氯化氰 | 506-77-4
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:-6 °C
-
沸点:12.7 °C
-
密度:1.186 g/cm3
-
物理描述:Colorless, liquid below 55°F (12.8°C) or gas above 55°F (12.8°C).
-
颜色/状态:Colorless gas or liquid (below 55 °F) ...[NOTE: Shipped as a liquified gas. A solid below 20 °F.]
-
气味:Acrid, choking odor
-
闪点:51 °C
-
溶解度:In water, 27.5 mg/L at 25 °C
-
蒸汽密度:2.1 (USCG, 1999) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:Vapor pressure, kPa at 21.1 °C: 1987
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:Not Applicable. Not flammable. (USCG, 1999)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition ... it will ... produce highly toxic and corrosive fumes such as /hydrogen chloride, hydrogen cyanide and nitrogen oxides/.
-
腐蚀性:Corrosive
-
汽化热:26.75 kJ/mL
-
表面张力:24.6 dynes/cm = 0.0246 N/m at 10 °C
-
电离电位:12.49 eV
-
聚合:Cyanogen chloride may polymerize violently if contaminated with chlorine.
-
气味阈值:... Pungent odor detectable at 2.5 mg/cu m (1 ppm).
-
相对蒸发率:Volatility at 25 °C: 3,960 mg/L at saturation
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:23.8
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险品标志:T
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R20/21/22,R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2853002000
-
危险类别:2.3
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1589
制备方法与用途
所需设备包括500mL三颈瓶,其中装有汞封搅拌、导气管和出气管。导入气体需先通过含硫酸的干燥瓶进行干燥处理。出气管连接蛇形冷凝管,并使用冰盐混合物冷却。冷凝管末端配有一个广口接受管,插入125mL锥形瓶中。该接受瓶与装有硫酸的洗气瓶相连,以防止硫酸倒吸。
将40g干燥的氰化钠粉末和140mL CCl4放入反应瓶中,并将其浸没在冰盐混合剂中至温度降至-5~-10℃。随后,用氮气排除装置中的空气,在反应混合物中加入3~4mL冰醋酸并开启搅拌器。接着通入氯气,确保整个反应过程维持在-5℃或更低的低温环境中。控制氯气体积流量,避免从出气洗瓶中逸出氯气。大约经过4~4.5小时后完成反应。
将接受瓶置于干冰冷却至-40~-50℃的丙酮溶液中,并用氮气流代替氯气继续通入约1~1.5小时以加热到60~65℃。此时,通过缓慢引入氮气流进行蒸馏。当蒸馏完成后移开接受瓶,连接一根长41mm、直径19mm的分馏柱,并将其四周包裹在干冰冷却至-25℃的丙酮中。对烧瓶进行微热处理,促使粗氯化氰回流并逐出过量的氯气。最终产物为浅黄色,产率为72%~78%,产量约36~39g。
操作过程中应注意安全,将反应在通风良好的柜中进行,并确保佩戴防毒面具。
合成制备方法氯与氰化钠作用生成氯化氰(NaCN+Cl2=NaCl+CNCl)的装置如图所示。同样地,500mL三颈瓶内装有汞封搅拌、导气管和出气管,并通过含硫酸的干燥瓶对导入气体进行干燥处理。出气管连接蛇形冷凝管并用冰盐混合物冷却,最终广口接受管插入125mL锥形瓶中,并与装有硫酸的洗气瓶相连以防止倒吸。
将40g干燥的氰化钠粉末和140mL 放入反应瓶中。将烧瓶及其内容物浸没在冰盐混合剂中至温度降至-5~-10℃。使用氮气排除装置中的空气,在反应混合物中加入3~4mL冰醋酸并开启搅拌器,通入氯气,并确保反应瓶维持在-5℃或更低的低温环境。
控制氯气体积流量以避免从出气洗瓶逸出氯气。反应约需4~4.5小时完成。随后将接受瓶置于干冰冷却至-40~-50℃的丙酮溶液中,并用氮气流代替氯气继续通入1~1.5小时,使烧瓶升温到60~65℃。通过引入缓慢流动的氮气进行蒸馏操作。
