二氢-2-甲基-3(2H)-噻吩酮 | 13679-85-1
中文名称
二氢-2-甲基-3(2H)-噻吩酮
中文别名
2-甲基四氢噻吩-3-酮;2-甲基-3-四氢噻吩酮
英文名称
2-methyltetrahydrothiophen-3-one
英文别名
2-methylthiolan-3-one;dihydro-2-methyl-3(2H)-thiophenone;blackberry thiophenone;2-methyldihydrothiophen-3(2H)-one
CAS
13679-85-1
化学式
C5H8OS
mdl
MFCD00078280
分子量
116.184
InChiKey
YMZZPMVKABUEBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:82 °C28 mm Hg(lit.)
-
密度:1.119 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.)
-
闪点:160 °F
-
LogP:0.20
-
溶解度:insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, fats
-
折光率:1.510-1.520
-
保留指数:947;952;951;956;949;958;947;952;947
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下保持稳定,应避免与氧化物接触。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.8
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.8
-
拓扑面积:42.4
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2934999090
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P305+P351+P338
-
危险性描述:H315,H319,H335
-
储存条件:常温下应密闭保存,在阴凉、通风、干燥处存放。
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
1.1 产品标识符
: 2-甲基四氢噻吩-3-酮
产品名称
1.2 鉴别的其他方法
无数据资料
1.3 有关的确定了的物质或混合物的用途和建议不适合的用途
仅用于研发。不作为药品、家庭或其它用途。
模块 2. 危险性概述
2.1 GHS-分类
易燃液体 (类别 4)
皮肤刺激 (类别 2)
眼睛刺激 (类别 2A)
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触) (类别 3)
2.2 GHS 标记要素,包括预防性的陈述
象形图
警示词 警告
危险申明
H227 可燃液体
H315 造成皮肤刺激。
H319 造成严重眼刺激。
H335 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
警告申明
预防措施
P210 远离热源、火花、明火和热表面。- 禁止吸烟。
P261 避免吸入粉尘/烟/气体/烟雾/蒸气/喷雾.
P264 操作后彻底清洁皮肤。
P271 只能在室外或通风良好之处使用。
P280 戴防护手套/穿防护服/戴护目镜/戴面罩.
事故响应
P302 + P352 如果皮肤接触:用大量肥皂和水清洗。
P304 + P340 如吸入: 将患者移到新鲜空气处休息,并保持呼吸舒畅的姿势。
P305 + P351 + P338 如与眼睛接触,用水缓慢温和地冲洗几分钟。如戴隐形眼镜并可方便地取
出,取出隐形眼镜,然后继续冲洗.
P312 如感觉不适,呼救中毒控制中心或医生.
P321 具体处置(见本标签上提供的急救指导)。
P332 + P313 如觉皮肤刺激:求医/就诊。
P337 + P313 如仍觉眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
P362 脱掉沾污的衣服,清洗后方可再用。
P370 + P378 火灾时: 用干的砂子,干的化学品或耐醇性的泡沫来灭火。
安全储存
P403 + P233 存放于通风良的地方。 保持容器密闭。
P403 + P235 保持低温,存放于通风良好处。
P405 存放处须加锁。
废弃处置
P501 将内容物/ 容器处理到得到批准的废物处理厂。
2.3 其它危害物 - 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
3.1 物 质
: C5H8OS
分子式
: 116.18 g/mol
分子量
组分 浓度或浓度范围
Dihydro-2-methylthiophen-3(2H)-one
<=100%
化学文摘登记号(CAS 13679-85-1
No.) 237-183-3
EC-编号
模块 4. 急救措施
4.1 必要的急救措施描述
一般的建议
请教医生。 向到现场的医生出示此安全技术说明书。
吸入
如果吸入,请将患者移到新鲜空气处。 如呼吸停止,进行人工呼吸。 请教医生。
