甲萘威 | 63-25-2
中文名称
甲萘威
中文别名
1-萘基-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯;O-(1-萘基)-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯;;甲基氨基甲酸1-萘(基)酯;卡巴立;N-甲基氨基甲酸-1-萘酯;胺甲萘;西维因粉剂;虫卯酯;西维因;1-萘基-N-甲基氨基甲酸脂;O-(1-萘基)-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯;(1-萘基)-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯;西维因原粉(90%-95%)
英文名称
1-naphthalenol methylcarbamate
英文别名
Carbaryl;naphthalen-1-yl N-methylcarbamate
CAS
63-25-2
化学式
C12H11NO2
mdl
MFCD00021467
分子量
201.225
InChiKey
CVXBEEMKQHEXEN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:142-146 °C (lit.)
-
沸点:315°C
-
密度:d2020 1.232
-
闪点:202.7°C
-
溶解度:Moderately soluble in acetone, cyclohexanone, N,N-dimethylformamide (400–450 g/kg), and isophorone (Windholz et al., 1983; Worthing and Hance, 1991)
-
暴露限值:NIOSH REL: TWA 5 mg/m3, IDLH 100 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA 5 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 5 mg/m3.
-
物理描述:Carbaryl appears as a white crystalline solid. Insoluble in water. Combustible, although difficult to ignite. Toxic by inhalation (dust, etc.). Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless to light tan crystals
-
气味:... Odorless ...
-
蒸汽压力:1.36X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
自燃温度:Not flammable (USCG, 1999)
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/.
-
腐蚀性:Non-corrosive to metals, packaging materials, and application equipment
-
碰撞截面:150 Ų [M+H]+ [CCS Type: DT, Method: single field calibrated]
-
保留指数:1871;1856;1859.4;1863.8;1903.5;1859.3;1860.5;1848.4;1865;1915;1867.8
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.4
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.083
-
拓扑面积:38.3
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
Sevin, 标记有(14)C, 在昆虫、大鼠以及小鼠、大鼠和兔肝脏的微粒体预处理中,通过芳香族羟基化、N-甲基羟基化、氨基甲酰基团的 hydrolysis 和共轭作用而被代谢。
Sevin, labeled with (14)C, is metabolized in insects, in rat, and by microsomal prepn of mouse, rat & rabbit liver, by aromatic hydroxylation, n-methyl hydroxylation, hydrolysis of carbamyl grouping, & by conjugation.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在畜产品中确定的代谢物中,有五种被认为是重要的……:卡巴立尔;5,6-二氢-5,6-二羟基卡巴立尔;以及5-甲氧基-6-羟基卡巴立尔,以及所有可以在酸性条件下水解为卡巴立尔、5,6-二氢-5,6-二羟基卡巴立尔或5-甲氧基-6-羟基卡巴立尔的残留物。美国环保局(EPA)将这些化合物纳入了卡巴立尔的饮食风险评估中,并在仅对畜产品进行卡巴立尔耐受性重新评估时考虑了它们。
