N-甲基四氟酞酰亚胺 | 33795-85-6
中文名称
N-甲基四氟酞酰亚胺
中文别名
N-甲基-4,5,6,7-四氟邻苯二甲酰亚胺;3,4,5,6-四氟-N-甲基酞亚胺;3,4,5,6-四氟-N-甲基邻苯二甲酰亚胺
英文名称
N-methyl-tetrafluorophthalimide
英文别名
3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-N-methylphthalimide;N-Methyl tetrafluorophthalimide;4,5,6,7-tetrafluoro-2-methylisoindole-1,3-dione
CAS
33795-85-6
化学式
C9H3F4NO2
mdl
MFCD01631699
分子量
233.122
InChiKey
AULXVJOTNZUFIY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:157-161 °C(lit.)
-
沸点:303.9±42.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.672±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
稳定性/保质期:
如果按照规格使用和储存,则不会分解,也不存在已知的危险反应。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.3
-
重原子数:16
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.111
-
拓扑面积:37.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:6
安全信息
-
危险等级:IRRITANT
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S22,S24/25
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2925190090
-
危险性防范说明:P264,P280,P302+P352+P332+P313+P362+P364,P305+P351+P338+P337+P313
-
危险性描述:H315,H319
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 2,3,4,5-tetrafluoro-N-methylbenzamide 129725-50-4 C8H5F4NO 207.127
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Process Improvements in the Synthesis of 2,4,5-Trifluorobenzoic Acid. Selective Hydrodefluorination of Tetrafluorophthalimides摘要:An improved preparation of the fluoroquinolone antibacterial intermediate 2,4,5-trifluorobenzoic acid is described. A combination of a selective hydrodefluorination and hydrolysis reaction of 3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-N-methylphthalimide leading to 3,5,6-trifluorophthalic acid was key to the success of the profess. In addition the development of a two-step, one-pot imidization/halogen exchange from tetrachlorophthalic anhydride to 3,4,5,6-tetrafluoro-N-methylphthalimide in sulfolane solvent is detailed.DOI:10.1021/op970244c
-
作为产物:描述:N-甲基四氯邻苯二甲酰亚胺 在 potassium fluoride 、 四-(二乙胺基)溴化磷 作用下, 以 二甲基亚砜 为溶剂, 120.0 ℃ 、200.0 kPa 条件下, 反应 2.0h, 以96%的产率得到N-甲基四氟酞酰亚胺参考文献:名称:一种3,4,5,6-四氟-N-甲基邻苯二甲酰亚胺的 合成工艺摘要:本发明属于四氟邻苯二甲酰胺制备技术领域,具体涉及一种3,4,5,6‑四氟‑N‑甲基邻苯二甲酰亚胺的绿色合成工艺。该合成工艺包括如下步骤:将3,4,5,6‑四氯‑N‑甲基邻苯二甲酰亚胺与氟化钾在相转移催化剂四(二乙胺基)溴化磷催化作用下发生氟化反应制,所述氟化反应进行时反应体系的压力为0.01‑0.5MPa。本发明提供的制备方法反应温度低、反应时间短,反应结束后的反应液中产物纯度可以达到92%以上,收率也可达到92%以上,可直接用于下一步反应,实现连续化工业生产。公开号:CN110407735B
文献信息
-
Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of N-analogous corollosporines作者:Helfried Neumann、Dirk Strübing、Michael Lalk、Stefan Klaus、Sandra Hübner、Anke Spannenberg、Ulrike Lindequist、Matthias BellerDOI:10.1039/b517101f日期:——Corollosporine is an antimicrobial metabolite, which was isolated from the marine fungus Corollospora maritima. Owing to its basic 4-hydroxyphthalic acid anhydride structure, it has become an attractive target for a structure/activity relationship modelling of derived compounds with potential antibiotic activity. In this regard we report on the straightforward synthesis of hetero analogous corollosporines, which were easily prepared by a three-step reaction sequence, taking advantage of a novel multicomponent reaction (AAD-reaction) and a subsequent aromatization/Grignard reaction protocol. Furthermore, the obtained products were tested in several biological assays to evaluate their antimicrobial activity.