皮肤接触
用肥皂和大量的水冲洗。 请教医生。
眼睛接触
用大量水彻底冲洗至少15分钟并请教医生。
食入
禁止催吐。 切勿给失去知觉者通过口喂任何东西。 用水漱口。 请教医生。
4.2 主要症状和影响,急性和迟发效应
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
4.3 及时的医疗处理和所需的特殊处理的说明和指示
无数据资料
模块 5. 消防措施
5.1 灭火介质
灭火方法及灭火剂
用水雾,抗乙醇泡沫,干粉或二氧化碳灭火。
5.2 源于此物质或混合物的特别的危害
碳氧化物, 硫氧化物
5.3 给消防员的建议
如必要的话,戴自给式呼吸器去救火。
5.4 进一步信息
用水喷雾冷却未打开的容器。
模块 6. 泄露应急处理
6.1 作业人员防护措施、防护装备和应急处置程序
使用个人防护用品。 避免吸入蒸气、烟雾或气体。 保证充分的通风。 移去所有火源。
人员疏散到安全区域。 谨防蒸气积累达到可爆炸的浓度。蒸气能在低洼处积聚。
6.2 环境保护措施
如能确保安全,可采取措施防止进一步的泄漏或溢出。 不要让产品进入下水道。
6.3 泄漏化学品的收容、清除方法及所使用的处置材料
围堵溢出,用防电真空清洁器或湿刷子将溢出物收集起来,并放置到容器中去,根据当地规定处理(见第13部
分)。 放入合适的封闭的容器中待处理。
6.4 参考其他部分
丢弃处理请参阅第13节。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
7.1 安全操作的注意事项
避免接触皮肤和眼睛。 避免吸入蒸气和烟雾。
切勿靠近火源。-严禁烟火。采取措施防止静电积聚。
7.2 安全储存的条件,包括任何不兼容性
贮存在阴凉处。 使容器保持密闭,储存在干燥通风处。
打开了的容器必须仔细重新封口并保持竖放位置以防止泄漏。
7.3 特定用途
无数据资料
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
8.1 容许浓度
最高容许浓度
没有已知的国家规定的暴露极限。
8.2 暴露控制
适当的技术控制
根据良好的工业卫生和安全规范进行操作。 休息前和工作结束时洗手。
个体防护设备
眼/面保护
带有防护边罩的安全眼镜符合 EN166要求请使用经官方标准如NIOSH (美国) 或 EN 166(欧盟)
检测与批准的设备防护眼部。
皮肤保护
所选择的保护手套必须符合EU的89/686/EEC规定和从它衍生出来的EN 376标准。
戴手套取 手套在使用前必须受检查。
请使用合适的方法脱除手套(不要接触手套外部表面),避免任何皮肤部位接触此产品.
使用后请将被污染过的手套根据相关法律法规和有效的实验室规章程序谨慎处理. 请清洗并吹干双手
身体保护
防渗透的衣服, 防护设备的类型必须根据特定工作场所中的危险物的浓度和数量来选择。
呼吸系统防护
如危险性评测显示需要使用空气净化的防毒面具,请使用全面罩式多功能防毒面具(US)或ABEK型
(EN
14387)防毒面具筒作为工程控制的候补。如果防毒面具是保护的唯一方式,则使用全面罩式送风防
毒面具。 呼吸器使用经过测试并通过政府标准如NIOSH(US)或CEN(EU)的呼吸器和零件。
模块 9. 理化特性
9.1 基本的理化特性的信息
a) 外观与性状
形状: 液体
b) 气味
无数据资料
c) 气味阈值
无数据资料
d) pH值
无数据资料
e) 熔点/凝固点
无数据资料
f) 沸点、初沸点和沸程
82 °C 在 37 hPa - lit.
g) 闪点
71 °C - 闭杯
h) 蒸发速率
无数据资料
i) 易燃性(固体,气体)
无数据资料
j) 高的/低的燃烧性或爆炸性限度 无数据资料
k) 蒸气压
无数据资料
l) 蒸汽密度
无数据资料
m) 密度/相对密度
1.119 g/cm3 在 25 °C
n) 水溶性
无数据资料
o) n-辛醇/水分配系数
无数据资料
p) 自燃温度
无数据资料
q) 分解温度
无数据资料
r) 粘度
无数据资料
模块 10. 稳定性和反应活性
10.1 反应性
无数据资料
10.2 稳定性
无数据资料
10.3 危险反应
无数据资料
10.4 应避免的条件
热,火焰和火花。
10.5 不相容的物质
强氧化剂
10.6 危险的分解产物
其它分解产物 - 无数据资料
模块 11. 毒理学资料
11.1 毒理学影响的信息
急性毒性
无数据资料
皮肤刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
眼睛刺激或腐蚀
无数据资料
呼吸道或皮肤过敏
无数据资料
生殖细胞致突变性
无数据资料
致癌性
IARC:
此产品中没有大于或等于 0。1%含量的组分被 IARC鉴别为可能的或肯定的人类致癌物。
生殖毒性
无数据资料
特异性靶器官系统毒性(一次接触)
吸入 - 可能引起呼吸道刺激。
特异性靶器官系统毒性(反复接触)
无数据资料
吸入危险
无数据资料
潜在的健康影响
吸入 吸入可能有害。 引起呼吸道刺激。
摄入 如服入是有害的。
皮肤 通过皮肤吸收可能有害。 造成皮肤刺激。
眼睛 造成严重眼刺激。
接触后的征兆和症状
据我们所知,此化学,物理和毒性性质尚未经完整的研究。
附加说明
化学物质毒性作用登记: 无数据资料
模块 12. 生态学资料
12.1 生态毒性
