二氯乙酸五氯苯酯 | 19745-69-8
中文名称
二氯乙酸五氯苯酯
中文别名
——
英文名称
pentachlorophenyl dichloroacetate
英文别名
Dichloressigsaeure-pentachlorphenylester;(2,3,4,5,6-pentachlorophenyl) 2,2-dichloroacetate
CAS
19745-69-8
化学式
C8HCl7O2
mdl
——
分子量
377.266
InChiKey
KDDDLTRKFSGKHG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:86 °C
-
沸点:413.1±45.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.796±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):6.2
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.125
-
拓扑面积:26.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2915400090
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Chemical Synthesis and Biological Activities of Two Disaccharide Dipeptides Corresponding to the Repeating Units of Bacterial Peptidoglycan摘要:两种二糖二肽,即O-(N-乙酰-β-d-氨基葡萄糖苷)-(1→4)-N-乙酰肽聚糖-L-丙氨酸-D-异谷氨酸(2)和O-(N-乙酰-β-肽聚糖-L-丙氨酸-D-异谷氨酸)-(1→4)-N-乙酰-D-氨基葡萄糖(3),对应于细胞壁肽聚糖的部分结构,通过相同的氨基葡萄糖二糖作为共同中间体合成而成。因此,选择性地在中间体的任一糖基上引入乳酸基团,分别获得了两个二糖,这些二糖在还原端或非还原端含有肽聚酸。肽基部分的偶联及去保护处理生成了2和3。生物测试结果显示,2和3的免疫刺激活性与N-乙酰肽聚糖-L-丙氨酸-D-异谷氨酸的活性相同,而后者是表达这些活性所需的最小结构。DOI:10.1246/bcsj.59.1411
