N-(2-nitrophenyl)propionamide | 19314-20-6
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
N-(2-nitrophenyl)propionamide
英文别名
N-(O-Nitrophenyl)propanamide;N-(2-nitrophenyl)propanamide
CAS
19314-20-6
化学式
C9H10N2O3
mdl
MFCD00791258
分子量
194.19
InChiKey
XVMDKPCEVIEDLV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:62.7-63.6 °C
-
沸点:393.1±25.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.287±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.5
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.222
-
拓扑面积:74.9
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
SDS
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:N-(2-nitrophenyl)propionamide 在 human butyrylcholinesterase EC 3.1.1.8 、 Tris buffer 作用下, 以 水 、 乙腈 为溶剂, 生成 2-硝基苯胺参考文献:名称:On the active site for hydrolysis of aryl amides and choline esters by human cholinesterases摘要:Cholinesterases, in addition to their well-known esterase action, also show an aryl acylamidase (AAA) activity whereby they catalyze the hydrolysis of amides of certain aromatic amines. The biological function of this catalysis is not known. Furthermore, it is not known whether the esterase catalytic site is involved in the AAA activity of cholinesterases. It has been speculated that the AAA activity, especially that of butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE), may be important in the development of the nervous system and in pathological processes such as formation of neuritic plaques in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The substrate generally used to study the AAA activity of cholinesterases is N-(2-nitrophenyl)acetamide. However, use of this substrate requires high concentrations of enzyme and substrate, and prolonged periods of incubation at elevated temperature. As a consequence, difficulties in performing kinetic analysis of AAA activity associated with cholinesterases have hampered understanding this activity. Because of its potential biological importance, we sought to develop a more efficient and specific substrate for use in studying the AAA activity associated with BuChE, and for exploring the catalytic site for this hydrolysis. Here, we describe the structure-activity relationships for hydrolysis of anilides by cholinesterases. These studies led to a substrate, N-(2-nitrophenyl)trifluoroacetamide, that was hydrolyzed several orders of magnitude faster than N-(2-nitrophenyl)acetamide by cholinesterases. Also, larger N-(2-nitrophenyl)alkylamides were found to be more rapidly hydrolyzed by BuChE than N-(2-nitrophenyl)acetamide and, in addition, were more specific for hydrolysis by BuChE. Thus, N-(2-nitrophenyl)alkylamides with six to eight carbon atoms in the acyl group represent suitable specific substrates to investigate further the function of the AAA activity of BuChE. Based on the substrate structure-activity relationships and kinetic studies, the hydrolysis of anilides and esters of choline appears to utilize the same catalytic site in BuChE. (c) 2006 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.02.021
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:On the active site for hydrolysis of aryl amides and choline esters by human cholinesterases摘要:Cholinesterases, in addition to their well-known esterase action, also show an aryl acylamidase (AAA) activity whereby they catalyze the hydrolysis of amides of certain aromatic amines. The biological function of this catalysis is not known. Furthermore, it is not known whether the esterase catalytic site is involved in the AAA activity of cholinesterases. It has been speculated that the AAA activity, especially that of butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE), may be important in the development of the nervous system and in pathological processes such as formation of neuritic plaques in Alzheimer's disease (AD). The substrate generally used to study the AAA activity of cholinesterases is N-(2-nitrophenyl)acetamide. However, use of this substrate requires high concentrations of enzyme and substrate, and prolonged periods of incubation at elevated temperature. As a consequence, difficulties in performing kinetic analysis of AAA activity associated with cholinesterases have hampered understanding this activity. Because of its potential biological importance, we sought to develop a more efficient and specific substrate for use in studying the AAA activity associated with BuChE, and for exploring the catalytic site for this hydrolysis. Here, we describe the structure-activity relationships for hydrolysis of anilides by cholinesterases. These studies led to a substrate, N-(2-nitrophenyl)trifluoroacetamide, that was hydrolyzed several orders of magnitude faster than N-(2-nitrophenyl)acetamide by cholinesterases. Also, larger N-(2-nitrophenyl)alkylamides were found to be more rapidly hydrolyzed by BuChE than N-(2-nitrophenyl)acetamide and, in addition, were more specific for hydrolysis by BuChE. Thus, N-(2-nitrophenyl)alkylamides with six to eight carbon atoms in the acyl group represent suitable specific substrates to investigate further the function of the AAA activity of BuChE. Based on the substrate structure-activity relationships and kinetic studies, the hydrolysis of anilides and esters of choline appears to utilize the same catalytic site in BuChE. (c) 2006 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.02.021
文献信息
-
PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF BIS-QUATERNARY AMMONIUM SALT, AND NOVEL INTERMEDIATE申请人:Okamoto Kuniaki公开号:US20120130107A1公开(公告)日:2012-05-24Object To provide a method for producing a bis-quaternary ammonium salt efficiently and a novel synthetic intermediate thereof. Solution The present invention relates to a method for producing a bis-quaternary ammonium salt represented by a general formula [3] which comprises reacting a disulfonic acid ester represented by a general formula [1] (in the formula, definitions of two R 1 's and T are as described in claim 1 ) with a tertiary amine represented by a general formula [2] (in the formula, definitions of R 3 to R 5 are as described in claim 1 ), and a disulfonic acid ester represented by a general formula [1′] (in the formula, two R 16 's represent independently a halogen atom or a C1-C3 fluoroalkyl group, and two m's represent independently an integer of 1 to 5).
