二氢-2,4,6-三氧代-1,3,5-三嗪-1,3(2H,4H)-二丙酸 | 2904-40-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:289 °C
-
密度:1.592±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:溶于二甲基甲酰胺
-
稳定性/保质期:
遵照规定使用和储存,则不会分解。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1.8
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.44
-
拓扑面积:144
-
氢给体数:3
-
氢受体数:7
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2933699090
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Bis(2-carboxyethyl) Isocyanurate
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
皮肤腐蚀/刺激 第2级
严重损伤/刺激眼睛 2A类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 警告
危险描述 造成皮肤刺激
造成严重眼刺激
防范说明
[预防] 处理后要彻底清洗双手。
穿戴防护手套/护目镜/防护面具。
[急救措施] 眼睛接触:用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续冲洗。
眼睛接触:求医/就诊
皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
脱掉被污染的衣物,清洗后方可重新使用。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 异氰尿酸双(2-羧乙基)酯
百分比: >98.0%(T)
CAS编码: 2904-40-7
俗名: Isocyanuric Acid Bis(2-carboxyethyl) Ester
异氰尿酸双(2-羧乙基)酯 修改号码:5
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
分子式: C9H11N3O7
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用大量肥皂和水轻轻洗。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
外形(20°C): 固体
外观: 晶体-粉末
异氰尿酸双(2-羧乙基)酯 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
颜色: 白色类白色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
289°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂]
溶于: 二甲基甲酰胺
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx)
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
异氰尿酸双(2-羧乙基)酯 修改号码:5
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 1,3-di(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)-(1H,3H,5H)-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6-trione 23900-05-2 C11H15N3O7 301.256
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:二氢-2,4,6-三氧代-1,3,5-三嗪-1,3(2H,4H)-二丙酸 、 1-环氧乙烷基甲基-3,5-二-2-丙烯基-1,3,5-三嗪-2,4,6(1H,3H,5H)-三酮 在 四甲基氯化铵 作用下, 以 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 5.0h, 以29 g的产率得到参考文献:名称:신규한 이소시아누레이트 화합물 및 이를 포함하는 반사방지막 조성물摘要:这项发明涉及用于半导体光刻工艺的防反射涂料组合物,更具体地,涉及一种新的异硅酸酯化合物和包含其的防反射涂料组合物,以提高防反射涂料的折射率。根据本发明,这种新的异硅酸酯化合物是制造用于半导体制造工艺的防反射涂料组合物的核心材料,具有高折射率、快速蚀刻速度和出色的涂覆性能的特点。本发明的防反射涂料具有优异的均匀涂覆性能,即使在存在很大差异的晶圆上也表现出卓越的平坦化特性。公开号:KR101590608B1
-
作为试剂:描述:zinc perchlorate 、 1,4-双[(1H-咪唑-1-基)甲基]苯 在 氨 、 二氢-2,4,6-三氧代-1,3,5-三嗪-1,3(2H,4H)-二丙酸 作用下, 以 甲醇 、 水 为溶剂, 以54 %的产率得到poly[tris(N,N'-phenylenedimethylenebis(imidazole)-μ2N,N')zinc(II)] diperchlorate参考文献:名称:6-connected Zn(II)-MOF: Efficient photocatalytic dye degradation and remarkable luminescent detection of biomolecules and hazardous ions摘要:DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2023.136371
文献信息
-
Two Mg(II) coordination polymers based on the flexible carboxylic ligands: Synthesis, crystal structures, luminescent and adsorption properties作者:Rong-Ying Chen、Dan Tian、Tong-Liang Hu、Ze ChangDOI:10.1016/j.inoche.2014.09.029日期:2014.11Complexes 1 and 2 exhibit a structure progression from a rare two-dimensional (2D) kgd sheet to a three-dimensional pillar-layer structure involving the layer of Mg(II)–carboxylate connected by bci2 − ligands. The structure dissimilarity between them was dependent on the different number of arms of the two ligands. In addition, the solid state luminescent property and CO2 adsorption of complex 1 were also摘要 两种新型 Mg(II) 基配位聚合物,[Mg3(tci)2(DMAC)4]·2DMF}n (1) 和 [Mg(bci)(H2O)2]n (2) (H3tci = tris (2-羧乙基)异氰脲酸酯,H2bci = 双(2-羧乙基)异氰脲酸酯,DMAC = N,N'-二甲基乙酰胺,DMF = N,N'-二甲基甲酰胺),通过使用两个不同臂数的相似柔性配体合成,并通过单晶X射线衍射、红外光谱、元素分析、X射线粉末衍射和TGA表征。配合物 1 和 2 表现出从罕见的二维 (2D) kgd 片到三维柱层结构的结构进展,其中包括通过 bci2 - 配体连接的 Mg(II)-羧酸盐层。它们之间的结构差异取决于两个配体的不同臂数。此外,
-
A series of goblet-like heterometallic pentanuclear [LnIIICuII4] clusters featuring ferromagnetic coupling and single-molecule magnet behavior作者:Qilong Zhu、Shengchang Xiang、Tianlu Sheng、Daqiang Yuan、Chaojun Shen、Chunhong Tan、Shengmin Hu、Xintao WuDOI:10.1039/c2cc35935a日期:——A series of fascinating goblet-like clusters based on [LnIIICuII4] cores have been assembled from a flexible carboxylate ligand, which exhibit a dominant ferromagnetic exchange coupling and single-molecule magnet behavior.
