肼 | 302-01-2
分子结构分类
中文名称
肼
中文别名
肼(无水);联氨;联胺
英文名称
hydrazine
英文别名
hydrazine hydrate;diamine
CAS
302-01-2
化学式
H4N2
mdl
MFCD00011417
分子量
32.0452
InChiKey
OAKJQQAXSVQMHS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:1,4°C
-
沸点:65 °C
-
密度:1.011 g/mL at 25 °C
-
蒸气密度:>1 (vs air)
-
闪点:−4 °F
-
溶解度:极易溶于水、乙醇、甲醇
-
介电常数:52.0(20℃)
-
暴露限值:TLV-TWA (skin) 1 ppm (1.3 mg/m3 ) (MSHA and OSHA), 0.1 ppm (ACGIH).
-
LogP:-0.16 at 20℃
-
物理描述:Hydrazine, anhydrous appears as a colorless, fuming oily liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Flash point 99°F. Explodes during distillation if traces of air are present. Toxic by inhalation and by skin absorption. Corrosive to tissue. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Used as a rocket propellant and in fuel cells.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless fuming, oily liquid ... (Note: A solid below 36 °F)
-
气味:Penetrating odor resembling ammonia.
-
蒸汽密度:Relative vapor density (air = 1): 1.1
-
蒸汽压力:14.4 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:270 °C
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions - Nitrogen oxides (NOx).
-
粘度:0.974 uPa-sec at 20 °C
-
燃烧热:-8345 btu/Lb = -4636 cal/g = -194.1X10+5 J/kg
-
汽化热:44.7 kJ/mol at 25 °C
-
表面张力:66.7 mN/m at 25 °C
-
电离电位:8.93 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor perception threshold for hydrazine is 160 mg/L.
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.46979 at 22.3 °C/D; 1.46444 at 35 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa = 7.96
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-1.5
-
重原子数:2
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:-2147483.648
-
拓扑面积:52
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
敏捷固氮菌已被发现能将氮固定为主要产物肼。
Hydrazine has been found to be a primary product of nitrogen fixation by Azotobacter agile.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Hydrazine ... is ... acetylated very rapidly in most species. The reaction is so fast that the monoacetyl metabolite is not detected, and the excreted diacetyl metabolite accounts almost entirely for the administered dose.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Hydrazine is possibly degraded to ammonia, as evidenced by elevation of blood ammonia in dogs given hydrazine; however, diacetylhydrazine is not. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
使用(15)N标记的肼和常规方法,可以解释大约75%的单次肼剂量(1 mmol/kg)。在48小时内,大约30%以肼的形式出现在尿液中,大约20%以衍生化合物的形式出现,这种衍生化合物可以通过酸水解转化为肼。大约25%转化为氮。
(15)N-labeled hydrazine and conventional methods were used to account for approx 75% of single doses of hydrazine (1 mmol/kg). In 48 hr, about 30% appeared in urine as hydrazine and about 20% emerged as derivative that is acid-hydrolyzable to hydrazine. About 25% converted to nitrogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
联胺经口服或皮肤接触后,可能比吸入更快地被吸收进入血液。一旦进入血液,它们可能被输送到身体的所有组织中。接触后不久,组织中联胺的水平会下降,因为它们会代谢为多种产物,如乙酰联胺、二乙酰联胺、丙酮酸腙、尿素和非环状化合物(1,4,5,6-四氢-6-氧代-3-吡啶甲酸)。然而,这些代谢物会与一些重要的蛋白质发生相互作用,可能对身体有害。一些研究表明,代谢物和未改变的联胺会在一天内离开身体。
呼出的空气中也可以发现少量联胺。(L154, A112)
Hydrazines are likely to be more rapidly absorbed into the blood after ingestion or exposure to the skin than after inhalation. Once in the blood, they are probably carried to all the tissues of the body. Soon after exposure, the levels of hydrazines in the tissues fall since they are metabolised in several products such as acetyl-, diacetylhydrazine, pyruvate hydrazone, urea, and acyclic compound (1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-6-oxo-3-pyridazine carboxylic acid). However, these metabolites interacts with some important proteins and might be harmful to the body. Some studies showed that metabolites and unchanged hydrazine leave the body within one day.