完成蒸馏后移开接受瓶并连接一根41mm长、直径19mm的分馏柱,并将该柱四周包裹在干冰冷却至-25℃的丙酮中,微热烧瓶促使粗氯化氰回流并逐出过量的氯气。最终产物为浅黄色,产率约为72%~78%,产量约36~39g。
操作时应确保安全措施到位,在通风良好的柜内进行反应,并佩戴防毒面具。
用途简介氯化氰主要用于有机合成。
用途氯化氰同样用于有机合成。[18]
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:氯化氰 在 alloys of Fe 作用下, 以>99的产率得到氰参考文献:名称:Gmelin Handbuch der Anorganischen Chemie, Gmelin Handbook: C: MVol.D1, 4.3.2, page 46 - 47摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:METHOD FOR PRODUCING CYANOGEN-HALIDE, CYANATE ESTER COMPOUND AND METHOD FOR PRODUCING THE SAME, AND RESIN COMPOSITION摘要:一种用于高效生产抑制副作用的氰卤化物,以及以高收率生产高纯度氰酸酯化合物的方法包括将卤素分子与含有氢氰酸和/或金属氰化物的水溶液接触,使得氢氰酸和/或金属氰化物与卤素分子在反应溶液中发生反应以获得氰卤化物,其中基于1摩尔卤素分子使用超过1摩尔的氢氰酸或金属氰化物,当未反应的氢氰酸或未反应的金属氰化物的物质量定义为摩尔(A),生成的氰卤化物的物质量定义为摩尔(B),反应在(A):(A)+(B)介于0.00009:1和0.2:1之间的状态中终止。公开号:US20150299110A1
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Preparation of nitriles摘要:公开号:US02606917A1
文献信息
-
Interaction of aryltrimethylstannanes with cyanogen chloride and bromide. A route to aryl cyanides作者:E.H. Bartlett、C. Eaborn、D.R.M. WaltonDOI:10.1016/s0022-328x(00)88327-8日期:1972.12Phenyltrimethylstannane has been found to react with cyanogen chloride in methylene chloride in the presence of aluminium chloride to give benzonitrile in 60% yield; o-, m-, and p-tolyltrimethylstannane similarly give o-, m-, and p-tolunitrile, respectively. With cyanogen bromide the aryl bromides are formed.
-
Synthesis of fluorinated tertiary diamines and diazanes作者:Nimesh R. Patel、Robert L. Kirchmeier、Jean'ne M. ShreeveDOI:10.1016/s0022-1139(00)80224-9日期:1990.7A variety of fluorinated and partially fluorinated tertiary diamines and diazanes have been prepared from 1-[bis(trifluoromethyl)amtno]tetrafluoro-2- azapropene, which is obtained from the dimerization of 2-azapropene in the presence of CsF. Addition of ClF results in the formation of the tertiary diamine (CF3)2NCF2N(Cl)CF3. Insertion of alkenes and nitriles into the nitrogenchlorine bond, as well已经由1- [双(三氟甲基)氨基]四氟-2-氮杂丙烯制备了各种氟化和部分氟化的叔二胺和二氮杂,它们是在CsF存在下由2-氮杂丙烯的二聚作用获得的。ClF的添加导致叔二胺(CF 3)2 NCF 2 N(Cl)CF 3的形成。烯烃和腈插入氮-氯键中以及与SF 5 Cl和CF 3 C(O)Cl发生光解反应很容易发生。尝试制备包含来自多氟烷亚胺,例如,R基团多氟烷diazanes ˚F NC(OR ˚F ')2(R ˚FCF 3,SF 5 ; ř ˚F 'CH 2 CF 3,CH(CF 3)2)导致与的ClF亚胺的反应的carbonnitrogen双键断裂生成R ˚F的NCI 2和F 2 C(OR ˚F ')2。类似地(CF 3)2 NC(OCH 2 CF 3)NCF 3用的ClF给出CF 3的NCI 2和(CF 3)2 NCF 2 OCH 2 CF 3。
