenylsilyl)benzyl alcohol;[2-[dimethyl(phenyl)silyl]phenyl]methanol
CAS
853955-69-8
化学式
C15H18OSi
mdl
——
分子量
242.393
InChiKey
GEEGNBYRNRXTOT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:53-54 °C
-
沸点:342.1±34.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.04±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.0
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.2
-
拓扑面积:20.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:2-(二甲基苯基硅烷基)苄醇 在 bis(1,5-cyclooctadiene)nickel (0) 、 sodium periodate 、 四氧化锇 、 水 、 caesium carbonate 、 N-甲基吗啉氧化物 、 1,3-双(2,4,6-三甲基苯基)氯化咪唑 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 、 环戊基甲醚 、 水 为溶剂, 反应 48.0h, 生成 (3R*,5S*)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-3-phenyldihydrofuran-2(3H)-one参考文献:名称:Diastereoselective Coupling of 1,3-Diene, Ketone, and Organometallic Reagents by Nickel Catalyst: Stereoselective Construction of Tetrasubstituted Carbon Centers摘要:研究了镍催化的 1,3-二烯、酮和有机硼或有机硅试剂的三组分偶联反应。使用 PhB(OH)2 进行的偶联反应产生了单一非对映异构体的 1,3-炔取代 4-戊烯-1-醇衍生物,而在类似条件下使用四有机硅试剂进行的反应则只产生了相应的 1,3-反异构体。在这两个反应中,都以高度非对映选择性的方式构建了一个四取代碳中心。DOI:10.1246/cl.2009.594
-
作为产物:描述:((2-bromobenzyl)oxy)dimethyl(phenyl)silane 在 lithium 、 水 、 碳酸氢钠 作用下, 以 乙醚 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以97%的产率得到2-(二甲基苯基硅烷基)苄醇参考文献:名称:Intramolecular nucleophilic attack at silicon in o-silylbenzyl alcohols. Generation of allyl and benzyl anion equivalents摘要:Substituted silyl ethers of o-bromobenzyl alcohols and the derived o-silylbenzyl alcohols were used to transfer allyl and benzyl groups from silicon to the electrophiles benzaldehyde and benzophenone in excellent yields. gamma-Oxidosilane intermediates (and possibly hypercoordinated silicon intermediates) are postulated. (C) 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.tet.2011.09.127
文献信息
-
Silicon-Based Cross-Coupling Reagent and Production Method of Organic Compound Using the Same申请人:Nakao Yoshiaki公开号:US20090069577A1公开(公告)日:2009-03-12In one embodiment of the present invention, a silicon-based cross-coupling reagent is disclosed which is a highly stable tetraorganosilicon compound allowing for a cross-coupling reaction under mild reaction conditions without using fluoride ions, transition metal promoter, or strong bases, and the residue of the silicon reagent can be recovered and reused. The silicon-based cross-coupling reagent is a silicon compound in which an o-hydroxymethylphenyl group is connected to a silicon atom for intramolecular activation.