Small amounts can also be found in the expired air. (L154, A112)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
识别和使用:联胺是一种无色油状液体。它被用作锅炉水处理的吸氧剂,无电极镍涂层的试剂,以及火箭推进剂。它还用于制药、炸药、聚合物和聚合物添加剂、抗氧化剂、金属还原剂、有机基团的氢化、摄影、静电复印和染料等多种领域。它已被测试为一种实验性疗法。
人体研究:与无水联胺的皮肤接触会导致类似腐蚀性烧伤并溶解毛发。报告了过敏性接触性皮炎。眼睛接触可能导致暂时性失明。眼睛溅入液体会导致角膜损伤和烧伤。在急性人类中毒的情况下,报告了呕吐、呼吸道的严重刺激伴随肺水肿的发展、中枢神经系统抑制以及肝脏和肾脏损伤。报告了过敏性接触性皮炎。根据对航空航天工作人群的研究,接触联胺增加了患肺癌和结肠癌的风险。
动物研究:将3至5毫升的联胺水合物应用于兔角膜时,产生了中等严重的刺激,而1毫升的刺激要小得多。将3毫升的无水联胺涂抹在兔皮肤上1分钟,然后清洗处理区域。尽管进行了清洗,涂抹后60至90分钟内仍发生死亡。急性毒性的特征是肝脏损伤,包括脂肪变性、红细胞破坏和贫血、厌食、体重减轻、虚弱、呕吐、兴奋性、低血糖和抽搐。将狗、猴子、大鼠和小鼠分成若干组,每天24小时、每周7天接触6.2或1 ppm的联胺,或每天6小时、每周5天接触1或5 ppm的联胺,持续6个月。小鼠和狗出现了死亡,但猴子和大鼠没有。狗表现出血液学缺陷和网织红细胞数量的增加。在 mice 和狗中,肝脏变化包括中等到严重的脂肪浸润,在猴子中轻微到中等,在大鼠中未出现。将大鼠在怀孕期间口服8 mg/kg bw的联胺。出现了母体毒性,包括死亡和体重减轻,以及胎儿毒性,包括胎儿体重和存活能力降低。尽管有些胎儿苍白且水肿,但没有出现重大的先天性畸形。在几种小鼠品系中观察到肺部肿瘤数量的增加,但联胺没有增加大鼠在皮下注射或气管内给药后的肿瘤产量。在大多数标准的遗传毒性终点测试中,联胺呈阳性。
生态毒性研究:将脂头鲦鱼的卵(Pimephales promelas)在分裂中期暴露于联胺24或48小时。暴露24小时的胚胎对0.1 mg/L的浓度表现出几种缺陷,如心率略有或中度降低、血红蛋白水平、身体运动和眼色素量。暴露于1.0 mg/L联胺浓度48小时的胚胎似乎没有存活的可能。存活的胚胎表现出严重的畸形,并且幼虫的生长减少。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: Hydrazine is a colorless oily liquid. It is used as an oxygen scavenger in boiler water treatment, as an electrodeless nickel coating reagent, and in rocket propellant. It is also used in a variety of other fields including pharmaceuticals, explosives, polymers and polymer additives, antioxidants, metal reductants, hydrogenation of organic groups, photography, xerography, and dyes. It has been tested as an experimental therapy. HUMAN STUDIES: Skin contact with anhydrous hydrazine leads to caustic-like burns and dissolves hair. Allergic contact dermatitis has been reported. Exposure to the eyes can produce temporary blindness. Liquid splashes to the eyes can produce corneal injury and burns. In cases of acute human poisoning, vomiting, severe irritation of the respiratory tract with the development of pulmonary edema, central nervous system depression, and hepatic and renal damage have been reported. Allergic contact dermatitis has been reported. Exposure to hydrazine increases the risk of incident lung cancers and colon cancers, based on a study in a cohort of aerospace workers. ANIMAL STUDIES: Hydrazine hydrate produced moderately severe irritation when 3 to 5 mL was applied to rabbit cornea, whereas 1 mL was much less irritating. Rabbit skin that was treated with 3 mL of anhydrous hydrazine for 1 min, followed by washing the treated area. Despite washing, mortality ensued 60 to 90 min after application. Acute toxicity has been characterized by liver damage consisting of fatty degeneration, red blood cell destruction and anemia, anorexia, weight