十八炔 | 629-89-0
中文名称
十八炔
中文别名
1-十八炔,TECH.85;1-十八炔;正十八炔;1-十八炔,TECH.85%
英文名称
1-octadecyne
英文别名
octadec-1-yne;octadecyne;1-Octadecin
CAS
629-89-0
化学式
C18H34
mdl
MFCD00015088
分子量
250.468
InChiKey
IYDNQWWOZQLMRH-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:22,5°C
-
沸点:180°C 15mm
-
密度:0,803 g/cm3
-
闪点:25 °C
-
保留指数:1238
-
稳定性/保质期:
远离氧化物,常温常压下保持稳定。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):8.9
-
重原子数:18
-
可旋转键数:14
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.888
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
安全信息
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1
-
危险性防范说明:P501,P331,P301+P310,P405
-
危险品运输编号:2811
-
危险性描述:H304
-
储存条件:存放在密封容器内,并置于阴凉、干燥处。请将储藏地点远离氧化剂和火源。
SDS
1-十八炔 修改号码:5
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 1-Octadecyne
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
吸入性危害物质 第1级
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 危险
危险描述
若吞咽并进入呼吸道可能致命
防范说明
[急救措施] 食入:立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。切勿催吐。
[储存] 存放处须加锁。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 1-十八炔
百分比: >95.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 629-89-0
俗名: Cetylacetylene , Hexadecylacetylene
分子式: C18H34
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
1-十八炔 修改号码:5
模块 4. 急救措施
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。切勿引吐。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用特殊的个人防护用品(针对有毒颗粒的P3过滤式空气呼吸器)。远离溢出物/泄露
紧急措施: 处并处在上风处。
泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果可能,使用封闭系统。如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
存放于惰性气体环境中。
存放处须加锁。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
气敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统。同时安装淋浴器和洗眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具,自携式呼吸器(SCBA),供气呼吸器等。使用通过政府标准的呼吸器。依
据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防渗手套。
眼睛防护: 护目镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防渗防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-块状
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄色
1-十八炔 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 25°C (凝固点)
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
1-十八炔 修改号码:5
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 1-Octadecyne
修改号码: 5
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害
吸入性危害物质 第1级
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志
信号词 危险
危险描述
若吞咽并进入呼吸道可能致命
防范说明
[急救措施] 食入:立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。切勿催吐。
[储存] 存放处须加锁。
[废弃处置] 根据当地政府规定把物品/容器交与工业废弃处理机构。
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 1-十八炔
百分比: >95.0%(GC)
CAS编码: 629-89-0
俗名: Cetylacetylene , Hexadecylacetylene
分子式: C18H34
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
1-十八炔 修改号码:5
模块 4. 急救措施
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 立即呼叫解毒中心/医生。漱口。切勿引吐。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用特殊的个人防护用品(针对有毒颗粒的P3过滤式空气呼吸器)。远离溢出物/泄露
紧急措施: 处并处在上风处。
泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果可能,使用封闭系统。如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
存放于惰性气体环境中。
存放处须加锁。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
气敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统。同时安装淋浴器和洗眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具,自携式呼吸器(SCBA),供气呼吸器等。使用通过政府标准的呼吸器。依
据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防渗手套。
眼睛防护: 护目镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防渗防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-块状
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄色
1-十八炔 修改号码:5
模块 9. 理化特性
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 25°C (凝固点)
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
1-十八炔 修改号码:5
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— octadec-2-yne 61847-97-0 C18H34 250.468 —— 12-heptadecyn-1-ol 56554-76-8 C17H32O 252.44 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— octadec-2-yne 61847-97-0 C18H34 250.468 —— 13-triacontyne 145315-02-2 C30H58 418.791 —— 21-docosyn-1-ol 61097-38-9 C22H42O 322.575 —— 1-octadecynyl iodide 106510-32-1 C18H33I 376.365 —— 1-octadecynyl bromide —— C18H33Br 329.364 —— heneicos-4-yn-1-ol 337917-87-0 C21H40O 308.548 —— triacont-13-yn-1-ol 111301-34-9 C30H58O 434.79