-
Preparation and properties of tristrifluoromethylhydrazyl compounds作者:R. C. Dobbie、H. J. EmeléusDOI:10.1039/j19660000933日期:——with cyanogen chloride on irradiation to give bistrifluoromethylaminocarbylamine chloride, (CF3)2N·N:CCl2. Fluorination of the carbylamine chloride with sodium fluoride gives (C3F8N2)2; a structure for the dimer is proposed. Reaction with mercuric fluoride produces a crystalline mercurial, [(CF3)2N·N(CF3)]2Hg. Perfluorohexamethyltetrazine, N-bromotristrifluoromethylhydrazine, tristrifluoromethylhydrazine
-
Fluorocarbon derivatives of nitrogen. Part 5. Replacement of imidoyl halogen by the bistrifluoromethylamino-oxy group: reactions of perfluoro-2-azapropene and related compounds with bis(bistrifluoro-methylamino-oxy)mercury(<scp>II</scp>) or NN-bistrifluoromethylhydroxylamine–caesium fluoride作者:Ronald E. Banks、Dilip R. ChoudhuryDOI:10.1039/p19810001443日期:——mercurial [(CF3)2NOCF2](CF3)N}2Hg (11), chlorinolysis of which provides the N-chloroamine CF3NCICF2ON(CF3)2(16); pyrolysis of the mercurial (11) gives a complex mixture containing the imine CF3NCFON(CF3)2(12) and material tentatively identified as CF3NC[ON(CF3)2]}2O. The N-chloro-compound (16) reacts with hydrogen chloride and silver cyanide to provide the corresponding amine CF3NHCF2ON(CF3)2 and the用双(双三氟甲基氨基-氧基)汞(II)处理全氟-2-氮杂丙烯,产生新的汞((CF 3)2 NOCF 2 ](CF 3)N} 2 Hg(11),经氯解可提供N -氯胺CF 3 NCICF 2 ON(CF 3)2(16); 汞的热解(11)得到了包含亚胺CF 3 N CFON(CF 3)2(12)和初步确定为CF 3 N C [ON(CF 3)2 ]}的物质的复杂混合物2 O的Ñ氯化合物(16)反应用氯化氢和氰化银,以提供相应的胺CF 3 NHCF 2 ON(CF 3) 2和相关的亚胺(12)。后者产物,与二-取代的类似物一起(CF 3) 2 NCF 2 ÑCFON(CF 3) 2,也可以通过处理全氟-2- azapropene用铯氟化物的拟采购NN-双三氟甲基羟胺加合物。该试剂还攻击全氟-1-氮杂环己烯以产生全氟-[2-(二甲基氨基-氧基)-1-氮杂环己烯]和全氟-[2,6-双(二甲基
-
HgF2-assisted additions to SN and CN triple bonds作者:Alfred Waterfeld、R�diger MewsDOI:10.1039/c39820000839日期:——Formal additions of CIF to the SN triple bond in NSF3 and to the CN triple bond in CF3CN and (CN)2 are achieved by the system Cl2–HgF2; N-bromo-amines and -imines are isolated from RfCN–Br2–HgF2·NSF3 and CF3SCl–HgF2 gives SF5N(SCF3)2 in high yield.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
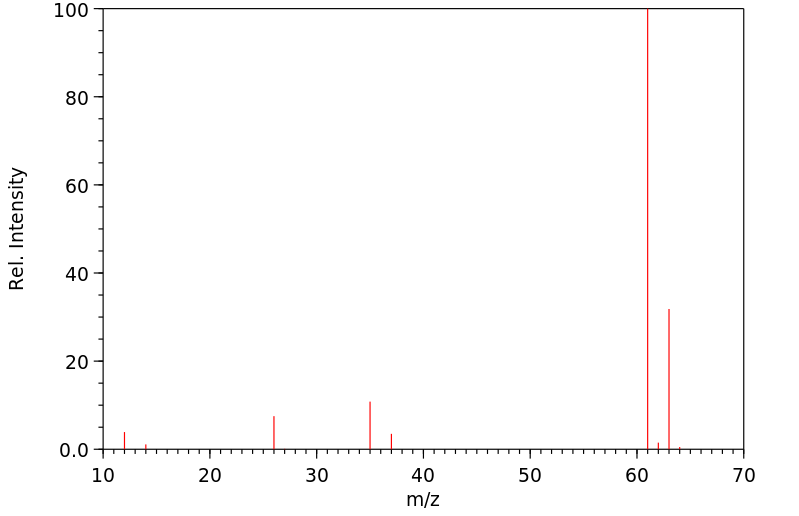
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息