loss, weakness, vomiting, excitability, hypoglycemia, and convulsions. Groups of dogs, monkeys, rats, and mice were exposed either 24 hr/day, 7 days/wk to 6.2 or 1 ppm, or 6 hr/day, 5 days/wk to 1 or 5 ppm hydrazine for 6 months. Mortality was seen in mice and dogs, but not in monkeys or rats. Dogs showed hematologic deficits and increased numbers of reticulocytes. Liver changes that consisted of moderate to severe fatty infiltration were marked in mice and dogs, were slight to moderate in monkeys, and were absent in the rat. Groups of rats were exposed orally during gestation to 8 mg/kg bw hydrazine. Maternal toxicity, including mortality and body weight loss, was seen, along with fetal toxicity that included reduced fetal weight and viability. Although some fetuses were pale and edematous, no major congenital malformations occurred. An increase in the number of lung tumors was observed in several strains of mice, but hydrazine did not increase the tumor yield in rats following either sc injection or intratracheal application. Hydrazine is positive in most standard assays for genetic toxicity endpoints. ECOTOXICITY STUDIES: Eggs of fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) at the mid-cleavage stage were exposed to hydrazine for 24 or 48 hr. Embryos, exposed for 24 hr, to 0.1 mg/L, showed several defects, such as slightly or moderately subnormal heart beat, hemoglobin levels, body movement, and amount of eye pigment. Embryos exposed to a hydrazine concentration of 1.0 mg/L for 48 hr appeared to have little chance of survival. Surviving embryos showed severe deformities and larvae exhibited reduced growth.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
至少观察到了两种作用机制。一种是那些带有自由氨基团的肼(肼和1,1-二甲基肼)与关键细胞分子直接结合。肼与α-酮酸(如维生素B6)反应,形成肼化合物。通过结合酮酸并形成肼,肼在体外抑制线粒体底物的氧气消耗。第二种机制涉及代谢产生的反应性物种,如自由基中间体或甲基重氮基离子。(L154)
At least two mechanisms of action have been observed. One involves the direct binding of those hydrazines with a free amino group (hydrazine and 1,1-dimethylhydrazine) to key cellular molecules. Hydrazine reacts with alpha-keto acids such as vitamin B6 to form hydrazoines compounds. By binding to keto acids and forming hydrazones, hydrazine inhibits oxygen consumption with mitochondrial substrates in vitro. A second mechanism involves the generation of reactive species such as free radical intermediates or methyldiazonium ions as a result of metabolism. (L154)
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
Evaluation: There is limited evidence in humans for the carcinogenicity of hydrazine. A positive association has been observed between exposure to hydrazine and cancer of the lung. There is sufficient evidence in experimental animals for the carcinogenicity of hydrazine. Hydrazine is probably carcinogenic to humans (Group 2A).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