-
Synthesis of Biaryls and Oligoarenes Using Aryl[2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]dimethylsilanes作者:Jinshui Chen、Masaaki Tanaka、Akhila K. Sahoo、Masahide Takeda、Akira Yada、Yoshiaki Nakao、Tamejiro HiyamaDOI:10.1246/bcsj.20090325日期:2010.5.15Through intramolecular activation, highly stable aryl[2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]dimethylsilanes can selectively transfer their aryl groups to effect a cross-coupling reaction with various aryl bromides and chlorides in the presence of a weak non-fluoride base and a palladium/copper catalyst. This reaction tolerates a wide range of functional groups, producing the corresponding functionalized biaryls in high yields with excellent chemoselectivity. Newly disclosed reaction conditions allow the recovery of a cyclic silyl ether in modest-to-good yields and reuse for the synthesis of the arylsilanes. The introduction of two isopropyl groups on the silicon center instead of methyl groups improves the stability and allows quantitative recovery of the silicon residue. Finally, aryl halides having an O-protected [2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]dimethylsilyl group cross-couple with the arylsilane reagents to give silyl-functionalized biaryls. Upon deprotection, the biaryls further react with the silylated electrophiles. The iterative cross-coupling–deprotection sequences allow rapid assembly of silylated oligoarenes. Syntheses of di- and trisilyloligoarenes are also achieved by use of orthogonal O-protecting groups.通过分子内活化,高度稳定的二甲基[2-(羟甲基)苯基]硅烷可以将其苯基选择性地转移到各种含有苯基卤化物的芳基溴化物和氯化物上,在非氟化弱碱和钯/铜催化剂的存在下进行交联反应。该反应耐受广泛的功能基团,以高产率和高化学选择性生成相应的功能化双芳基化合物。新披露的反应条件允许以中等至良好的产率回收环状硅醚,并可重复使用于合成芳基硅烷。在硅中心引入两个异丙基取代甲基可提高稳定性,并能定量回收硅残基。最后,拥有保护性O-[2-(羟甲基)苯基]二甲基硅烷基团的芳基卤化物与芳基硅烷反应剂交联,生成含硅功能化双芳基化合物。去保护后,双芳基化合物再与硅化亲电试剂反应。通过交叉耦合-去保护序列的迭代,可以快速组装含硅的寡芳烃。通过使用正交氧保护基团,还可以实现二硅和三硅寡芳烃的合成。
-
Organo[2-(hydroxymethyl)phenyl]dimethylsilanes as Mild and Reproducible Agents for Rhodium-Catalyzed 1,4-Addition Reactions作者:Yoshiaki Nakao、Jinshui Chen、Hidekazu Imanaka、Tamejiro Hiyama、Yoshitaka Ichikawa、Wei-Liang Duan、Ryo Shintani、Tamio HayashiDOI:10.1021/ja071969r日期:2007.7.1achievement of the corresponding enantioselective transformations using the tetraorganosilicon reagents, providing the silicon-based approach to optically active ketones and substituted piperidones that serve as synthetic intermediates of pharmaceuticals. A rhodium alkoxide species is suggested to be responsible for a transmetalation step on the basis of the observed kinetic resolution of a racemic chiral phenylsilane
-
Carboallylation of electron-deficient alkenes by palladium/copper catalysis作者:Kazuhiko Semba、Naoki Ohta、Yuko Yano、Yoshiaki NakaoDOI:10.1039/c8cc06023a日期:——A method for the carboallylation of electron-deficient alkenes with tetraorganosilicon reagents and allylic carbonates based on Pd/Cu catalysis has been developed. This method affords a wide range of structurally diverse carbon skeletons from readily available starting materials, and tolerates various functional groups.
-
Copper-catalyzed Carboxylation of Unactivated Aryl- and Alkenylsilanes with Carbon Dioxide作者:Woo-Jin Yoo、Junpei Kondo、Shū KobayashiDOI:10.1246/cl.190577日期:2019.10.5A mild synthetic protocol for the preparation of aryl and alkenyl carboxylic acids was developed through a copper-catalyzed carboxylation reaction of organosilanes with carbon dioxide. The key to t...