无数据资料
12.2 持久性和降解性
无数据资料
12.3 潜在的生物累积性
无数据资料
12.4 土壤中的迁移性
无数据资料
12.5 PBT 和 vPvB的结果评价
无数据资料
12.6 其它不良影响
无数据资料
模块 13. 废弃处置
13.1 废物处理方法
产品
此易爆炸产品可以在备有燃烧后处理和洗刷作用的化学焚化炉中燃烧
将剩余的和不可回收的溶液交给有许可证的公司处理。
受污染的容器和包装
按未用产品处置。
模块 14. 运输信息
14.1 联合国危险货物编号
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.2 联合国运输名称
欧洲陆运危规: 非危险货物
国际海运危规: 非危险货物
国际空运危规: 非危险货物
14.3 运输危险类别
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.4 包裹组
欧洲陆运危规: - 国际海运危规: - 国际空运危规: -
14.5 环境危险
欧洲陆运危规: 否 国际海运危规 国际空运危规: 否
海洋污染物(是/否): 否
14.6 对使用者的特别提醒
无数据资料
上述信息视为正确,但不包含所有的信息,仅作为指引使用。本文件中的信息是基于我们目前所知,就正
确的安全提示来说适用于本品。该信息不代表对此产品性质的保证。
参见发票或包装条的反面。
模块 15 - 法规信息
N/A
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:关于硫酚化合物X.关于硫酚酮(3)衍生物的Clemmensen还原摘要:1.在2-[ω-甲氧基丁基]-噻吩酮-(3)和2-甲基-噻吩酮-(3)的Clemmensen还原反应中产生的二聚产物被鉴定为二-[ω-甲氧基-γ-氧代-n-辛基]硫化物或作为二[γ-氧代-正戊基]硫化物识别。DOI:10.1002/hlca.19510340321
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:SYNTHETIC THIOPHANE DERIVATIVES摘要:DOI:10.1021/ja01233a514
文献信息
-
Stereoselective Michael additions on α-aminoacrylates as the key step to an<scp>l</scp>-Oic analogue bearing a quaternary stereocenter作者:Federico Maria Cecchinelli、Giuseppe Celentano、Alessandra Puglisi、Nicoletta GaggeroDOI:10.1039/c9ob02084e日期:——A novel, highly stereoselective route for pharmaceutically relevant octahydroindole-2-carboxylates bearing a quaternary stereocenter has been developed. The key chiral intermediates 3 have been prepared in good yields and enantiomeric excesses up to 98%. A broad substrate range has been tolerated under the reaction conditions.已开发出具有季立体中心的药学上相关的八氢吲哚-2-羧酸酯的新颖的,高度立体选择性的途径。关键的手性中间体3的制备得率很高,对映体过量高达98%。在反应条件下可以耐受较宽的底物范围。
-
Hydroxynitrile lyase catalysed synthesis of heterocyclic (R)- and (S)-cyanohydrins作者:Manuela Avi、Martin H. Fechter、Karl Gruber、Ferdinand Belaj、Peter Pöchlauer、Herfried GrienglDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2004.07.099日期:2004.11saturated five- and six-membered ring ketones sometimes bearing a methyl substituent were reacted with HCN under enzyme catalysis using recombinant hydroxynitrile lyase from Hevea brasiliensis, as a rule (S)-selective, and Prunus amygdalus, (R)-selective. The resulting cyanohydrins were stereochemically characterised. The steric outcome of these transformations was interpreted by molecular modelling.