表征谱图
-
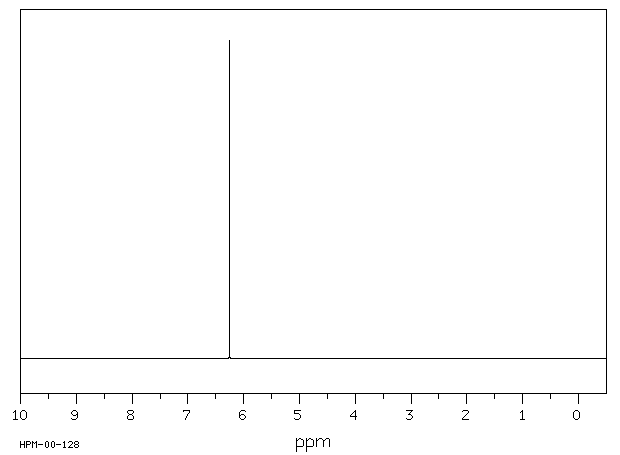
氢谱1HNMR
-
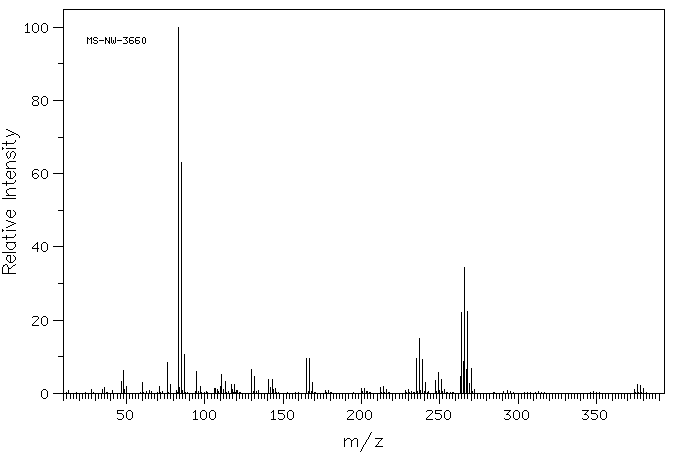
质谱MS
-
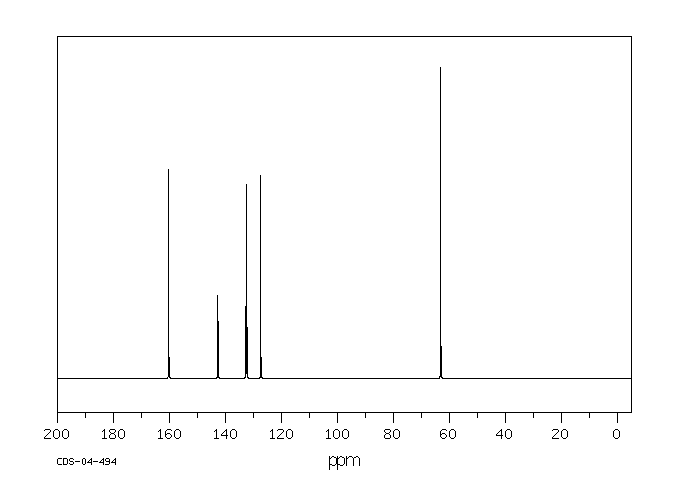
碳谱13CNMR
-
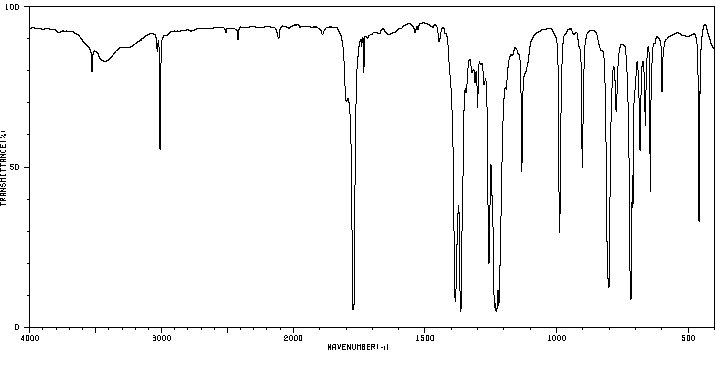
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
马来酰亚胺四聚乙二醇CH2CH2COOPFPESTER
马来酰亚胺六聚乙二醇CH2CH2COOPFPESTER
马来酰亚胺-酰胺-PEG8-四氟苯酚酯
马来酰亚胺-四聚乙二醇-五氟苯酯
马来酰亚胺-三聚乙二醇-五氟苯酚酯
靛酚乙酸酯
阿立哌唑标准品002
间硝基苯基戊酸酯
间氯苯乙酸乙酯
间乙酰苯甲酸
钾4-乙酰氧基苯磺酸酯
酚醛乙酸酯
邻苯二酚二乙酸酯
邻甲苯基环己甲酸酯
邻甲氧基苯乙酸酯
辛酸苯酯
辛酸对甲苯酚酯
辛酸五氯苯基酯
辛酸-(3-氯-苯基酯)
辛酰溴苯腈
苯酰胺,3,4-二(乙酰氧基)-N-[6-氨基-1,2,3,4-四氢-1-(4-甲氧苯基)-3-甲基-2,4-二羰基-5-嘧啶基]-
苯酚-乳酸
苯酚,4-异氰基-,乙酸酯(ester)
苯酚,4-[(四氢-2H-吡喃-2-基)氧代]-,乙酸酯
苯酚,3-(1,1-二甲基乙基)-,乙酸酯
苯酚,2-溴-3-(二溴甲基)-5-甲氧基-,乙酸酯
苯甲醇,4-(乙酰氧基)-3,5-二甲氧基-
苯甲酸,4-(乙酰氧基)-2-氟-
苯氧基氯乙酸苯酯
苯基金刚烷-1-羧酸酯
苯基氰基甲酸酯
苯基庚酸酯
苯基庚-6-炔酸酯
苯基己酸酯
苯基呋喃-2-羧酸酯
苯基吡啶-2-羧酸酯
苯基十一碳-10-烯酸酯
苯基乙醛酸酯
苯基乙酸酯-d5
苯基丙二酸单苯酯
苯基丙-2-炔酸酯
苯基丁-2,3-二烯酸酯
苯基4-乙基环己烷羧酸
苯基3-乙氧基-3-亚氨基丙酸盐
苯基2-(苯磺酰基)乙酸酯
苯基2-(4-甲氧基苯基)乙酸酯
苯基2-(2-甲氧基苯基)乙酸酯
苯基2-(2-甲基苯基)乙酸酯
苯基-乙酸-(2-甲酰基-苯基酯)
苯基-乙酸-(2-环己基-苯基酯)