苯线磷 | 22224-92-6
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
稳定性/保质期:
避免接触强氧化剂、强酸或强碱。对兔眼睛和皮肤没有明显的刺激性。动物实验未发现有致癌、致畸或致突变的作用。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.2
-
重原子数:19
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.538
-
拓扑面积:72.9
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
安全信息
-
储存条件:温度:0-6℃
制备方法与用途
乙醇与异丙胺与三氯氧磷连续反应制得乙基-异丙胺基磷酰氯,再与3-甲基-4-甲硫基苯酚反应而制得克线磷。本方法的关键是中间体3-甲基-4-甲硫基苯酚的合成,可由间甲酚与二甲二硫反应得到。
3-甲基-4-甲硫基苯酚的合成: 将200g混甲酚(含间甲酚65%)及145g二甲二硫(含量90%)投入反应瓶中,开动搅拌,用冰水浴将物料冷却至10℃。滴加95%硫酸136g,1h内滴完,控制温度在10-15℃,搅拌反应5小时后静置。分出废酸,加入15%碳酸钠溶液280ml,搅拌20min,再静置。分出水层,水洗,减压蒸除水和二甲二硫及未反应的混甲酚,得中间体。
O-乙基-N-异丙氨基磷酰氯的制备: 三氯氧磷与乙醇作用生成O-乙基磷酰二氯,再与异丙胺反应生成O-乙基-N-异丙氨基磷酰氯。
苯线磷的合成: 将O-乙基-N-异丙氨基磷酰氯与4-甲硫基-3-甲基苯酚在缚酸剂存在下合成苯线磷。
合成制备方法乙醇和异丙胺与三氯氧磷连续反应制得乙基-异丙胺基磷酰氯,再与3-甲基-4-甲硫基苯酚反应而制得克线磷。本方法的关键是中间体3-甲基-4-甲硫基苯酚的合成,可由间甲酚与二甲二硫反应得到。
3-甲基-4-甲硫基苯酚的合成: 将200g混甲酚(含间甲酚65%)及145g二甲基二硫(含量90%)投入反应瓶中,开动搅拌,用冰水浴将物料冷却至10℃。滴加95%硫酸136g,1h内滴完,控制温度在10-15℃,搅拌反应5小时后静置。分出废酸,加入15%Na2CO3溶液280mL,搅拌20min,再静置。分出水层,水洗,减压脱水和二甲二硫及未反应的混甲酚,制得3-甲基-4-甲硫基苯酚。
O-乙基-N-异丙氨基磷酰氯的制备: 三氯氧磷与乙醇作用生成O-乙基磷酰二氯,再与异丙胺反应生成O-乙基-N-异丙氨基磷酰氯。
苯线磷的合成: 将O-乙基-N-异丙氨基磷酰氯与4-甲硫基-3-甲基苯酚在缚酸剂存在下合成苯线磷。
用途简介苯线磷是一种高毒性、触杀性、内吸性的有机磷杀线虫剂,具有长残效期。药剂进入植物体内可上下传导,防治多种线虫,主要用于防治根瘤线虫、结节线虫和自由生活线虫,也可防治蚜虫、红蜘蛛等刺吸口器害虫。
- 防治花生、甜菜等作物线虫:使用10%颗粒剂300~600g/100m²撒施。
- 柑橘线虫:用450~750g/100m²撒施,也可沟施或穴施,药剂应施于作物根部附近土壤中。