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Kinetics of amphiphilic ketone epimerizations in cleavable surfactant hosts摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja00223a035
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:通过Bergman环化形成共轭聚萘摘要:通过Sonogashira偶联反应合成了一系列含有烯二炔的手性邻苯二甲酰亚胺。然后将这些烯二炔在真空下进行热伯格曼环化。获得了具有侧链手性基团的聚萘,并使用GPC,IR光谱,NMR光谱,UV-Vis光谱和光致发光分析对其进行了表征。在适当优化的条件下,根据最终产物的CD光谱,保持手性导向基团的手性。除去手性导向基团后,可见代表主链手性的弱CD信号。二烯炔化合物的结构的进一步修饰将通过这种相当简单的方式促进手性聚萘的合成。在具有刚性聚芳烃骨架的新型聚合物的构造中,将伯格曼环化扩展到聚合物化学是有希望的。©2010 Wiley Periodicals,Inc. J Polym Sci A部分:Polym Chem 48:2187–2193,2010年DOI:10.1002/pola.23988
文献信息
-
Biaryl-Based Macrocyclic and Polymeric Chiral (Salophen)Ni(II) Complexes: Synthesis and Spectroscopic Study作者:Hui-Chang Zhang、Wei-Sheng Huang、Lin PuDOI:10.1021/jo001276s日期:2001.1.1Polymeric/oligomeric and macrocyclic (salophen)Ni(II) complexes have been synthesized starting from both an achiral biphenol dialdehyde and an optically active BINOL dialdehyde. It was found that these polysalophens contain nonplanar coordination of Ni(II) units that are paramagnetic. This is different from the previously reported (salophen)Ni(II) complexes which are square planar and diamagnetic. The
-
Sphingosin und Sphingosin-ähnliche Verbindungen
-
Development of a benzophenone and alkyne functionalised trehalose probe to study trehalose dimycolate binding proteins作者:Ashna A. Khan、Faustin Kamena、Mattie S. M. Timmer、Bridget L. StockerDOI:10.1039/c2ob27257a日期:——Trehalose dimycolates (TDMs) are the most abundant glycolipids found in the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tb). TDMs play an important role in the pathogenesis of M. tb yet the only known receptor for TDM is the macrophage inducible C-type lectin (mincle). To understand more about the interaction of TDMs with immune cells, affinity based proteome profiling (AfBPP) can be used to determine receptors that bind TDMs. To this end, we present the synthesis of the first AfBPP-TDM probe and report on its ability to activate macrophages. By doing so, we establish that the AfBPP-TDM probe appears to be a suitable substrate for future proteomic profiling experiments.海藻糖二霉菌酸酯(Trehalose dimycolates, TDMs)是结核分枝杆菌(Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. tb)细胞壁中最丰富的糖脂类物质。TDMs在M. tb的发病机制中起着重要作用,但目前唯一已知的TDM受体是巨噬细胞诱导的C型凝集素(macrophage inducible C-type lectin, mincle)。为了更深入地了解TDMs与免疫细胞之间的相互作用,可以利用基于亲和性的蛋白质组学轮廓分析(Affinity based proteome profiling, AfBPP)来确定结合TDMs的受体。为此,我们介绍了首个AfBPP-TDM探针的合成,并报道了其激活巨噬细胞的能力。通过这一过程,我们确立了AfBPP-TDM探针似乎是未来蛋白质组学轮廓分析实验的合适底物。
-
The influence of distal substitution on the base-induced isomerization of long-chain terminal alkynes作者:Innus Mohammad、JiYoung Mun、Amber Onorato、Martha D. Morton、Abdullah I. Saleh、Michael B. SmithDOI:10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.09.026日期:2017.11compared to a long-straight chain terminal alkyne, a long chain terminal alkyne with a distal isopropyl unit (isobranched) isomerizes about two times faster when treated with strong base under identical conditions, and appears to follow pseudo first order kinetics. In both cases, equilibration to a 95–97:5–3 mixture of terminal:internal alkyne accompanies isomerization. The difference in rate may be due
-
Polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS) as an Additive in Sonogashira Reactions作者:Robert E. Maleczka Jr.、William P. GallagherDOI:10.1055/s-2003-37522日期:——Polymethylhydrosiloxane (PMHS) in combination with CsF facilitates the Sonogashira reaction of a variety of alkynes and electrophiles. These couplings appear to involve the in situ formation and reaction of an alkynylsiloxane. Such couplings can be run amine free at room temperature, reaction times are short, workup is easy, and product purification is straightforward. Thus, the advantages (and disadvantages) of running Sonogashira couplings with 1-silylalkynes are realized, without the need to preform the alkynyl silane.
