阿特拉津 | 1912-24-9
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:175°C
-
沸点:200°C
-
密度:1.187
-
闪点:11 °C
-
溶解度:二甲基亚砜:83.33 mg/mL(386.36 mM)
-
暴露限值:OSHA PEL: TWA 5 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 mg/m3.
-
LogP:2.59 at 20℃ and pH7.31-7.51
-
表面张力:57.6mN/m at 30mg/L and 21℃
-
解离常数:1.56 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Atrazine is a white crystalline solid. Melting point 173-175°C. Sinks in water. A selective herbicide used for season-long weed control in a variety of crops.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless powder
-
气味:Odorless
-
蒸汽压力:2.89X10-7 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
如果按照规格正确使用和储存,则不会发生分解,并且没有已知的危险反应。应避免与氧化物接触。致畸和致癌试验结果均为阴性。这种物质对鸟类和鱼类低毒,对眼睛无刺激性,但对皮肤有轻微刺激。
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrogen chloride gas.
-
腐蚀性:Atrazine technical and formulated products are noncorrosive to equipment and metal surfaces.
-
燃烧热:-9,500 btu/lb = -5,300 cal/g = -220X10+5 J/kg (est)
-
碰撞截面:150.74 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: stepped-field]
-
保留指数:1696;1708;1712;1729;1724;1711;1710;1726;1705;1726;1724.1;1720.6;1715.3;1696.8;1691;1724.2;1699;1699;1711;1718.5;1700;1700;1718.3;1714.6
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.6
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:4
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.625
-
拓扑面积:62.7
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 5 mg/m3
-
危险等级:9
-
危险品标志:Xn,N
-
安全说明:S16,S2,S36/37,S45,S60,S61,S7
-
危险类别码:R48/22,R50/53,R43
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2933699011
-
危险品运输编号:3077
-
RTECS号:XY5600000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:9
-
储存条件:请将贮藏器保持密封状态,并将其存放在阴凉、干燥处。同时,确保工作环境具备良好的通风或排气设施。
SDS
| 国标编号: | 61898 |
| CAS: | 1912-24-9 |
| 中文名称: | 阿特拉津 |
| 英文名称: | Atrazine;2-Chloro-4-ethylamino-6-isopropylamino-s-triazine |
| 别 名: | 2-氯-4-乙氨基-6-异丙氨基-1,3,5-三嗪;莠去津 |
| 分子式: | C 8 H 14 ClN 5 |
| 分子量: | 215.72 |
| 熔 点: | 171~174℃ |
| 密 度: | 相对密度(水=1)1.2(20 |
| 蒸汽压: | |
| 溶解性: | 难溶于水,微溶于多数有机溶剂 |
| 稳定性: | 稳定 |
| 外观与性状: | 纯品为无色结晶,原药为白色粉末 |
| 危险标记: | 15(有害品,远离食品) |
| 用 途: | 农用除草剂 |
2.对环境的影响:
一、健康危害
侵入途径:吸入、食入、经皮吸收。 健康危害:本品对皮肤和眼睛有刺激作用。属低毒除草剂。动物实验致癌、致畸为阳性。对人有致突变作用。
二、毒理学资料及环境行为
急性毒性:LD50672mg/kg(大鼠经口);850mg/kg(小鼠经口);750mg/kg(兔经口);7500mg/kg(兔经皮) 刺激性:人经皮500mg,中等刺激;人经眼100mg,严重刺激。
危险特性:不易燃烧。受高热分解,放出有毒的烟。 燃烧(分解)产物:一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物、氯化氢。
3.现场应急监测方法:
4.实验室监测方法:
气相色谱法《水和废水标准检验方法》15版,中国建筑工业出版社,1985年高效液相色谱法(中国环境监测总站,水质)
5.环境标准:
| 前苏联 | 车间空气中有害物质的最高容许浓度 | 2mg/m 3 |
| 前苏联(1978) | 环境空气中最高容许浓度 | 0.02mg/m 3 |
| 中国(GHZB1-1999) | 地面水环境质量标准(I、II、III类水域) | 0.003mg/L |
| 前苏联(1978) | 渔业用水中最高容许浓度 | 5μg/L |
6.应急处理处置方法:
一、泄漏应急处理
隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,小心扫起,避免扬尘,运至废物处理场所。用水刷洗泄漏污染区,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。
二、防护措施
呼吸系统防护:生产操作或农业使用时,必须佩戴防毒口罩。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,应该佩戴自给式呼吸器。 眼睛防护:戴化学安全防护眼镜。 防护服:穿相应的防护服。 手防护:戴防护手套。 其它:工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。实行就业前和定期的体检。
三、急救措施