分类:B2;可能的人类致癌物。分类依据:经口服、吸入或腹膜内给药后,在大鼠、小鼠和仓鼠中诱发了肿瘤。联胺在多项检测中表现出诱变性。人类致癌性数据:不足。动物致癌性数据:充分。
CLASSIFICATION: B2; probable human carcinogen. BASIS FOR CLASSIFICATION: Tumors have been induced in mice, rats and hamsters following oral, inhalation or intraperitoneal administration of hydrazine and hydrazine sulfate. Hydrazine is mutagenic in numerous assays. HUMAN CARCINOGENICITY DATA: Inadequate. ANIMAL CARCINOGENICITY DATA: Sufficient.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A3; 已确认的动物致癌物,对人类的相关性未知。
A3; Confirmed animal carcinogen with unknown relevance to humans.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Absorption of hydrazine through skin in dogs is rapid, and the hydrazine can be detected in femoral /artery/ blood within 30 seconds.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
氮肼(假设大部分是未改变的肼)在狗通过静脉注射或皮下给药肼后通过尿液排出。大剂量(50毫克/千克 - 是LD50的两倍)的5-11%在给药后的前4小时内排出,大约15毫克/千克剂量的50%在注射后的前两天内排出。
Hydrazino nitrogen (assumed to be largely unchanged hydrazine) is excreted in urine after iv or sc administration of hydrazine in dogs. 5-11% of large doses (50 mg/kg - twice the LD50) is excreted within first 4 hr and approximately 50% of 15 mg/kg dose is excreted within first 2 days after injection.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
联胺已经通过皮肤、胃肠道和肺部被迅速且很好地吸收,尽管它的蒸气并没有通过皮肤显著吸收。
Hydrazine has been rapidly and well absorbed by the skin, GI tract, and lungs, although its vapors are not absorbed significantly through the skin.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
联胺迅速被吸收并快速分布到并从大多数组织中消除。它可能会与谷氨酸、碳酸氢盐磷酸盐或尿素循环的氨基酸前体结合,竞争性地减缓谷氨酰胺和尿素的形成,从而导致氨的释放。在老鼠和老鼠中,部分吸收的联胺以不变的形式排出,部分以不稳定的结合物或通过尿液以酸水解衍生物的形式排出。当联胺被代谢时,会产生大量的氮,通过肺部排出。
Hydrazine is rapidly absorbed and rapidly distributed to and eliminated from most tissues. It may compete to slow down the formation of glutamine and urea by combining with glutamic acid, carbamyl phosphate, or amino acid precursor of the urea cycle, as a result of which ammonia is released. In mice and rats, a part of the absorbed hydrazine is excreted unchanged and a part as labile conjugates or as acid-hydrolysable derivatives via the urine. When hydrazine is metabolized, a significant amount of nitrogen is produced, which is excreted via the lungs.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露限值:Ceiling: 0.03 ppm (0.04 mg/m3) [2-hour]
-
危险等级:8
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:50 ppm
-
危险品标志:T,N
-
安全说明:S26,S36/37/39,S45,S53,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R43,R45,R50/53,R23/24/25,R34