-
Fused mesoionic heterocycles: synthesis of [1,2,3]triazolo[1,5-a]quinoline, [1,2,3]triazolo[1,5-a]quinazoline, [1,2,3]triazolo[1,5-a]quinoxaline and [1,2,3]triazolo[5,1-c]benzotriazine derivatives作者:Phillip A Abbott、Roger V Bonnert、Moya V Caffrey、Peter A Cage、Andrew J Cooke、David K Donald、Mark Furber、Steve Hill、Jane WithnallDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(02)00269-7日期:2002.4General methods are descibed for the synthesis of mesoionic derivatives of [1,2,3]triazolo[1,5-a]quinoline, [1,2,3]triazolo[1,5-a]quinazoline, [1,2,3]triazolo[1,5-a]quinoxaline and [1,2,3]triazolo[5,1-c]benzotriazine.
-
Rhodium-Catalyzed Addition of Organozinc Iodides to Carbon-11 Isocyanates作者:Braeden A. Mair、Moustafa H. Fouad、Uzair S. Ismailani、Maxime Munch、Benjamin H. RotsteinDOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.0c00729日期:2020.4.3Amides were prepared using rhodium-catalyzed coupling of organozinc iodides and carbon-11 (11C, t1/2 = 20.4 min) isocyanates. Nonradioactive isocyanates and sp3 or sp2 organozinc iodides generated amides in yields of 13%–87%. Incorporation of cyclotron-produced [11C]CO2 into 11C-amide products proceeded in yields of 5%–99%. The synthetic utility of the methodology was demonstrated through the isolation
-
A Sandwich Azobenzene–Diamide Dimer for Photoregulated Chloride Transport作者:Manzoor Ahmad、Surajit Metya、Aloke Das、Pinaki TalukdarDOI:10.1002/chem.202000400日期:2020.7.17within the sandwich complex were revealed from theoretical studies. Reversible trans–cis photoisomerization of the azobenzene was achieved without any significant contribution from the thermal cis →trans isomerization at room temperature. Photoregulatory transport activity across the lipid bilayer membrane inferred an outstanding off‐on response of the azobenzene photoswitch.
-
Conversion of Sterically Hindered Diacylated 1,2-Phenylenediamines into 2-Substituted Benzimidazoles作者:Julie Charton、Sophie Girault-Mizzi、Christian SergheraertDOI:10.1248/cpb.53.492日期:——for several biological targets. Formation by cyclodehydration from their monoacylated counterparts was shown to be strongly dependent upon the nature of the acyl group. In the case of a dicyclohexylmethyl group, cyclization was only observed in a p-toluenesulfonic acid/toluene mixture from the symmetrical diacylated precursor. Analysis of the mechanism was begun starting from mixed diacylated derivatives