皮肤接触:用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 眼睛接触:拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 吸入:脱离现场至空气新鲜处。就医。 食入:误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。洗胃。就医。
灭火方法:泡沫、干粉、砂土。
制备方法与用途
阿特拉津为无色结晶,熔点173~175℃。溶于水、甲醇、氯仿,在中性、微酸性及微碱性介质中稳定,但碱和无机酸在高温下可将其水解为无除草活性的羟基衍生物,无腐蚀性。其由2,4,6-三氯-1,3,5-三嗪先后与乙胺、异丙胺反应制得。
毒性大鼠急性经口LD50为3080mg/kg,小鼠为850mg/kg;口服- 大鼠 LD50: 672毫克/公斤; 口服- 小鼠 LD50: 850 毫克/ 公斤。皮肤刺激数据:兔子38毫克轻度;眼睛刺激数据:兔子6.32毫克重度。可燃性危险特性:燃烧产生有毒氮氧化物和氯化物气体。储运特性:库房通风低温干燥; 与食品原料分开储运。
急性毒性- 大鼠口服LD50: 672 毫克/公斤
- 小鼠口服LD50: 850 毫克/ 公斤
- 皮肤刺激:兔子38毫克轻度
- 眼睛刺激:兔子6.32毫克重度
燃烧产生有毒氮氧化物和氯化物气体。
储运特性库房通风低温干燥; 与食品原料分开储运。
灭火剂干粉、泡沫、砂土。
职业标准- TWA: 5 毫克/立方米
- STEL: 20 毫克/立方米
农药,毒性分级:中毒。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 扑灭津 propazine 139-40-2 C9H16ClN5 229.713 西玛津 Simazine 122-34-9 C7H12ClN5 201.659 2,4-二氯-6-异丙基氨基-1,3,5-三嗪 2,4-dichloro-6-isopropylamino-1,3,5-triazine 3703-10-4 C6H8Cl2N4 207.062 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 扑灭津 propazine 139-40-2 C9H16ClN5 229.713 二丁基阿特拉津 Deethylatrazine 6190-65-4 C6H10ClN5 187.632 —— Ethanol, 2-[[4-chloro-6-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]- 2904-53-2 C8H14ClN5O 231.685 西玛津 Simazine 122-34-9 C7H12ClN5 201.659 氟氯氢菊脂(去异丙基莠去津) Deisopropylatrazine 1007-28-9 C5H8ClN5 173.605 —— β-AIPOH —— C8H14ClN5O 231.685 —— α-AETOH 169523-79-9 C8H14ClN5O 231.685 2-氯-4-乙酰氨基-6-(异丙基氨基)-s-三嗪 2-chloro-4-(acetamido)-6-(isopropylamino)-s-triazine 83364-15-2 C8H12ClN5O 229.669 —— 6-chloro-N4-propyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine 37019-16-2 C6H10ClN5 187.632 2-氯-4-乙酰氨基-6-(乙基氨基)-s-三嗪 6-acetamido-2-chloro-4-isopropylamino-1,3,5-triazine 142179-76-8 C7H10ClN5O 215.642 2,4-二氯-6-异丙基氨基-1,3,5-三嗪 2,4-dichloro-6-isopropylamino-1,3,5-triazine 3703-10-4 C6H8Cl2N4 207.062 2-氯-4-乙酰氨基-6-氨基-s-三嗪 4-acetamido-6-amino-2-chloro-s-triazine 115339-34-9 C5H6ClN5O 187.589 —— N2-ethyl-N4-isopropyl-1,3,5-triazin-2,4-diamine 4150-65-6 C8H15N5 181.241 —— N2-ethyl-N4-isopropyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-triamine 112609-49-1 C8H16N6 196.255 N,N'-二乙基-N''-异丙基-1,3,5-三嗪-2,4,6-三胺 2,4-bis (ethylamino)-6-isopropylamino-s-triazine 30360-19-1 C10H20N6 224.309 —— 2-[[4-(ethylamino)-6-(propan-2-ylamino)-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl]amino]ethanol 125101-21-5 C10H20N6O 240.308 2-乙氨基-4-异丙基氨基-6-二甲氨基-1,3,5-三嗪 2-Ethylamino-4-isopropylamino-6-dimethylamino-1,3,5-triazin 100033-16-7 C10H20N6 224.309 —— 2,4-Bisisopropylamino-6-dimethylamino-1,3,5-triazin 74150-98-4 C11H22N6 238.336 N-亚硝基莠去津 N-nirosoatrazine 56525-09-8 C8H13ClN6O 244.684 2-羟基莠去津 Hydroxyatrazine 2163-68-0 C8H15N5O 197.24 4-(乙基氨基)-6-(异丙基氨基)-1,3,5-三嗪-2-硫醇 2-mercapto-4-isopropylamino-6-ethylamino-symm-triazine 5498-17-9 C8H15N5S 213.307 —— 2-fluoro-4-(isopropylamino)-6-(ethylamino)-s-triazine 777-56-0 C8H14FN5 199.231 2-氯-4,6-二氨基-1,3,5-三嗪 2-Chloro-4,6-diamino-1,3,5-triazine 3397-62-4 C3H4ClN5 145.551 —— Deethylhydroxyatrazine 19988-24-0 C6H11N5O 169.186 - 1
- 2
- 3