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:28251090
-
RTECS号:MU7175000
-
包装等级:I
-
危险类别:8
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3293
-
危险标志:GHS05,GHS06,GHS08,GHS09
-
危险性描述:H301 + H331,H314,H317,H350,H410
-
危险性防范说明:P201,P261,P273,P280,P301 + P310 + P330,P305 + P351 + P338
-
储存条件:储存时应注意以下事项:需存放在阴凉、通风良好的专用库房内,并实行“双人收发、双人保管”制度。远离火种和热源,库温不宜超过37℃。保持容器密封。与氧化剂、金属粉末及食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。使用防爆型照明和通风设施,禁止使用易产生火花的机械设备和工具。储存区应配备泄漏应急处理设备和合适的收容材料。
制备方法与用途
性质
无水肼又名联氨,是一种无色油状液体。分子量为32.05,熔点2℃,沸点113.5℃,相对密度1.004(25/4℃),折射率1.4644(35℃),闪点52℃。它能与水、醇混溶而不溶于氯仿和醚。无水肼有吸湿性,在空气中会发烟,并且燃烧时会产生紫色火焰,具有强烈的氨臭味。
用途肼是一种广泛应用于化工领域的原料。作为燃料,其高热值可用于火箭和燃料电池。通过以氨和次氯酸钠为原料进行氯化和胺化反应可制得无水肼。无水肼作为一种强还原剂,能够去除锅炉水中溶解的氧气,减少腐蚀;还可以用作塑料发泡剂、抗氧剂、聚合物交联剂、植物生长调节剂、农药及医药制品。
化学性质无水肼是一种油状无色液体,具有刺激性气味。它溶于水、醇和氨等物质中。
用途无水肼广泛用于制造异烟肼、照相显影药剂、喷气式发动机燃料、火箭燃料、抗氧剂、还原剂及高压锅炉给水脱氧剂等。此外,还用作植物生长抑制剂以及烟草、土豆、玉米的贮藏保鲜,医药上用来制备异烟肼。同时可用于尼龙、环氧树脂和食用盐酸的制造,作为再生催化剂、除草剂和燃料电池的重要原料。
生产方法工业生产无水肼通常采用拉希法或亚胺过氧化氢氧化法。拉希法以氨和次氯酸钠为原料,在反应器中按1:3(摩尔比)的比例进行氯化生成氯胺,再与无水氨反应制得肼。另一种方法是使用尿素作为原料,在高锰酸钾催化剂存在下与次氯酸钠-氢氧化钠溶液反应生成肼。
脱水剂法则是通过将烧碱和50%~54%的水合肼按质量比10:8混合,逐渐通入氮气以去除空气,并加热至约118℃使烧碱完全溶解。冷却后,在真空条件下蒸馏至含肼量达到90%-94%,再进行分馏、除湿处理制得高纯度无水肼。
类别- 腐蚀物品
- 毒性分级:高毒
- 急性毒性:
- 大鼠口服LD50: 60毫克/公斤
- 小鼠口服LD50: 59毫克/公斤
- 爆炸物危险特性:燃烧时可爆
- 可燃性危险特性:遇高热、明火或氧化剂可燃,受热分解产生有毒氮化合物气体
- 储运特性:储存于通风低温干燥的库房中,并与氧化剂和酸类分开存放
- TLV-TWA: 0.1 PPM (1.3毫克/立方米)
- STEL: 0.1毫克/立方米
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— hydrazyl radical 13598-46-4 H3N2 31.0372
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:在用于超分子催化的金属-有机胶囊内修饰酶底物结合摘要:建立超分子催化以通过底物封装来改变反应动力学,但操纵电子转移反应的热力学仍未得到探索。在此,我们报道了一种新的微环境屏蔽方法来诱导肼底物氧化还原电位的阳极转变,让人联想到金属-有机胶囊 H1 内 N-N 键裂解的酶促活化。配备催化活性钴位点和底物结合酰胺基团,H1封装肼以形成涉及底物的包合物中间体,当从电子供体获得电子时触发催化还原N-N键断裂。与游离肼的还原相比,概念性分子限制微环境降低了与初始电子转移反应相关的吉布斯自由能(高达 −70 kJ mol –1 )。动力学实验证明了 Michaelis-Menten 机制,该机制涉及底物结合预平衡的形成,然后是键断裂。然后,远端的 N 作为 NH 3释放,产品被挤压。将荧光素整合到H1中可实现 N 2 H 4的光还原初始速率为 ca。1530 nmol min –1转化为氨,与天然MoFe蛋白相当;因此,该方法为模拟酶促激活提供了一个有吸引力的流形。DOI:10.1021/jacs.3c00626
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:直接观察NH2 *与氧气,氨基酸和黑色素的反应。摘要:我们报告了直接观察到由于氧而使氨基自由基弱吸收的瞬态猝灭的情况,因此,通过完全直接的方法确定了相应的速率常数(k =(1.1 +/- 0.1)x 10(9) dm3 mol(-1)s(-1))。我们还报告了与几种氨基酸的氨基酸自由基反应的速率常数,以及黑色的Eumelanin和金色/红色的phaeomelanin的模型。这些反应导致了一种基于自由基的机理,该机理可以解释为什么氨水可用于商业头发(黑色素)的漂白,而避免了过多的氨基酸(头发蛋白质)的破坏。DOI:10.1021/jp076395r
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:三联芳环类化合物及其制备方法、药物组合物和应用摘要:本发明公开了一类三联芳环类化合物及其制备方法、药物组合物和应用。该类三联芳环类化合物的结构如式I所示,还包含其立体异构体、内消旋体、外消旋体、前药、结晶、药学上可接受的盐或它们的混合物,其具有PD‑L1抑制活性,能够显著抑制PD‑1/PD‑L1蛋白‑蛋白相互作用,阻断PD‑1/PD‑L1信号通路,因此可以广泛应用在预防和/或治疗肿瘤、感染性疾病、炎症性疾病、自身免疫性疾病和器官移植排斥的免疫调节剂类药物的制备中,同时化合物制备方法利于结构拓展。#imgabs0#公开号:CN118026948A
文献信息
-