-
Construction of a new luminescent Cd(ii) compound for the detection of Fe<sup>3+</sup> and treatment of Hepatitis B作者:Min-Min Huang、Li-Na XuDOI:10.1515/chem-2021-0085日期:2021.9.21
Abstract A novel porous Cd(
ii ) metal–organic framework (MOF) with the chemical composition of [H3O][Cd(bci)]}n ·2n (H2O) (1 , H3bci = bis(2-carboxyethyl)isocyanurate) was prepared via hydrothermal responses of H3bci and Cd(NO3)2·4H2O. Luminescent property investigations indicated that compound1 had high sensitivity toward Fe3+, and the detection limit of Fe3+ was as low as 2.15 × 10−4 M. The application values of Fe3+ on Hepatitis B were assessed, and its associated mechanism was identified simultaneously. First, the cytotoxic mediator (TNF-α) substance released into plasma was measured through the ELISA. In addition, real-time RT-PCR was employed to determine the Hepatitis B viral replication gene relative expression levels. Finally, the novel compound’s toxicity against human normal liver cells was tested by using the CCK-8 assay. -
Synthesis, Structure, and Luminescent Properties of a New Cd (II) Coordination Polymer Based on Bis(2-carboxyethyl) isocyanurate作者:Yuanyuan YuDOI:10.1080/15533174.2013.872136日期:2015.12.2A new Cd(II) coordination polymer, namely [Cd(Hbci)]n (1 H3bci = bis(2-carboxyethyl)isocyanurate), has been synthesized by the reactions of Cd(II) ions with H3bci under hydrothermal conditions. Single crystal X-ray analysis reveals that 1 features a two-dimensional (2D) layer framework with (3,6)-connected kgd topology. In addition, the luminescent properties of 1 were also investigated in the solid
-
A Eu<sup>III</sup>-MOF with Bis(2-carboxyethyl)isocyanurate for Luminescence Sensing of Fe<sup>3+</sup>and SCN<sup>-</sup>Ions作者:Yanan Zhang、Peng Zhang、Haiju Yin、Jing Cheng、Yifan KangDOI:10.1002/zaac.201700175日期:2017.9.18The water-stable 3D lanthanide-organic framework (Ln-MOF) [Eu(bci)(H2O)]·2H2O}n (1) [H2bci = bis(2-carboxyethyl)isocyanurate] was synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. Compound 1-Eu exhibits a 3D open-framework connected by Eu–(μ-O)2–Eu chains and bci ligands. Meanwhile, 1-Eu exhibits highly efficient luminescent sensing for environmentally relevant Fe3+ and SCN– ions through luminescence quenching
表征谱图
-
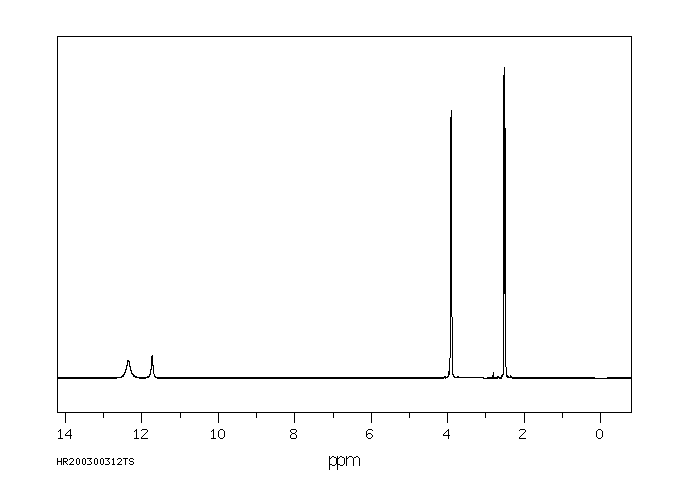
氢谱1HNMR
-
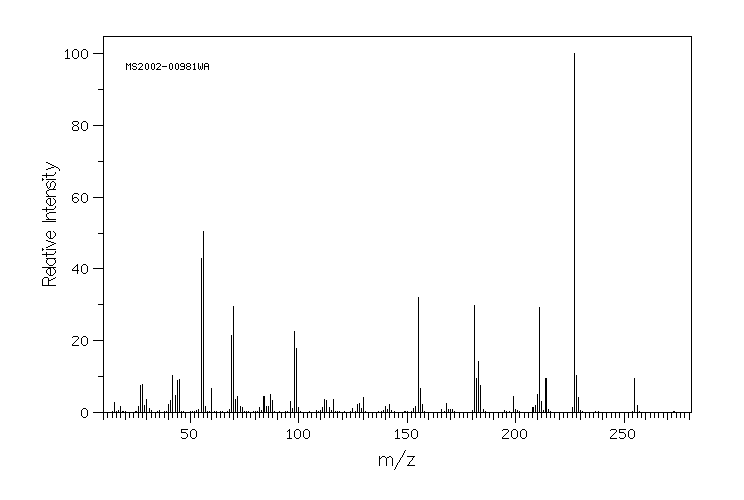
质谱MS
-
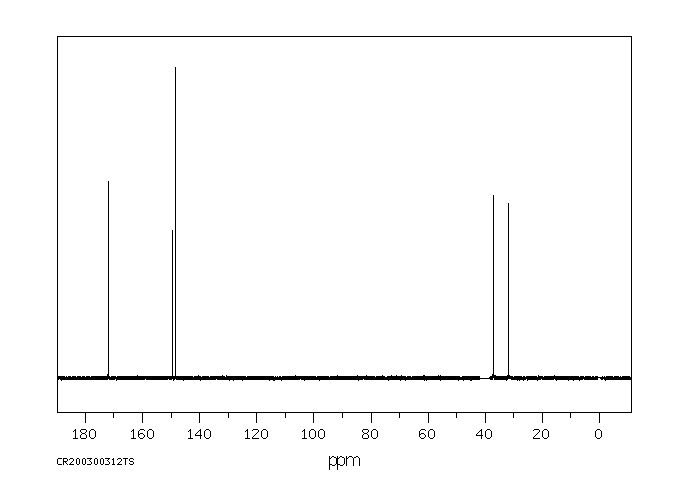
碳谱13CNMR
-
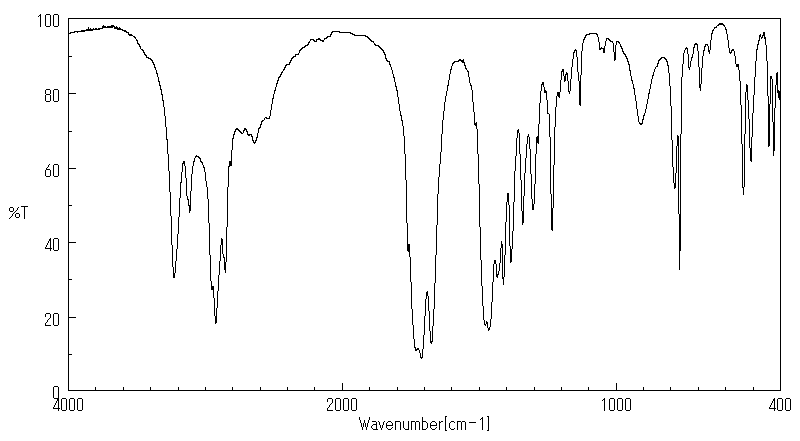
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息