- 防治马铃薯金线虫、结根线虫、自由习居线虫:使用75g有效成分/100m²撒施。
- 防治大豆根线虫、结根线虫等:用10~40g有效成分/100m²条施或40~60g有效成分撒施。
苯线磷是一种高毒性、触杀性、内吸性的有机磷杀线虫剂,具有长残效期。药剂进入植物体内可上下传导,防治多种线虫,主要用于防治根瘤线虫、结节线虫和自由生活线虫,也可防治蚜虫、红蜘蛛等刺吸口器害虫。对作物无害。例如,在防治花生、甜菜等作物的线虫时,可以使用10%颗粒剂300~600g/100m²撒施;在防治柑橘线虫时,则可使用450~750g/100m²撒施。药剂应在作物根部附近土壤中施用,并可根据具体情况采用沟施或穴施的方式。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:全氟顺式-2,3-二烷基恶唑烷酮在氨基磷酸酯,硫代磷酸酯和硫代磷酸酯农用化学品中的选择性硫氧化摘要:几个有机磷农药2A -g与硫醚,磷酰胺,硫代磷酰,和phosphorothionic功能用全氟反应顺式-2- Ñ丁基-3- Ñ -propyloxaziridine 1。硫化物的选择性氧化产生了亚砜衍生物3a- g,产率很高,而不会过度氧化成砜产物。亚砜3a-e在温和条件下进一步氧化为相应的砜4a-e。所有产品本身都是分析环境标准所感兴趣的,并且详细描述了其制备方法。DOI:10.1016/0040-4020(95)00413-3
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:全氟顺式-2,3-二烷基恶唑烷酮在氨基磷酸酯,硫代磷酸酯和硫代磷酸酯农用化学品中的选择性硫氧化摘要:几个有机磷农药2A -g与硫醚,磷酰胺,硫代磷酰,和phosphorothionic功能用全氟反应顺式-2- Ñ丁基-3- Ñ -propyloxaziridine 1。硫化物的选择性氧化产生了亚砜衍生物3a- g,产率很高,而不会过度氧化成砜产物。亚砜3a-e在温和条件下进一步氧化为相应的砜4a-e。所有产品本身都是分析环境标准所感兴趣的,并且详细描述了其制备方法。DOI:10.1016/0040-4020(95)00413-3
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
Thieno-pyrimidine compounds having fungicidal activity
表征谱图
-
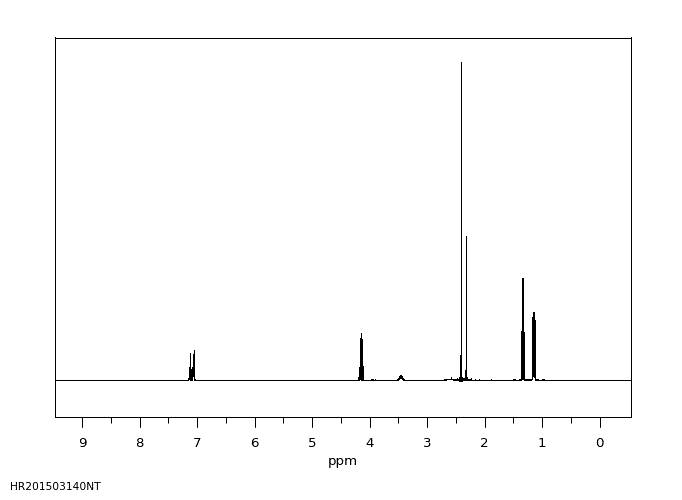
氢谱1HNMR
-
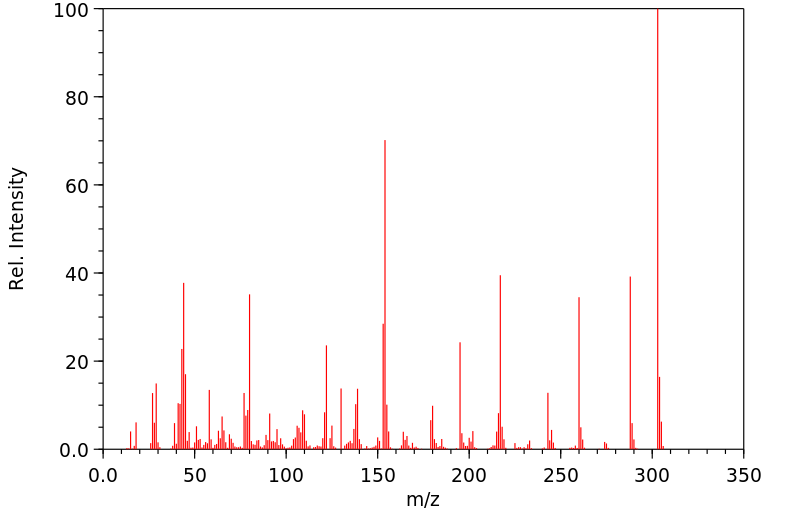
质谱MS
-
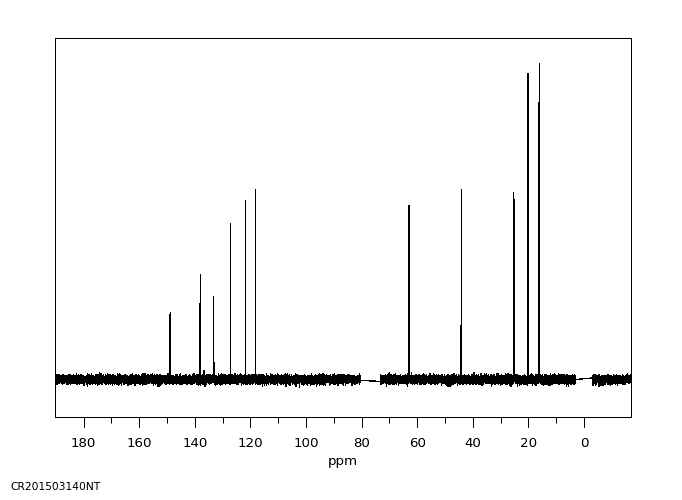
碳谱13CNMR
-
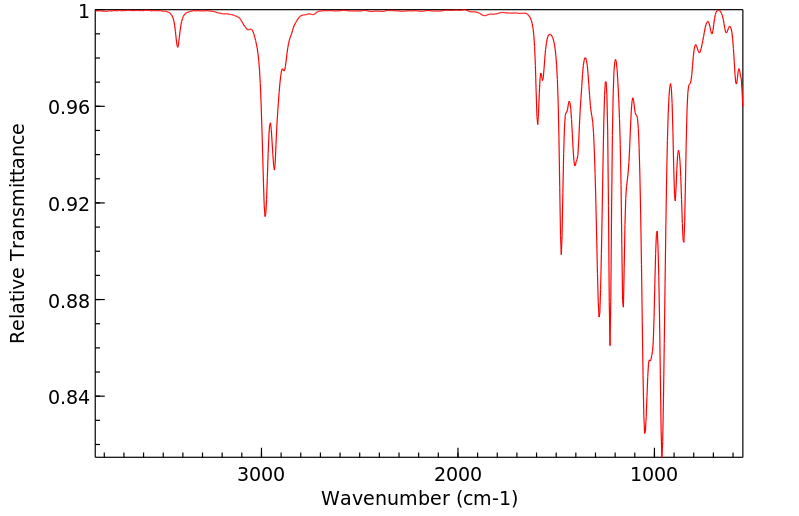
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息