Plant Growth Regulator Daminozide Is a Selective Inhibitor of Human KDM2/7 Histone Demethylases作者:Nathan R. Rose、Esther C. Y. Woon、Anthony Tumber、Louise J. Walport、Rasheduzzaman Chowdhury、Xuan Shirley Li、Oliver N. F. King、Clarisse Lejeune、Stanley S. Ng、Tobias Krojer、Mun Chiang Chan、Anna M. Rydzik、Richard J. Hopkinson、Ka Hing Che、Michelle Daniel、Claire Strain-Damerell、Carina Gileadi、Grazyna Kochan、Ivanhoe K. H. Leung、James Dunford、Kar Kheng Yeoh、Peter J. Ratcliffe、Nicola Burgess-Brown、Frank von Delft、Susanne Muller、Brian Marsden、Paul E. Brennan、Michael A. McDonough、Udo Oppermann、Robert J. Klose、Christopher J. Schofield、Akane KawamuraDOI:10.1021/jm300677j日期:2012.7.26N-demethylation of Nε-methyl lysine residues in histones and are current therapeutic targets. A set of human 2-oxoglutarate analogues were screened using a unified assay platform for JmjC demethylases and related oxygenases. Results led to the finding that daminozide (N-(dimethylamino)succinamic acid, 160 Da), a plant growth regulator, selectively inhibits the KDM2/7 JmjC subfamily. Kinetic and crystallographic
-
Substituted Heteroaromatic Carboxamide and Urea Compounds as Vanilloid Receptor Ligands申请人:Frank Robert公开号:US20120115903A1公开(公告)日:2012-05-10Substituted heteroaromatic carboxamide and urea compounds corresponding to formula (i) processes for the preparation thereof, pharmaceutical compositions containing these compounds and also a method of using these compounds in pharmaceutical compositions for treating or inhibiting pain and other conditions mediated at least in part via the vanilloid receptor 1.
-
[EN] AZOLE COMPOUNDS AS PIM INHIBITORS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS D'AZOLE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'INHIBITEURS DES PIM申请人:AMGEN INC公开号:WO2012129338A1公开(公告)日:2012-09-27The invention relates to bicyclic compounds of formulas I and Ia, and salts thereof. In some embodiments, the invention relates to inhibitors or modulators of Pim-1 and/or Pim-2, and/or Pim-3 protein kinase activity or enzyme function. In still further embodiments, the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising compounds disclosed herein, and their use in the prevention and treatment of Pim kinase related conditions and diseases, preferably cancer.
-
Pyridyl-alkylaminoethylene compounds申请人:Smith Kline & French Laboratories Limited公开号:US04013769A1公开(公告)日:1977-03-22The compounds are ethylene derivatives which are inhibitors of histamine activity, in particular, inhibitors of H-2 histamine receptors. A compound of this invention is 1-nitro-2-[2-((4-methyl-5-imidazolyl)methylthio)ethylamino]-2-[2-((3-chlor o-2-pyridyl)methylthio)ethylamino]ethylene.