-
Unprecedented selective homogeneous cobalt-catalysed reductive alkoxylation of cyclic imides under mild conditions作者:Jose R. Cabrero-Antonino、Rosa Adam、Veronica Papa、Mattes Holsten、Kathrin Junge、Matthias BellerDOI:10.1039/c7sc01175j日期:——metal-catalysed reductive C2-alkoxylation of cyclic imides (phthalimides and succinimides) is presented. Crucial for the success is the use of [Co(BF4)2·6H2O/triphos (L1)] combination and no external additives are required. Using the optimal cobalt-system, the hydrogenation of the aromatic ring of the parent phthalimide is avoided and only one of the carbonyl groups is selectively functionalized. The提出了第一个通用且有效的非贵金属催化的环状酰亚胺(邻苯二甲酰亚胺和琥珀酰亚胺)的还原性C2-烷氧基化反应。成功的关键是使用[Co(BF 4)2 ·6H 2 O / triphos(L1)]的组合,并且不需要外部添加剂。使用最佳的钴系统,避免了母体邻苯二甲酰亚胺的芳环的氢化,并且仅羰基中的一个被选择性地官能化。所得的产物,N-和芳基环取代的3-烷氧基-2,3-二氢-1H-异吲哚-1-酮和N-取代的3-烷氧基-吡咯烷基-2-酮衍生物是在温和的条件下以良好至优异的分离产率制备的。分子内还原偶联也可以在一步法中进行,从而得到三环化合物。本协议为药物和生物学关注的功能化N杂环化合物的直接合成开辟了新的贱金属工艺开发途径。
-
Selective Ruthenium-Catalyzed Reductive Alkoxylation and Amination of Cyclic Imides作者:Jose R. Cabrero-Antonino、Iván Sorribes、Kathrin Junge、Matthias BellerDOI:10.1002/anie.201508575日期:2016.1.4is the selective ruthenium‐catalyzed reductive alkoxylation and amination of phthalimides/succinimides. Notably, this novel methodology avoids hydrogenation of the aromatic ring and allows methoxylation of substituted imides with good to excellent selectivity for one of the carbonyl groups. The reported method opens the door to the development of new processes for the selective synthesis of various
-
Electroreductive Coupling of Phthalimides with α,β-Unsaturated Carbonyl Compounds and Subsequent Acid-Catalyzed Rearrangement to 4-Aminonaphthalen-1-ols: Density Functional Theory Study of the Acid-Catalyzed Rearrangement of Ketene Silyl Acetals作者:Naoki Kise、Tatsuhiro Manto、Toshihiko SakuraiDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.1c02512日期:2021.12.17The electroreductive coupling of phthalimides with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds in the presence of TMSCl and successive treatment of the electrochemically coupled products with TFA gave two types of rearranged products, 3- and 2-substituted 4-aminonaphthalen-1-ols. The substituent (R) on the nitrogen atom of phthalimides determined which type of 4-aminonaphthalen-1-ol was preferentially formed
-
Process for producing tetrafluorophthalic acid申请人:SDS Biotech K.K.公开号:US04769493A1公开(公告)日:1988-09-06A process for producing tetrafluorophthalic acid is disclosed, which comprises the steps of: (a) reacting an alkali metal fluoride and at least one imide compound represented by formula (I) or (II) ##STR1## wherein X.sup.1, X.sup.2, X.sup.3, and X.sup.4, which may be the same or different, each represents a chloride atom or a bromine atom, R.sup.1 represents a monovalent organic group, and R.sup.2 represents a divalent organic group, to provide an N-substituted tetrafluorophthalimide; and (b) hydrolyzing the tetrafluorophthalimide in the presence of an acid.
表征谱图
-
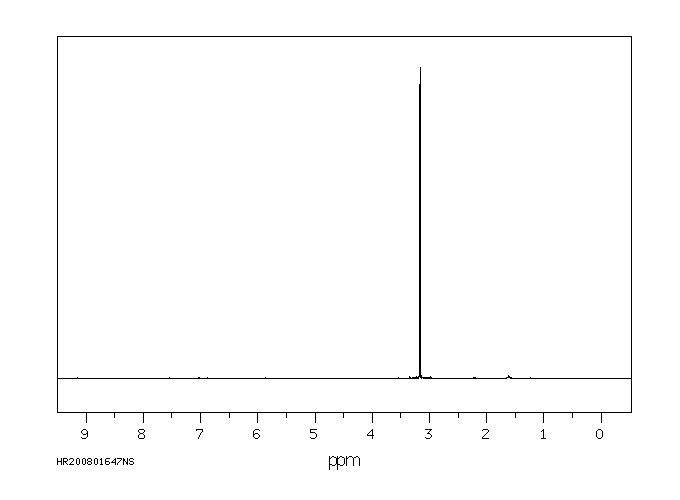
氢谱1HNMR
-
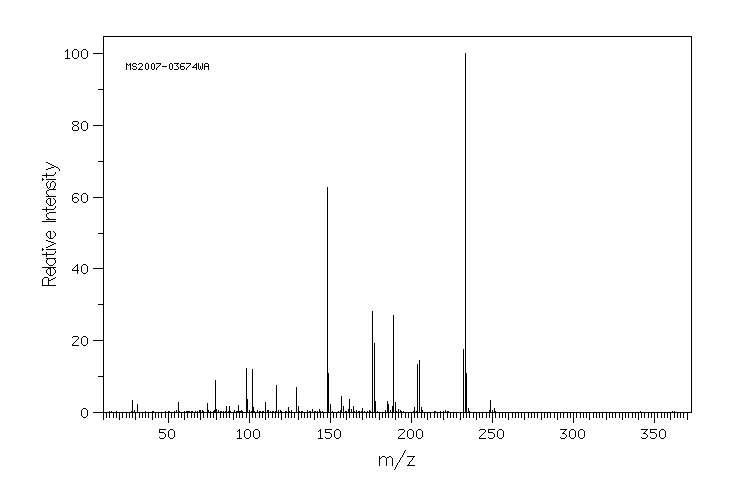
质谱MS
-
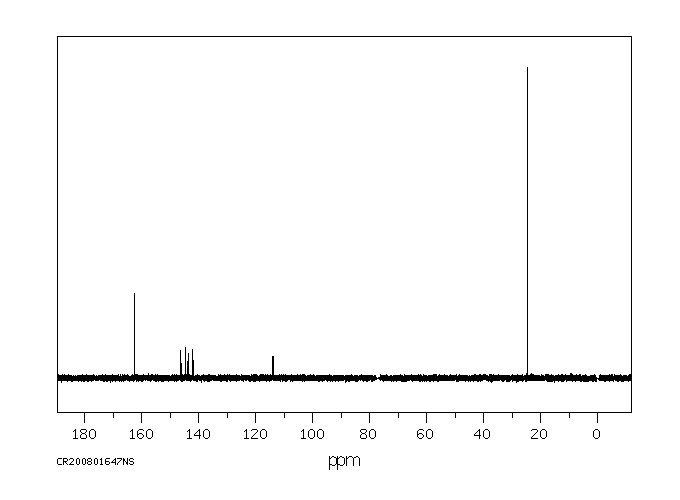
碳谱13CNMR
-
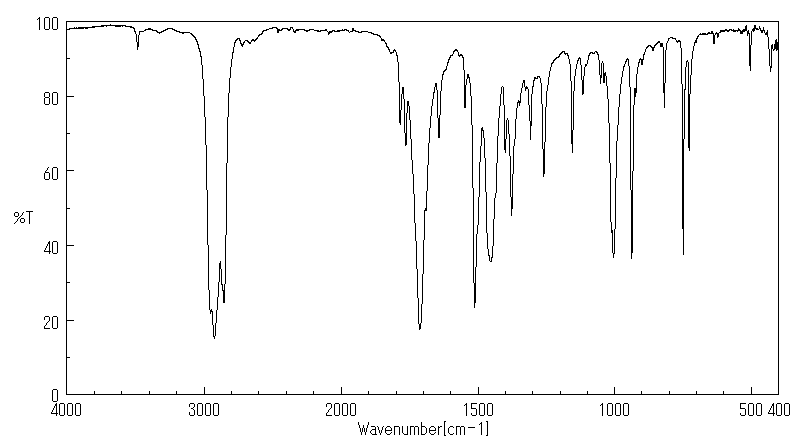
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(1Z,3Z)-1,3-双[[((4S)-4,5-二氢-4-苯基-2-恶唑基]亚甲基]-2,3-二氢-5,6-二甲基-1H-异吲哚
鲁拉西酮杂质33
鲁拉西酮杂质07
马吲哚
颜料黄110
顺式-六氢异吲哚盐酸盐
顺式-2-[(1,3-二氢-1,3-二氧代-2H-异吲哚-2-基)甲基]-N-乙基-1-苯基环丙烷甲酰胺
顺式-2,3,3a,4,7,7a-六氢-1H-异吲哚
顺-N-(4-氯丁烯基)邻苯二甲酰亚胺
降莰烷-2,3-二甲酰亚胺
降冰片烯-2,3-二羧基亚胺基对硝基苄基碳酸酯
降冰片烯-2,3-二羧基亚胺基叔丁基碳酸酯
阿胍诺定
阿普斯特降解杂质
阿普斯特杂质FA
阿普斯特杂质68
阿普斯特杂质29
阿普斯特杂质27
阿普斯特杂质26
阿普斯特杂质19
阿普斯特杂质08
阿普斯特杂质03
阿普斯特杂质
阿普斯特二聚体杂质
阿普斯特
防焦剂MTP
铝酞菁
铁(II)1,2,3,4,8,9,10,11,15,16,17,18,22,23,24,25-十六氟-29H,31H-酞菁
铁(II)2,9,16,23-四氨基酞菁
钠S-(2-{[2-(1,3-二氧代-1,3-二氢-2H-异吲哚-2-基)乙基]氨基}乙基)氢硫代磷酸酯
酞酰亚胺-15N钾盐
酞菁锡
酞菁二氯化硅
酞菁 单氯化镓(III) 盐
酞美普林
邻苯二甲酸亚胺
邻苯二甲酰基氨氯地平
邻苯二甲酰亚胺,N-((吗啉)甲基)
邻苯二甲酰亚胺阴离子
邻苯二甲酰亚胺钾盐
邻苯二甲酰亚胺钠盐
邻苯二甲酰亚胺观盐
邻苯二亚胺甲基磷酸二乙酯
那伏莫德
过氧化氢,2,5-二氢-5-苯基-3H-咪唑并[2,1-a]异吲哚-5-基
达格吡酮
诺非卡尼
螺[环丙烷-1,1'-异二氢吲哚]-3'-酮
螺[异吲哚啉-1,4'-哌啶]-3-酮盐酸盐
葡聚糖凝胶G-25