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Estimation of dioxin emission from fires in chemicals摘要:The formation of the 17 toxic 2,3,7,8-substituted PCDDs and PCDFs during combustion of selected chemicals were measured by high-resolution GC/MS. The 16 chemicals studied were commonly used chlorinated pesticides, industrial chemicals, and PVC. In a series of experiments carried out in a DIN 53,436 furnace, 2.5 g of these compounds were burned at 500 degrees C and 900 degrees C, respectively. The resultant yields ranged from 740 ng ITEQ/g for pentachlorophenol, to below 0.01 ng ITEQ/g for PVC and dichlobenil. The results show that some chemicals generate PCDD/F in very high possibly dangerous - amounts during burning, whereas others generate insignificant amounts. The influence of scale were studied for chlorobenzene and 4-chloro-3-nitro-benzoic acid in additional experiments, carried out in a cone calorimeter burning 20 g substance, and in ISO 9705 room test burning about 50 kg. A good agreement between the results for large and small scale indicated that formation of PCCD/F during a fire may be estimated from laboratory experiments. This suggest laboratory test may be used to screen for chemicals posing a hazard for release of PCDD/F during fires. (C) 1999 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/s0045-6535(99)00231-3
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Gontscharuk W. W., Wakulenko W. F., Taran P. N., Samsoni-Todorow A. O., Khimija i tekhnol. wody, 16 (1994) N 3, S 250-255摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE AND 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO))MÉTHYL]-N-(TÉTRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE ET DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO)MÉTHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'HERBICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG公开号:WO2021013969A1公开(公告)日:2021-01-28The present invention related to compounds of Formula (I): or an agronomically acceptable salt thereof, wherein Q, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are as described herein. The invention further relates to compositions comprising said compounds, to methods of controlling weeds using said compositions, and to the use of compounds of Formula (I) as a herbicide.本发明涉及以下式(I)的化合物或其农业上可接受的盐,其中Q、R2、R3、R4、R5和R6如本文所述。该发明还涉及包含所述化合物的组合物,使用这些组合物控制杂草的方法,以及将式(I)的化合物用作除草剂的用途。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
[EN] HERBICIDALLY ACTIVE HETEROARYL-S?BSTIT?TED CYCLIC DIONES OR DERIVATIVES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DIONES CYCLIQUES SUBSTITUÉES PAR HÉTÉROARYLE À ACTIVITÉ HERBICIDE OU DÉRIVÉS DE CELLES-CI申请人:SYNGENTA LTD公开号:WO2011012862A1公开(公告)日:2011-02-03The invention relates to a compound of formula (I), which is suitable for use as a herbicide wherein G is hydrogen or an agriculturally acceptable metal, sulfonium, ammonium or latentiating group; Q is a unsubstituted or substituted C3-C8 saturated or mono-unsaturated heterocyclyl containing at least one heteroatom selected from O, N and S, or Q is heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; m is 1, 2 or 3; and Het is an optionally substituted monocyclic or bicyclic heteroaromatic ring; and wherein the compound is optionally an agronomically acceptable salt thereof.