表征谱图
-
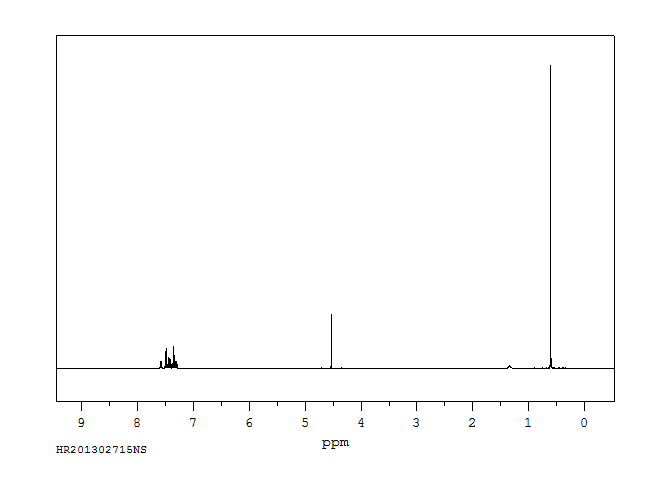
氢谱1HNMR
-
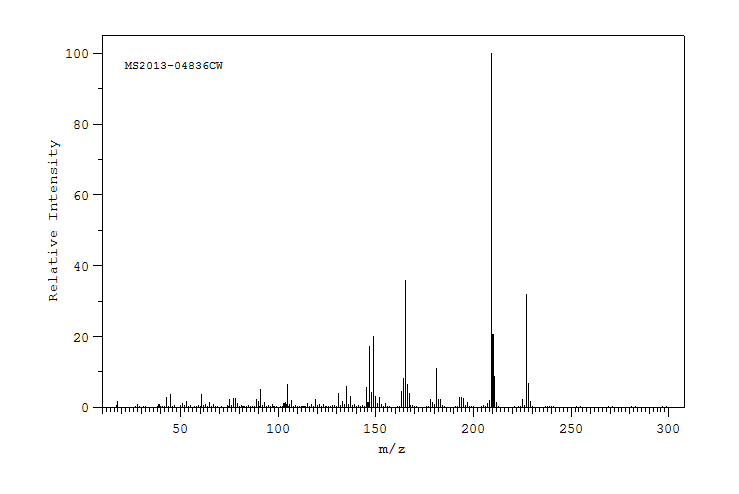
质谱MS
-
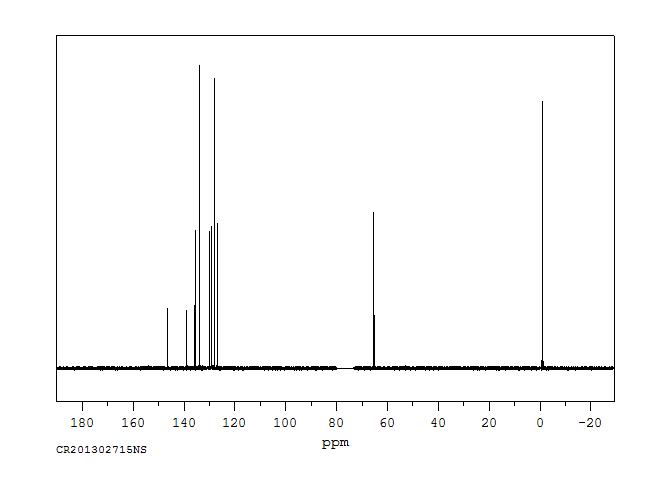
碳谱13CNMR
-
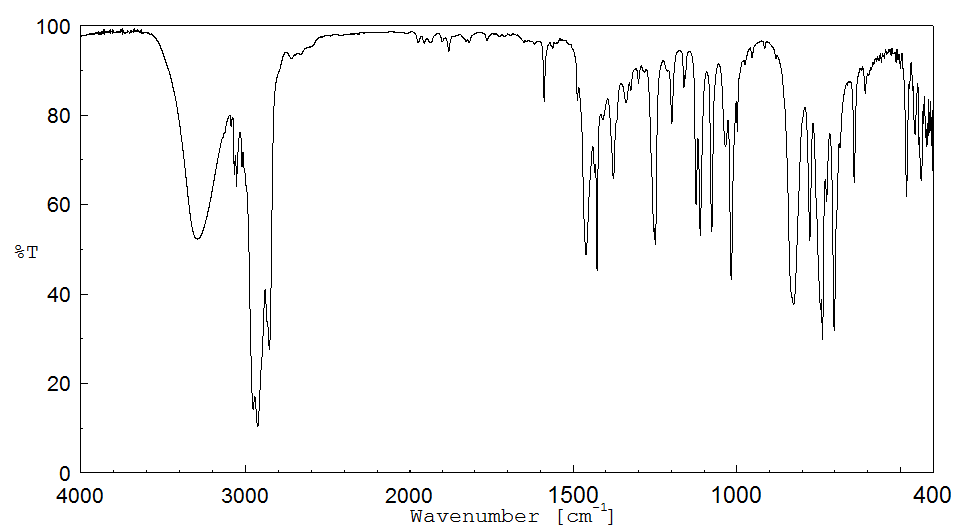
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