-
Mechanism of formation of sulphur aroma compounds from l-ascorbic acid and l-cysteine during the Maillard reaction作者:Ai-Nong Yu、Zhi-Wei Tan、Fa-Song WangDOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.11.111日期:2012.6The sulphur aroma compounds produced from a phosphate-buffered solution (pH 8) of l-cysteine and l-, l-[1-13C] or l-[4-13C] ascorbic acid, heated at 140±2°C for 2h, were examined by headspace SPME in combination with GC-MS. MS data indicated that C-1 of l-ascorbic acid was not involved in the formation of sulphur aroma compounds. The sulphur aroma compounds formed by reaction of l-ascorbic acid with由L-半胱氨酸和L-,L- [1-13C]或L- [4-13C]抗坏血酸的磷酸盐缓冲溶液(pH 8)产生的硫香气化合物,在140±2°C下加热2h通过顶空SPME与GC-MS结合进行检测。MS数据表明1-抗坏血酸的C-1不参与硫香气化合物的形成。通过L-抗坏血酸与L-半胱氨酸反应形成的硫芳香化合物主要包含噻吩,噻唑和含硫的脂环族化合物。在这些化合物中,1-丁烷硫醇,二乙基二硫化物,5-乙基-2-甲基噻唑,顺式和反式-3,5-二甲基-1,2,4-三硫杂环戊烷,噻吩并[2,3-b]噻吩,噻吩并[3] ,2-b]噻吩,顺式和反式-3,5-二乙基-1,2,4-三硫杂环戊烷,1,2,5,6-四噻吩,2-乙基噻吩并[2,3-b]噻吩,2,4 ,6-三甲基-1,3,5-trithiane和环状八原子硫(S8)仅通过L-半胱氨酸 href=https://www.molaid.com/MS_37224 target="_blank">氨酸降解而形成,其余部分则通过l-抗坏血酸降解产物(例如羟基丁二酮,丁二酮,乙醛,
-
Heterocyclic Volatiles Formed by Heating Cysteine or Hydrogen Sulfide with 4-Hydroxy-5-methyl-3(2<i>H</i>)-furanone at pH 6.5作者:Frank B. Whitfield、Donald S. MottramDOI:10.1021/jf0008644日期:2001.2.1The reaction of 4-hydroxy-5-methyl-3(2H)-furanone (HMF) with cysteine or hydrogen sulfide at pH 6.5 for 60 min at 140 degrees C produced complex mixtures of volatile compounds, the majority of these containing either sulfur or nitrogen. Of the 68 compounds detected, 63 were identified, some tentatively, by GC-MS. Among the identified compounds were thiophenes (10), thiophenones (6), thienothiophenes
-