-
TRIAZOLE ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF
表征谱图
-
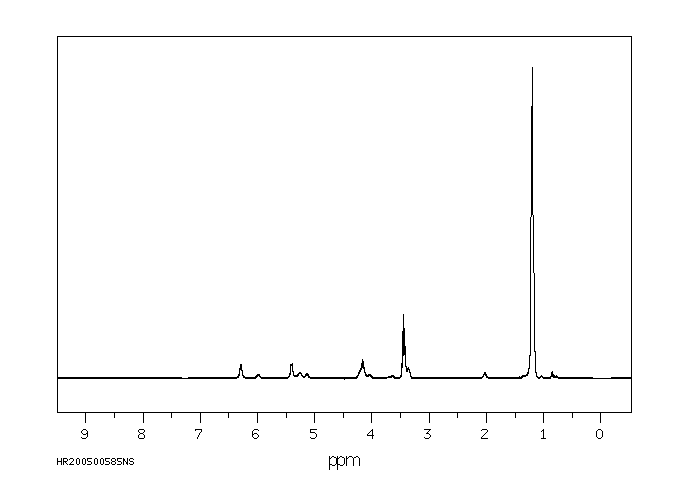
氢谱1HNMR
-
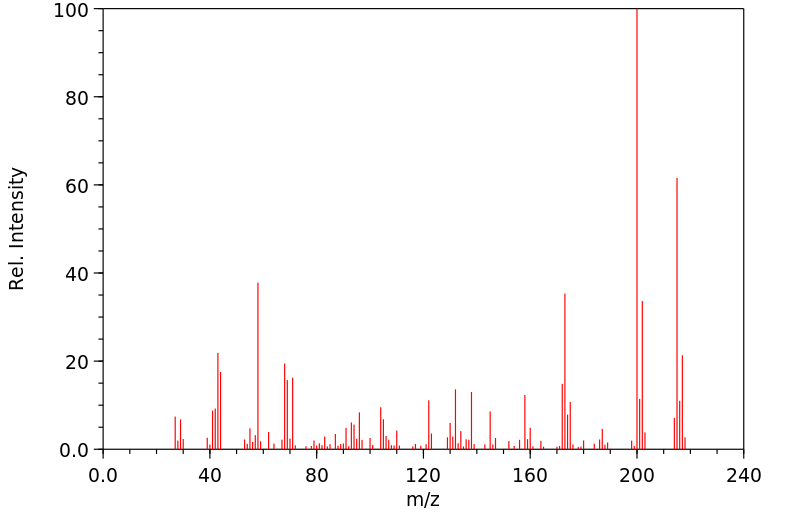
质谱MS
-
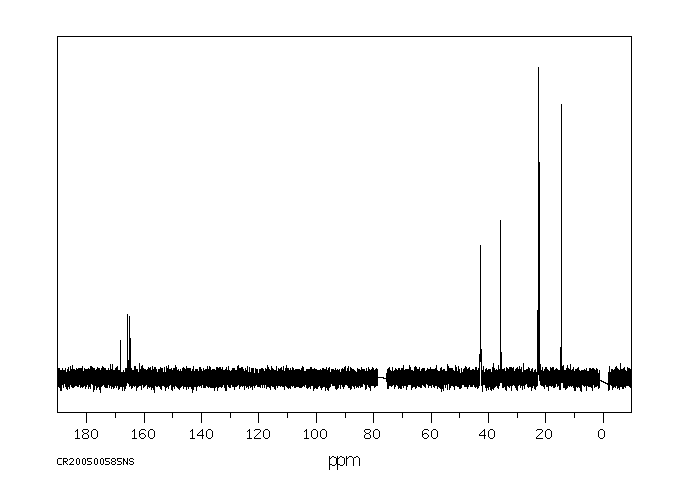
碳谱13CNMR
-
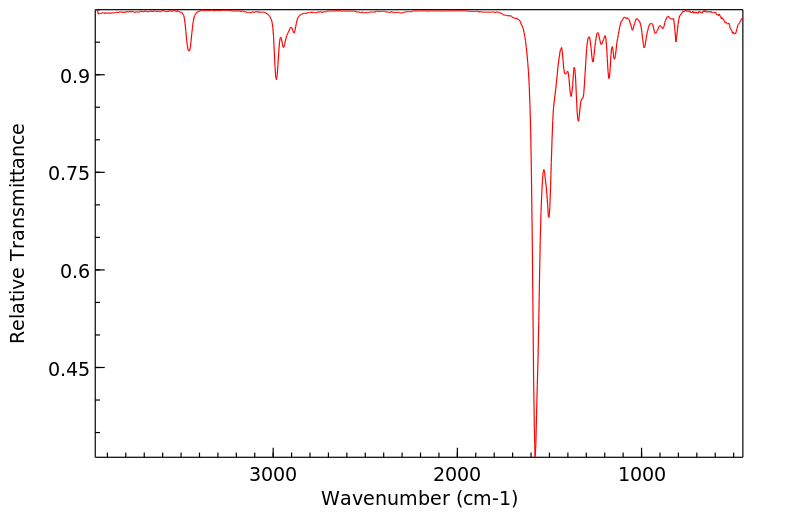
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息