四溴菊酯 | 66841-25-6
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:143℃
-
沸点:185~190℃ (0.1mmHg)
-
密度:1.70 g/cm3 (20℃)
-
颜色/状态:Orange-yellow solid
-
闪点:26 °C
-
溶解度:1.20e-07 M
-
蒸汽压力:3.6X10-11 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable for 6 months at 50 °C. Acidic media reduce hydrolysis and epimerization.
-
旋光度:Specific rotation: +21 deg to +27 deg (50 g/l toluene).
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of /nitrogen oxides/ and /bromides/
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):8
-
重原子数:30
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.36
-
拓扑面积:59.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:4
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:N,Xn
-
安全说明:S26,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R36/38,R22,R50/53
-
WGK Germany:3
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2588
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
SDS
制备方法与用途
拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂具有触杀和胃毒作用,性质稳定且持效期长。对某些害虫的毒性甚至高于溴氰菊酯。
应用四溴菊酯广泛用于防治鞘翅目、同翅目及直翅目害虫,尤其适用于禾谷类、棉花、玉米、果树、烟草、蔬菜和水稻上的鳞翅目害虫。其推荐使用量为0.075~1.95g有效成分/100m²。
合成方法四溴菊酯可通过以下反应制备:
二溴菊酸与溴在20℃条件下加成,再经过氯化亚砜转化为四溴菊酰氯,并最终与α-氰基间苯氧基苯甲醇合成四溴菊酯。具体步骤可参见制备方法一、二和三。
毒性四溴菊酯对雄大鼠的急性经口LD₅₀为99.2mg/kg,雌大鼠为157.2mg/kg;兔急性经皮LD₅₀>2000mg/kg;大鼠急性吸入LC₅₀为0.286mg/kg(4小时)。对兔皮肤和眼睛有轻微刺激作用。长期试验结果显示,大鼠、小鼠和狗的每日无作用剂量分别为0.75mg/kg、3mg/kg 和1mg/kg。未发现四溴菊酯具有致畸性,也不影响生殖功能。致癌试验结果为阴性。对虹鳟鱼、蓝鳃鱼及水蚤的毒性较低,分别在LC₅₀ 0.0016mg/L(96小时)、0.0043mg/L(96小时)和38mg/L(48小时)。鹌鹑急性经口LD₅₀>2510mg/kg。蜜蜂接触LD₅₀为0.00012mg/只。
化学性质四溴菊酯为黄色至橘黄色树脂状物质,相对密度在20℃时约为1.7,蒸气压低(25℃下约为1.73×10⁻¹¹Pa),旋光度+21°~+27°(50g/L甲苯溶液)。该化合物可溶于丙酮、二甲苯、甲苯、二氯甲烷和二甲基亚砜等有机溶剂,在水中溶解度为70mg/L。在室温下,即使放置6个月也不会分解,并对光稳定无腐蚀性。
用途拟除虫菊酯类杀虫剂通过抑制离子通道关闭能力干扰调节钠离子流的离子通道,导致神经细胞产生过度兴奋最终死亡,从而达到杀死害虫的目的。
生产方法制备四溴菊酯的方法包括:
上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 溴氰菊酯 deltametrin 52918-63-5 C22H19Br2NO3 505.206
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:COLE, L. M.;CASIDA, J. E.;RUZO, L. O., J. AGR. AND FOOD CHEM., 1982, 30, N 5, 916-920摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Insecticidal resin coating film申请人:MITSUI TOATSU CHEMICALS, Inc.公开号:EP0257415A1公开(公告)日:1988-03-02An insecticidal resin coating film comprising a combination of an acrylonitrile and/or methacrylonitrile copolymer resin and an insecticidal component selected from the group consisting of specified compounds exhibits an insecticidal effect, since the compound is kept on the surface of the coating film in a state capable of exhibiting its insecticidal effect for a long period of time.
-
STABLE SOLID PESTICIDAL PREPARATION申请人:Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited公开号:EP0304492A1公开(公告)日:1989-03-01A stable solid pesticidal preparation which contains a benzyl ester type synthetic pyrethroid having a cyano group in α-position and an organophosphate compound as effective ingredients supported on a mineral carrier, with at least one weakly acidic salt of an alkali or alkaline earth metal being incorporated therein.
-
Sustained release pesticidal or plant growth regulating composition申请人:SUMITOMO CHEMICAL COMPANY, LIMITED公开号:EP0646314A1公开(公告)日:1995-04-05There are discolsed a pesticidal composition containing a water-insoluble alginate, which is prepared by treating a solid composition containing (a) a pesticidally active ingredient which is a pest-controlling active ingredient or a plant growth-regulating active ingredient and (b) an alginic acid or a water-soluble alginate with an aqueous solution containing a divalent or polyvalent cation which can convert said alginic acid or water-soluble alginate into a water-insoluble alginate. Also disclosed is a pesticidal composition containing a water-insoluble alginate, which is prepared by coating a solid substance containing the pesticidally active ingredient with a water-insoluble alginate. The composition of the invention has excellent sustained-release effects of the pesticidally active ingredient.