表征谱图
-
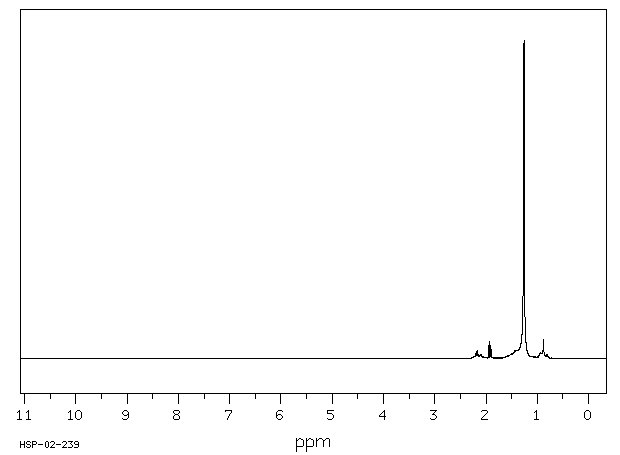
氢谱1HNMR
-
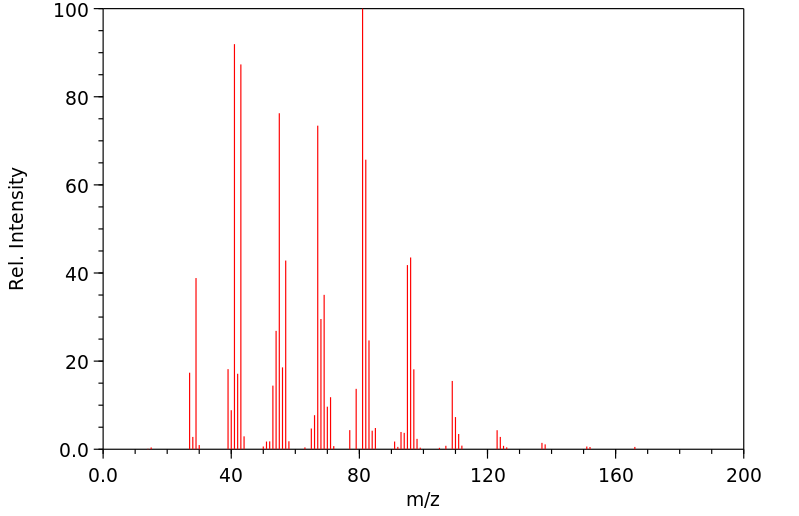
质谱MS
-
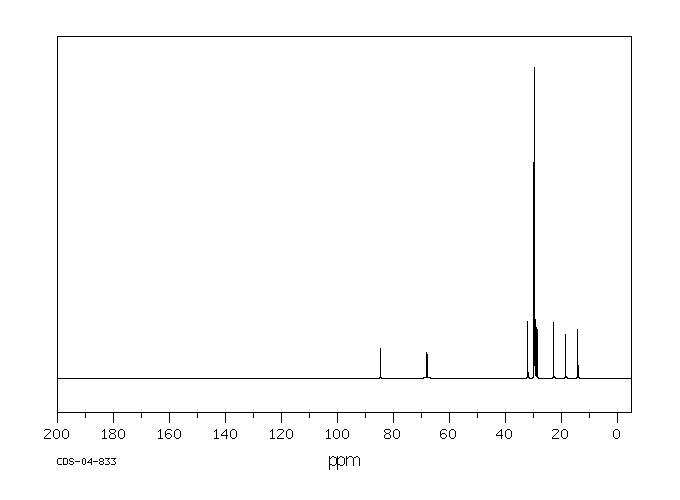
碳谱13CNMR
-
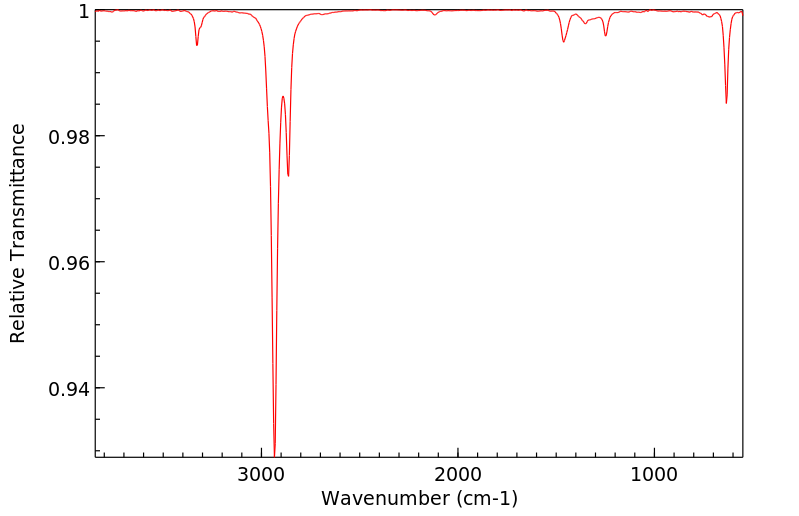
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
锗烷,三甲基[3-(三甲基甲锡烷基)-2-炔丙基]-
锗烷,三甲基-2-炔丙基-
铜,1-戊炔基-
甲基炔丙基硫化物
甲基乙炔和丙二烯混合物
甲基丙-2-炔基氰基二硫代亚氨酸酯
甲基-D3-乙炔
环戊基乙炔
环己基乙炔
环丙乙炔
炔丙胺
炔丙基膦
炔丙基碘化物
炔丙基叔丁基二甲基硅烷
