1-isopropylpyrene | 78751-46-9
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
1-isopropylpyrene
英文别名
3-Isopropylpyren;Pyrene, 1-(1-methylethyl)-;1-propan-2-ylpyrene
CAS
78751-46-9
化学式
C19H16
mdl
——
分子量
244.336
InChiKey
NKYGXKGQZDYKBR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:396.7±9.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.152±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):6.2
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.16
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:1-isopropylpyrene 、 乙酸乙酯 以26%的产率得到参考文献:名称:BERG A.; LAM J.; HANSEN P. E., ACTA CHEM. SCAND., 40,(1986) N 8, 665-677摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Berg, Arne; Lam, Joergen; Hansen, Poul Erik, Acta chemica Scandinavica. Series B: Organic chemistry and biochemistry, 1986, vol. 40, # 8, p. 665 - 677摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
Fluorescence Enhancement of Pyrene Chromophores Induced by Alkyl Groups through σ–π Conjugation: Systematic Synthesis of Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary Alkylated Pyrenes at the 1, 3, 6, and 8 Positions and Their Photophysical Properties作者:Yosuke Niko、Susumu Kawauchi、Shun Otsu、Katsumi Tokumaru、Gen-ichi KonishiDOI:10.1021/jo400128c日期:2013.4.5We have systematically synthesized 1-, 3-, 6-, and 8-alkyl-substituted pyrene derivatives using the latest synthesis methods and investigated the effects of alkyl substitution on the photophysical properties of the pyrene chromophore. Like the trimethylsilyl group, which is known to enhance the fluorescence properties of some chromophores through sigma*-pi* conjugation, alkyl groups (primary, secondary, and tertiary) enhanced the fluorescence quantum yield of the pyrene chromophore through sigma-pi conjugation in most cases. While these enhancements in the fluorescence quantum yield were beyond expectations, the results were supported by absolute measurements. These results also indicate that ubiquitous alkyl groups can be used to tune the photophysical properties of the pyrene chromophore, as well as to improve the solubility or prevent aggregation. In other words, they can be used to develop new photofunctional materials.
-
Nitration of isopropylpyrenes. Strained models for protonation and transfer-nitration in the condensed phase作者:Kenneth Khosrow Laali、Tze Ming Liang、Poul Erik HansenDOI:10.1021/jo00035a022日期:1992.4Protic mono- and dinitration of 1,3,5,7,9-pentaisopropylpyrene (1) occurred at the available alpha positions to give 2 and 3. Despite steric crowding, 2 and 3 did not exhibit a torsional barrier to i-Pr rotation at ambient temperatures; however, buttressing of the peri i-Pr groups was evident (H-1 NMR, UV, and force field energy minimizations). Persistent (dihydroxyiminium)pyrenium dications 2a+2 and 3a+2 were formed by low temperature protonation of 2 and 3 with CF3SO3H (TfOH)/SO2 or with FSO3H/SO2. Intramolecular cyclization of the nitro group of 2a+2 gave the rearranged pyrenium ion 2c+. 1 reacted with NO2+BF4- in acetonitrile solvent to give two pyrenium ions stable at rt, viz. the Wheland intermediate of alpha-nitration 2b+2 and the (dihydroxyiminium)pyrenium dication 2a+2; the latter was also the predominant pyrenium ion formed in the reaction of 1 with NO+BF4- in acetonitrile. Reaction of 1 with NO2+BF4- in chloroform solvent gave alpha-nitration products and a persistent radical cation RC. The simultaneous presence of alpha-nitration products and a persistent pyrenium RC was also observed in the reaction of 1 with NO+BF4- in chloroform, where broader NMR line widths and a stronger ESR signal suggested more extensive oxidation. Protic and aprotic nitrations of 1,3,6,8-tetraisopropylpyrene (10) occurred at the alpha-beta positions; a minor addition product (26) was also found. A mixture of isomeric dinitropyrenes was obtained in NO2+ nitration of 1-isopropylpyrene (13). In line with low temperature protonation studies, aprotic nitrations of 2-isopropyl- and 4-isopropylpyrenes occurred predominantly at the alpha positions. The crowded pyrenium ion of 3 and 2 transfer nitrate to aromatics (toluene, mesitylene, benzene) under mild conditions in competition with a more facile transalkylation.