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
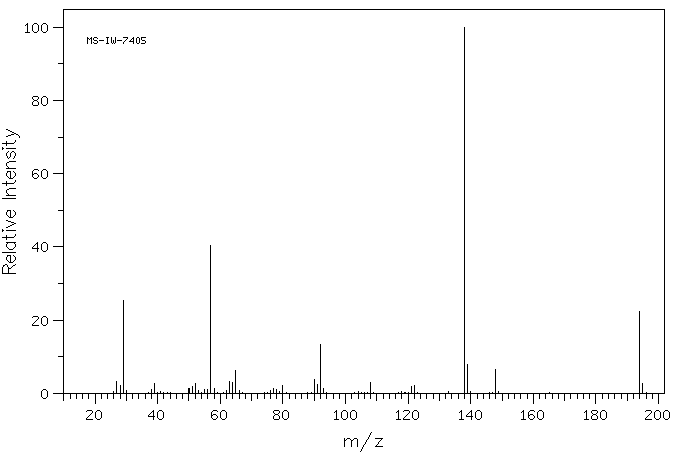
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
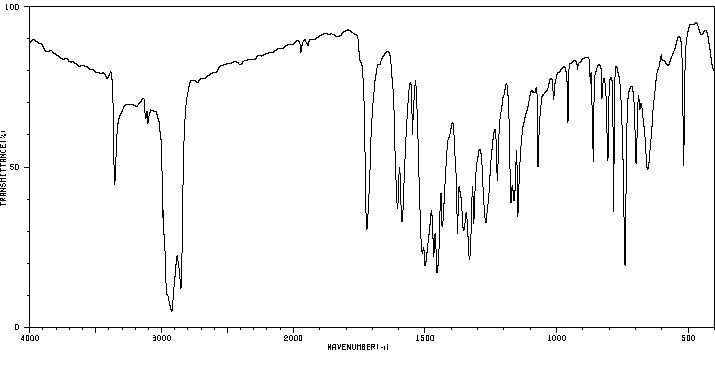
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(βS)-β-氨基-4-(4-羟基苯氧基)-3,5-二碘苯甲丙醇
(S,S)-邻甲苯基-DIPAMP
(S)-(-)-7'-〔4(S)-(苄基)恶唑-2-基]-7-二(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-2,2',3,3'-四氢-1,1-螺二氢茚
(S)-盐酸沙丁胺醇
(S)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧磷杂环戊二烯
(S)-2,2'-双[双(3,5-三氟甲基苯基)膦基]-4,4',6,6'-四甲氧基联苯
(S)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(R)富马酸托特罗定
(R)-(-)-盐酸尼古地平
(R)-(-)-4,12-双(二苯基膦基)[2.2]对环芳烷(1,5环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[((6-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(4-叔丁基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-7-双(3,5-二叔丁基苯基)膦基7''-[(3-甲基吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-1,1''-螺双茚满
(R)-(+)-4,7-双(3,5-二-叔丁基苯基)膦基-7“-[(吡啶-2-基甲基)氨基]-2,2”,3,3'-四氢1,1'-螺二茚满
(R)-3-(叔丁基)-4-(2,6-二苯氧基苯基)-2,3-二氢苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂环戊烯
(R)-2-[((二苯基膦基)甲基]吡咯烷
(R)-1-[3,5-双(三氟甲基)苯基]-3-[1-(二甲基氨基)-3-甲基丁烷-2-基]硫脲
(N-(4-甲氧基苯基)-N-甲基-3-(1-哌啶基)丙-2-烯酰胺)
(5-溴-2-羟基苯基)-4-氯苯甲酮
(5-溴-2-氯苯基)(4-羟基苯基)甲酮
(5-氧代-3-苯基-2,5-二氢-1,2,3,4-oxatriazol-3-鎓)
(4S,5R)-4-甲基-5-苯基-1,2,3-氧代噻唑烷-2,2-二氧化物-3-羧酸叔丁酯
(4S,4''S)-2,2''-亚环戊基双[4,5-二氢-4-(苯甲基)恶唑]
(4-溴苯基)-[2-氟-4-[6-[甲基(丙-2-烯基)氨基]己氧基]苯基]甲酮
(4-丁氧基苯甲基)三苯基溴化磷
(3aR,8aR)-(-)-4,4,8,8-四(3,5-二甲基苯基)四氢-2,2-二甲基-6-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环[4,5-e]二恶唑磷
(3aR,6aS)-5-氧代六氢环戊基[c]吡咯-2(1H)-羧酸酯
(2Z)-3-[[(4-氯苯基)氨基]-2-氰基丙烯酸乙酯
(2S,3S,5S)-5-(叔丁氧基甲酰氨基)-2-(N-5-噻唑基-甲氧羰基)氨基-1,6-二苯基-3-羟基己烷
(2S,2''S,3S,3''S)-3,3''-二叔丁基-4,4''-双(2,6-二甲氧基苯基)-2,2'',3,3''-四氢-2,2''-联苯并[d][1,3]氧杂磷杂戊环
(2S)-(-)-2-{[[[[3,5-双(氟代甲基)苯基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基}-N-(二苯基甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[((1S,2S)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2S)-2-[[[[[[((1R,2R)-2-氨基环己基]氨基]硫代甲基]氨基]-N-(二苯甲基)-N,3,3-三甲基丁酰胺
(2-硝基苯基)磷酸三酰胺
(2,6-二氯苯基)乙酰氯
(2,3-二甲氧基-5-甲基苯基)硼酸
(1S,2S,3S,5S)-5-叠氮基-3-(苯基甲氧基)-2-[(苯基甲氧基)甲基]环戊醇
(1S,2S,3R,5R)-2-(苄氧基)甲基-6-氧杂双环[3.1.0]己-3-醇
(1-(4-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(3-溴苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氯苯基)环丁基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2-氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(1-(2,6-二氟苯基)环丙基)甲胺盐酸盐
(-)-去甲基西布曲明
龙蒿油
龙胆酸钠
龙胆酸叔丁酯
龙胆酸
龙胆紫-d6
龙胆紫