1-萘-2-基-3-苯基硫脲 | 6335-93-9
中文名称
1-萘-2-基-3-苯基硫脲
中文别名
——
英文名称
1-naphthalen-2-yl-3-phenyl-thiourea
英文别名
1-(2'-naphthyl)-3-phenylthiourea;N-(2-naphthyl)-N'-phenylthiurea;N-[2]Naphthyl-N'-phenyl-thioharnstoff;N-Phenyl-N'-β-naphthyl-thioharnstoff;N-2-Naphthyl-N'-phenylthioharnstoff;1-(Naphthalen-2-yl)-3-phenylthiourea;1-naphthalen-2-yl-3-phenylthiourea
CAS
6335-93-9
化学式
C17H14N2S
mdl
——
分子量
278.378
InChiKey
IPJJRJZXOAMHLE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:160 °C
-
沸点:442.0±28.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.314±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.3
-
重原子数:20
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:56.2
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:1
安全信息
-
海关编码:2930909090
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,3-二(萘-2-基)硫脲 N,N'-di(2-naphthyl)thiourea 1166-32-1 C21H16N2S 328.437 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1,3-二(萘-2-基)硫脲 N,N'-di(2-naphthyl)thiourea 1166-32-1 C21H16N2S 328.437 2-萘基硫脲 naphthalen-2-yl-thiourea 3394-04-5 C11H10N2S 202.28 1-萘-2-基-3-苯脲 NSC 44661 6299-42-9 C17H14N2O 262.311
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Reissert; Brueggemann, Chemische Berichte, 1924, vol. 57, p. 987摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:CXV。-杂环化合物的不饱和度和互变异构迁移率。第二部分 α-和ββ-萘噻唑摘要:DOI:10.1039/jr9300000941
文献信息
-
2-Aminothiazoles as Therapeutic Leads for Prion Diseases作者:Alejandra Gallardo-Godoy、Joel Gever、Kimberly L. Fife、B. Michael Silber、Stanley B. Prusiner、Adam R. RensloDOI:10.1021/jm101250y日期:2011.2.242-Aminothiazoles are a new class of small molecules with antiprion activity in prion-infected neuroblastoma cell lines ( J. Virol. 2010, 84, 3408). We report here structure−activity studies undertaken to improve the potency and physiochemical properties of 2-aminothiazoles, with a particular emphasis on achieving and sustaining high drug concentrations in the brain. The results of this effort include2-氨基噻唑是一类在朊病毒感染的神经母细胞瘤细胞系中具有抗朊病毒活性的新型小分子 ( J. Virol. 2010 , 84 , 3408)。我们在此报告了为提高 2-氨基噻唑的效力和理化性质而进行的结构-活性研究,特别强调在大脑中实现和维持高药物浓度。这项工作的结果包括生成信息结构-活性关系 (SAR) 和识别先导化合物,这些化合物可以口服吸收并在动物体内达到高浓度。例如,新的氨基噻唑类似物 (5-甲基吡啶-2-基)-[4-(3-苯基异恶唑-5-基)-噻唑-2-基]-胺 ( 27 ) 表现出 EC 50在朊病毒感染的神经母细胞瘤细胞 (ScN2a-cl3) 中浓度为 0.94 μM,在啮齿动物流质饮食中口服给药三天后,小鼠大脑中的浓度达到 ~25 μM。本文所述的研究表明 2-氨基噻唑是寻找朊病毒疾病有效疗法的有希望的新线索。
-
Thiocarbonyl Surrogate via Combination of Sulfur and Chloroform for Thiocarbamide and Oxazolidinethione Construction作者:Wei Tan、Jianpeng Wei、Xuefeng JiangDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00819日期:2017.4.21An efficient and practical thiocarbonyl surrogate via combination of sulfur and chloroform has been developed. A variety of thiocarbamides and oxazolidinethiones have been established, including chiral thiourea catalysts and chiral oxazolidinethione auxiliaries with high selectivity. Meanwhile, pesticides Diafenthiuron (an acaricide), ANTU (a rodenticide), and Chloromethiuron (an insecticide) were
-
Fused polycyclic nitrogen-containing heterocycles 11. 4-Hydroxy-3,5-diphenyl-2-phenyliminothiazolidines as new key compounds in the synthesis of thiazolo[3,4-a]quinoxaline derivatives作者:V. A. Mamedov、I. Z. Nurkhametova、S. K. Kotovskaya、A. T. Gubaidullin、Ya. A. Levin、I. A. Litvinov、V. N. CharushinDOI:10.1007/s11172-005-0156-0日期:2004.11A procedure was developed for the synthesis of thiazolo[3,4-a]quinoxaline derivatives based on a new strategy for construction of the pyrazine ring. The key step of the process involves the reaction of 4-hydroxy-3,5-diphenyl-2-phenyliminothiazolidines with o-phenylenediamines.
-
Electrocatalytic Desulfurizative Amination of Thioureas to Guanidines作者:Wei Jiang、Bing Wang、Chunlan Song、Jie LiuDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.3c01612日期:2023.10.20N-containing molecules with a wide range of applications. Described here is a selective and efficient electrochemical approach to the synthesis of guanidines from easily accessible thioureas and amines. The key to success for this reaction is the in situ generation of a hypervalent iodine reagent as a catalyst from iodoarene by anodic oxidation. This mild desulfurizative amination presents ample substrate scope
-
DE153418申请人:——公开号:——公开(公告)日:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
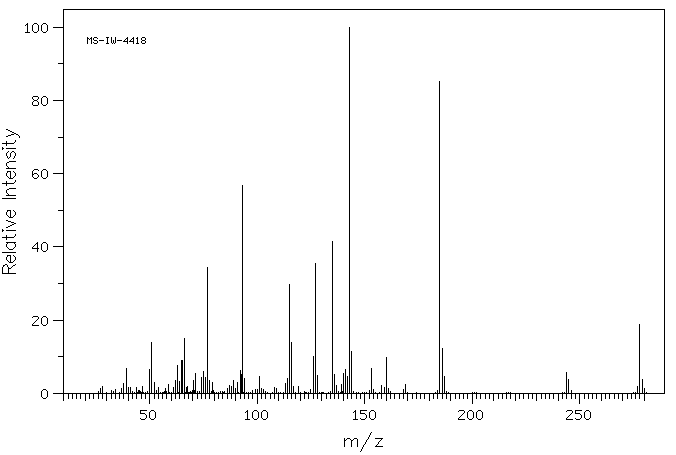
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
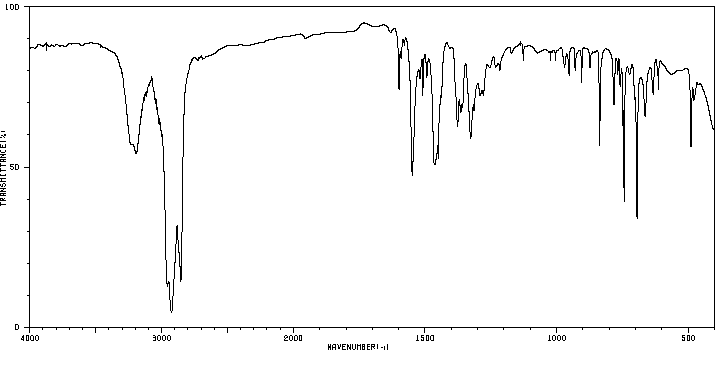
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