Characteristic flavor formation of thermally processed N-(1-deoxy-α-d-ribulos-1-yl)-glycine: Decisive role of additional amino acids and promotional effect of glyoxal作者:Huan Zhan、Heping Cui、Junhe Yu、Khizar Hayat、Xian Wu、Xiaoming Zhang、Chi-Tang HoDOI:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131137日期:2022.35-dimethylpyrazine formation; the nonionized amino group of additional lysine were involved in α-dicarbonyls formation, causing pyrazine and methylpyrazine accumulation in the ARP model. Moreover, the high dosage and pH stabilization of additional GO probably promoted the ARP degradation and deoxyosones retro-aldol cleavage, resulting in methylpyrazine rather than furanoids formation. The present work研究了氨基酸和 α-二羰基在热加工过程中 Amadori 重排产物 (ARP) 风味形成中的作用。挥发性化合物的比较和它们的浓度时ñ - (1-脱氧α- d-ribulos-1-yl)-甘氨酸在 100 °C 下与不同的氨基酸或乙二醛 (GO) 反应。ARP 模型中的其他氨基酸,例如甘氨酸 (Gly),通过衍生的甲醛的链延长而促进了呋喃类化合物的多样性。而额外谷氨酸的单阴离子充当亲核试剂,有利于 2-乙基-3,5-二甲基吡嗪和 2,5-二甲基吡嗪的形成;额外赖氨酸的非电离氨基参与 α-二羰基的形成,导致 ARP 模型中吡嗪和甲基吡嗪的积累。此外,额外的 GO 的高剂量和 pH 稳定可能促进了 ARP 降解和脱氧酮逆醛醇裂解,导致甲基吡嗪而不是呋喃类化合物的形成。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
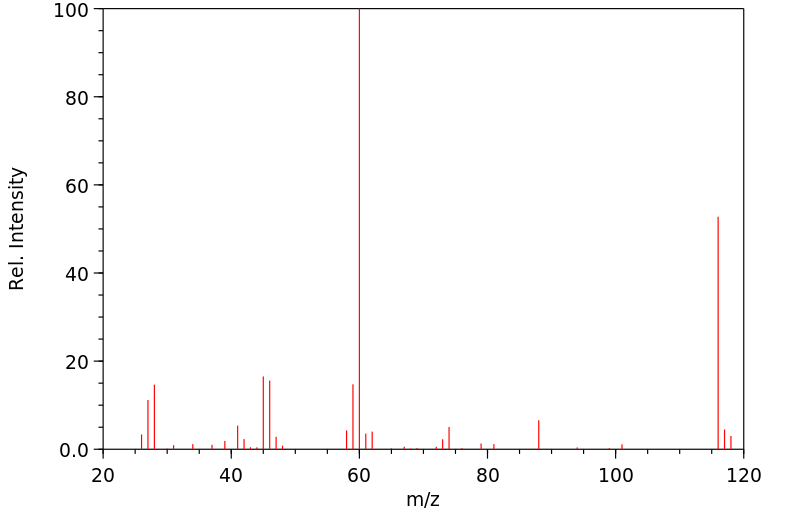
质谱MS
-
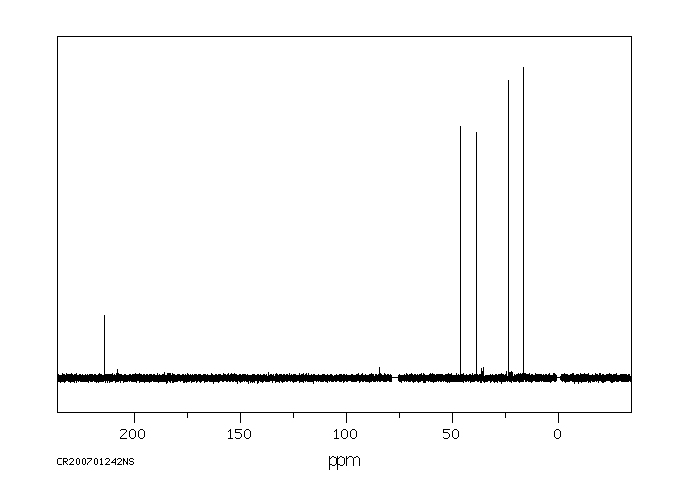
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
苯甲酸,4-(1,3-二噁烷-2-基)-
红色基KL
甲基四氢-2-噻吩羧酸酯
甲基4-氧代四氢-2-噻吩羧酸酯
环丁砜
烯丙基-(3-甲基-1,1-二氧代-四氢-1lambda*6*-噻吩-3-基)-胺
氯(四氢噻吩)金(I)
四甲基亚砜
四氢噻吩二醇
四氢噻吩-3-酮
四氢噻吩-3-羧酸-1,1-二氧
四氢噻吩-2,5-二酮
四氢噻吩-1,1-二亚基二胺
四氢噻吩
四氢-噻吩-3-醇
四氢-N-甲基-N-亚硝基-3-噻吩胺1,1-二氧化物
四氢-3-噻吩羧酸甲酯
四氢-3-噻吩羧酸
四氢-3-噻吩磺酰氯 1,1-二氧化物
四氢-3-噻吩硫醇1,1-二氧化物
四氢-3-噻吩甲酰氯1,1-二氧化物
四氢-3-噻吩甲腈1,1-二氧化物
四氢-3-噻吩基甲基丙烯酸酯
四氢-3,4-噻吩二胺1,1-二氧化物
四氢-2-噻吩羧酸
四亚甲基-D8砜
噻吩,四氢-2,2,5,5-四甲基-
反式-3-辛基亚磺酰基-4-羟基四氢噻吩1,1-二氧化物
八氟四氢噻吩 1,1-二氧化物
全氟四氢噻吩
二甲基砜茂烷
二氢-5,5-二甲基噻吩-3(2H)-酮
二氢-2-甲基-3(2H)-噻吩酮
乙基四氢-3-噻吩羧酸酯
乙基(5Z)-5-(羟基亚胺)-4-氧代-4,5-二氢-3-噻吩羧酸酯
乙基(4E)-4-(羟基亚胺)四氢-3-噻吩羧酸酯
Γ--硫代丁内酯
beta-乙基-beta-甲基-硫代丁内酯
alpha-乙基,alpha-甲基-硫代丁内酯
[[[(四氢噻吩1,1-二氧化物)-3-基]亚氨基]二(亚甲基)]二膦酸
[(1,1-二氧代四氢噻吩-3-基)氨基]二硫代甲酸
[(1,1-二氧代四氢-3-噻吩基)甲基]胺
[(1,1-二氧代-3-四氢噻吩基)氨基]二硫代甲酸钾盐
REL-(3AS,6AS)-六氢-2H-噻吩并[2,3-C]吡咯1,1-二氧化物盐酸盐
N-(四氢呋喃-2-基甲基)-N-四氢噻吩-3-基胺
N-烯丙基四氢-3-噻吩胺1,1-二氧化物
N-丁基-N-(1,1-二氧代四氢噻吩-3-基)胺盐酸盐
N-(1,1-二氧代四氢噻吩-3-基)乙酰胺
N'-(1,1-二氧代-四氢噻吩-3-基)-N,N-二甲基-乙烷-1,2-二胺
7-硫杂双环[2.2.1]庚-5-烯-2-羧酸