-
Residual control of parasites by long-acting shampoo formulations申请人:LABORATOIRES VIRBAC公开号:EP0714601A1公开(公告)日:1996-06-05The invention relates to shampoo compositions comprising a detergent and at least one active compound selected from juvenile hormone-like nitrogen containing heterocyclic compounds, other insect growth regulators such as methoprene or fenoxycarb, synthetic pyrethroids and mixtures thereof, wherein the dose of the active compound is sufficient for leaving on the haircoat of a warm-blooded animal after rinse out the shampoo an ovicidally and/or insecticidally and/or acaricidally residual effective amount against ectoparasites of said compound. Such shampoo compositions are useful for a residual control of ectoparasites on warm-blooded animals.
-
Dry pesticidal composition申请人:SUMITOMO CHEMICAL COMPANY, LIMITED公开号:EP0699389A2公开(公告)日:1996-03-06This invention relates to a dry pesticidal composition containing an active ingredient for controlling pests, a surfactant, a modified starch, a carbonate and a solid acid, wherein said constituents of said composition are combined together by means of a water-soluble polymer which is soluble in a volatile solvent. The composition has sufficient hardness and high solubility in water.
表征谱图
-
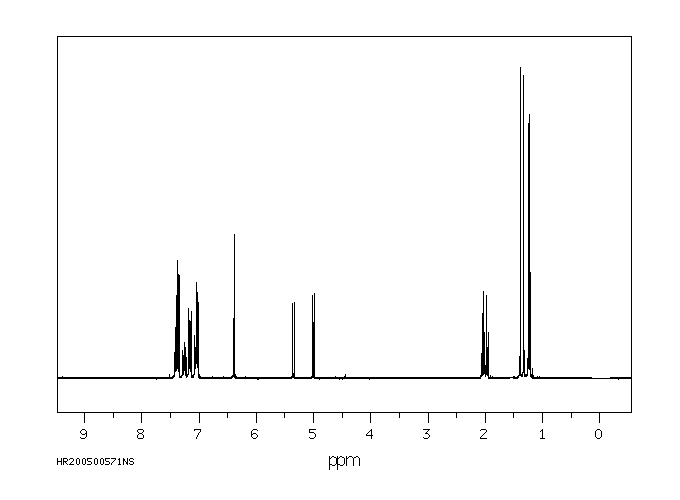
氢谱1HNMR
-
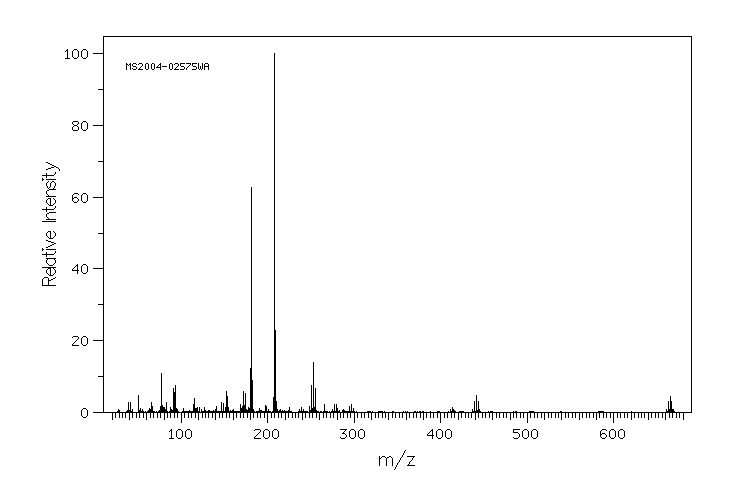
质谱MS
-
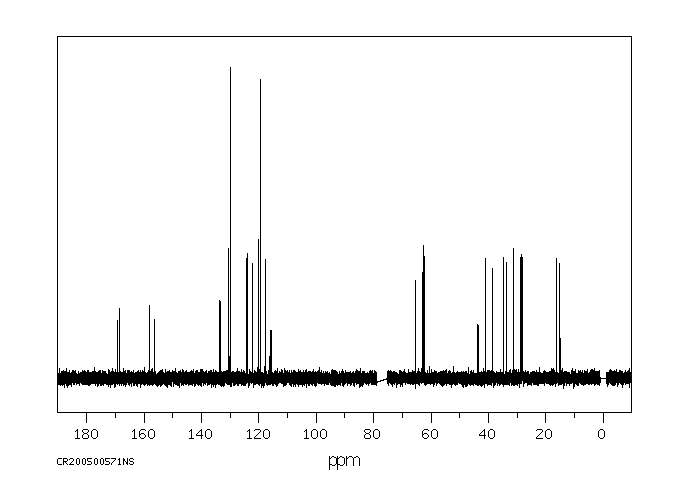
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息