-
The α-Effect in Hydrazinolysis of 4-Chloro-2-Nitrophenyl X-Substituted-Benzoates: Effect of Substituent X on Reaction Mechanism and the α-Effect作者:Min-Young Kim、Tae-Eun Kim、Jieun Lee、Ik-Hwan UmDOI:10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.8.2271日期:2014.8.20Second-order rate constants (
$k_N$ ) have been measured spectrophotometrically for the reaction of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenyl X-substituted-benzoates (6a-6h) with a series of primary amines including hydrazine in 80 mol %$H_2O$ /20 mol % DMSO at$25.0^\circ}C$ . The Br$\o}$ nsted-type plot for the reaction of 4-chloro-2-nitrophenyl benzoate (6d) is linear with$\beta}_nuc}$ = 0.74 when hydrazine is excluded from the correlation. Such a linear Br$\o}$ nsted-type plot is typical for reactions reported previously to proceed through a stepwise mechanism in which expulsion of the leaving group occurs in the rate-determining step (RDS). The Hammett plots for the reactions of 6a-6h with hydrazine and glycylglycine are nonlinear. In contrast, the Yukawa-Tsuno plots exhibit excellent linear correlations with$\rho}_X$ = 1.29-1.45 and r = 0.53-0.56, indicating that the nonlinear Hammett plots are not due to a change in RDS but are caused by resonance stabilization of the substrates possessing an electron-donating group (EDG). Hydrazine is ca. 47-93 times more reactive than similarly basic glycylglycine toward 6a-6h (e.g., the$\alpha}$ -effect). The$\alpha}$ -effect increases as the substituent X in the benzoyl moiety becomes a stronger electron-withdrawing group (EWG), indicating that destabilization of the ground state (GS) of hydrazine through the repulsion between the nonbonding electron pairs on the two N atoms is not solely responsible for the substituent-dependent$\alpha}$ -effect. Stabilization of transition state (TS) through five-membered cyclic TSs, which would increase the electrophilicity of the reaction center or the nucleofugality of the leaving group, contributes to the$\alpha}$ -effect observed in this study.二次速率常数($k_N$ )已通过分光光度法测定,用于4-氯-2-硝基苯基X取代苯甲酸酯(6a-6h)与一系列伯胺(包括80摩尔%$H_2O$ /20摩尔% DMSO中的25.0°C下的联氨)的反应。当联氨被排除在相关性之外时,4-氯-2-硝基苯基苯甲酸酯(6d)反应的Br$\o}$ nsted型图是线性的,$\beta}_nuc}$ = 0.74。这种线性Br$\o}$ nsted型图是典型的反应,先前报道这些反应通过逐步机制进行,其中离去基团的排出发生在速率决定步骤(RDS)中。6a-6h与联氨和甘氨酰甘氨酸反应的Hammett图是非线性的。相比之下,Yukawa-TSuno图显示出极佳的线性相关性,$\rho}_X$ = 1.29-1.45,r = 0.53-0.56,表明非线性Hammett图并非由于RDS的变化,而是由于具有供电子基团(EDG)的底物的共振稳定化所导致。联氨对6a-6h的反应性大约是同样碱性的甘氨酰甘氨酸的47-93倍(例如,$\alpha}$ 效应)。随着苯甲酰基中取代基X成为更强的吸电子基团(EWG),$\alpha}$ 效应增加,表明通过两个N原子上的非键电子对之间的排斥来破坏联氨的基态(GS)并不是唯一导致取代基依赖的$\alpha}$ 效应的原因。通过五元环过渡态(TS)的稳定化,这将增加反应中心的亲电性或离去基团的离核性,有助于在本研究中观察到的$\alpha}$ 效应。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
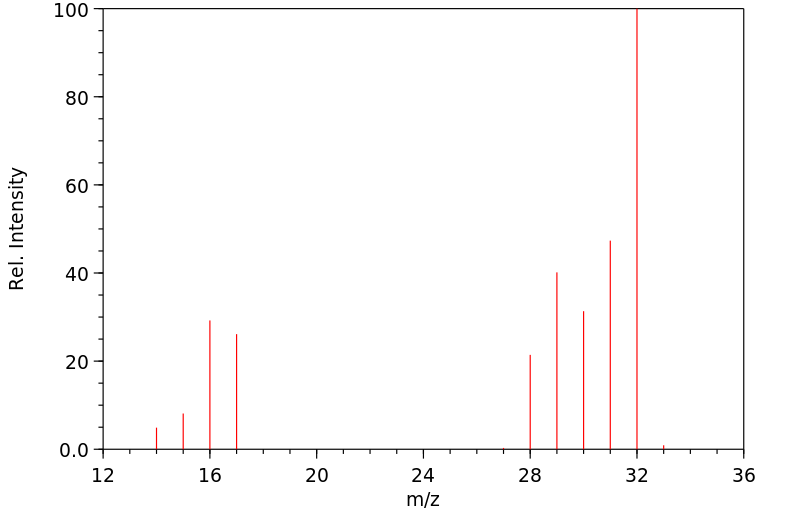
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息