-
Mitra,A.; Ray,R.M., Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 1979, vol. 56, p. 907 - 910作者:Mitra,A.、Ray,R.M.DOI:——日期:——
-
Protonation and sulfinylation of isomeric isopropylpyrenes, 2,7-di-tert-butylpyrene, and tetracyclohexyl- and tetracyclopentylpyrenes: remarkably stable, sterically crowded pyrenium cations作者:Kenneth Khosrow Laali、Poul Erik HansenDOI:10.1021/jo00024a018日期:1991.111-Isopropyl- (1), 2-isopropyl- (2), 4-isopropyl- (3), 1,3,6,8-tetraisopropyl- (4), and 1,3,5,7,9-pentaisopropylpyrene (5), 2,7-di-tert-butylpyrene (6), and 1,3,5,8-tetracyclohexyl- (7) and 2,4,7,9-tetracyclopentylpyrene (8) in FSO3H or CF3SO3H (TfOH) in SO2 or SO2ClF solvent gave stable monopyrenium ions. In agreement with theory, exclusive alpha protonation occurred at low temperature (-75 --> -65-degrees-C) irrespective of the position of the substituents. The position of alpha-protonation is controlled by inductive stabilization of the alkyl (cycloalkyl) groups. Unlike hexahydropyrene which is diprotonated in FSO3H.SbF5 (1:1) Magic acid, with isopropylpyrenes stable dications could not be generated; in SO2 solvent the Wheland intermediates of sulfinylation were observed, whereas in SO2ClF solvent oxidation and monoprotonation were competitive. Charge distribution patterns in the sulfinylation sigma-complexes are similar to those of protonated pyrenium ions. Stable pyrenium cations deprotonate or desulfinylate on quenching without dealkylation or disproportionation. At higher temperatures (ca. -40-degrees-C), ipso-protonated 4 undergoes isomerization in FSO3H/SO2 solvent; other alkyl (cycloalkyl)pyrenium cations show no isomerization/disproportionation. Upon standing in Magic Acid, hexahydropyrene is oxidized to pyrene.
-
MITRA A.; RAY R. M., J. INDIAN CHEM. SOC., 1979, 56, NO 9, 907-910作者:MITRA A.、 RAY R. M.DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
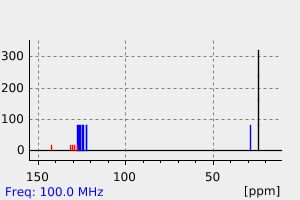
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-1,2-二(1-芘基)环丁烷
顺式-1,2-二(1-芘基)环丁烷
顺式-(-)-苯并(a)芘-7,8-二醇-9,10-环氧化物
雄甾烷
还原黑29
还原黄4
还原金橙G
还原绿2
还原绿1
还原紫3B
还原紫 10
还原深蓝BO
还原橙4
还原橙2
还原兰黑BBN
还原亮橙IRK
试剂N1,N1,N3,N3,N6,N6,N8,N8-Octakis(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3,6,8-pyrenetetramine
蒽酮紫79
蒽缔蒽酮
蒽并(1,2,3,4-ghi)苝
蒽嵌蒽
蒽[9,1,2-cde]苯并[rst]戊芬
萘并[2'.8',2.4]晕苯
萘并[2',1',8',7':4,10,5]蒽并[1,9,8-abcd]晕苯
萘并[1,8-gh:4,5-g'h']二喹啉
萘并(8,1,2-bcd)苝
萘并(2,3-a)晕苯
萘并(2,1,8-qra)萘并萘-7 12-二酮
萘并(1,2,3-mno)醋菲烯
萘[2,3-a]芘
菲并[1,10,9,8-opqra]苝
茚并(1,2,3-cd)芘
苯胺,2-氯-3-(苯基甲氧基)-
苯并[xyz]庚芬
苯并[wx]萘并[2,1,8,7-hijk]庚省
苯并[rst]菲并[1,10,9-cde]戊芬
苯并[rst]戊酚-5-甲醛
苯并[pqr]四苯-5-基甲酸根
苯并[pqr]四苯-11-基甲酸根
苯并[pqr]二萘并[8,1,2-bcd:2',1',8'-lmn]苝
苯并[p]萘并[1,8,7-ghi]屈
苯并[l]芘-8-醇
苯并[ghi]苝
苯并[e]芘
苯并[b]芘-6-基甲醇
苯并[b]芘-6,12-二酮
苯并[b]芘-3,6-二酮
苯并[b]芘-1,6-二酮
苯并[a]芘-9,10-环氧化物
苯并[a]芘-7-醇