炔丙基三甲基硅烷
炔丙基三乙基硅烷
氘乙炔
戊-1-炔-3-胺
戊-1,3-二炔
戊-1,2-二烯-4-炔
异氰基-乙炔
己基(己-5-炔基)甲基硅烷
己-1-炔银
四碳化铀
反式-4-(2-丙炔基)-环己烷甲醇
双(三甲基锡)乙炔
双(三氟甲基)锌
十四碳-1,4-二炔
十四碳-1,3-二炔
十八碳-1,17-二炔
十八炔
十三碳-1,7-二炔
十三碳-1,12-二炔
十一碳-1,5-二炔
亚硫酸二(2-丙炔基)酯
二甲基炔丙基溴化硫
二炔丙基硫醚
二乙炔基-二甲基-锗烷
二丙-1-炔基汞
二[2-甲氧基乙基汞(II)]乙炔
二(三正丁基甲锡烷基)乙炔
二(3-羟基-1-丙炔基)汞(II)
乙炔锂乙二胺配合物
乙炔银
乙炔基环己烷钠
乙炔基环丙烷氯化镁
乙炔基(三甲基)锗烷
乙炔基(三甲基)硅烷铜(1+)
乙炔基(三甲基)硅烷溴化镁
乙炔基(三甲基)硅烷氯化镁