Of the metabolites identified in livestock commodities, five are considered significant ... : carbaryl; 5,6-dihydro-5,6-dihydroxy carbaryl; and 5-methoxy-6-hydroxy carbaryl and all residues which can be hydrolyzed to carbaryl, 5,6-dihydro-5,6-dihydroxy carbaryl, or 5-methoxy-6-hydroxy carbaryl under acidic conditions. The /EPA/ included these compounds in the dietary risk assessment for carbaryl, and in the reassessment of carbaryl tolerances for livestock commodities only.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
单次口服给药对大鼠进行了甲萘威的给药。在提取尿液后,通过柱层析和薄层色谱法,初步鉴定出了1,5-萘二酚,含量较小的甲萘威,5-羟基甲萘威,以及微量的N-羟甲基甲萘威。一个主要代谢物被鉴定为5,6-二氢-5,6-二羟基甲萘威,以自由形式(剂量的1.4%)和葡萄糖苷酸形式(剂量的10.5%)存在。还观察到了萘基葡萄糖苷酸和硫酸盐。
Single oral dose of carbaryl was admin to rats. After extraction of ... urine, column & TLC chromotography, tentative identification was made for 1,5-naphthalenediol with small amt of carbaryl, 5-hydroxycarbaryl, & trace of n-hydroxymethylcarbaryl was also present. A major metab ... identified as 5,6-dihydro-5,6-dihydroxycarbaryl, was found free (1.4% of the dose) & as the glucuronide (10.5% of the dose). Naphthyl glucuronide & sulfate were also observed.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
在大鼠尿液中,除了1-萘酚外,还观察到了1-萘基甲基氨基甲酸酯N-葡萄糖苷酸、1-萘基甲基亚氨基碳酸酯O-葡萄糖苷酸、4-(甲基氨基甲酰氧基)-1-萘基葡萄糖苷酸、1-萘基葡萄糖苷酸、1-萘基硫酸盐、4-(甲基氨基甲酰氧基)-1-萘基硫酸盐、3种未识别的化合物以及被认为是1-萘基N-羟甲基氨基甲酸酯的化合物。在豚鼠中也观察到了类似的结果。
In urine of rats in addn to 1-naphthol, 1-naphthyl methylcarbamate N-glucuronide, 1-naphthyl methylimido-carbonate O-glucuronide, 4-(methylcarbamoyloxy)-1-naphthyl glucuronide, 1-naphthyl glucuronide, 1-naphthyl sulfate, 4-(methylcarbamoyloxy)-1-naphthyl sulfate, 3 unidentified cmpd & cmpd believed to be 1-naphthyl N-hydroxymethylcarbamate were observed. Similar results were observed with guinea pigs.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
Carbaryl has known human metabolites that include 4-hydroxycarbaryl, 5-hydroxycarbaryl, and carbaryl methylol.
来源:NORMAN Suspect List Exchange
毒理性
食物代表了一般人群摄入甲萘威的主要来源。一般人群在家庭和娱乐区域的害虫控制操作中可能会暴露于甲萘威。工人在甲萘威的生产、配方、包装、运输、储存以及在应用前后可能会暴露于甲萘威。如果防护措施不足,工业和农业工人的皮肤可能会有显著暴露。甲萘威在肺和消化道中被迅速吸收。甲萘威的主要代谢途径是环羟基化和水解。因此,形成了许多代谢物,并与水溶性硫酸盐、葡萄糖醛酸苷和巯基尿酸结合,通过尿液排出。水解导致1-萘酚、二氧化碳和甲基胺的形成。羟基化产生4-羟基甲萘威、5-羟基甲萘威、N-羟甲基甲萘威、5-6-二氢-5-6-二羟基甲萘威和1,4-萘二醇。人类的主要代谢物是1-萘酚。在正常暴露条件下,甲萘威在动物体内的积累是不太可能的。甲萘威主要通过尿液排出,因为其水解产物1-萘酚主要被解毒为水溶性结合物。甲萘威代谢物在肠道和肝脏之间的循环也很显著,尤其是在口服给药后。甲萘威代谢物也存在于吸收剂量的唾液和牛奶中的一小部分。鸟类的急性毒性较低。甲萘威对蜜蜂和蚯蚓非常有毒。急性毒性根据物种、配方和载体而有很大差异。甲萘威是一种轻微的眼睛刺激物,几乎没有或没有致敏潜力。甲萘威的累积潜力较低。已经证明甲萘威对多种物种的哺乳动物繁殖和围产期发育有不利影响。对繁殖的影响包括生育能力下降、窝产仔数减少和出生后存活率降低。发育毒性表现为子宫内死亡增加、胎儿体重减轻和畸形的发生。除少数研究外,所有不良的生殖和发育效应仅在引起明显母体毒性的剂量下观察到,而且在许多情况下,母体动物对甲萘威的敏感性高于胎儿。母体毒效应包括致死性、生长减少和难产。现有证据表明甲萘威不具有任何DNA损伤性质。在大量的细菌基因突变测试中得到了阴性结果。现有数据库不支持甲萘威对人类遗传变化风险的假设。甲萘威在大鼠和小鼠身上的致癌潜力已经进行了许多研究。其中大部分研究的结果是阴性的。甲萘威对神经系统的影响主要是与胆碱酯酶抑制有关,通常是短暂的。甲萘威据报道影响凝血。甲萘威结合游离血氨基酸。据报道,在哺乳动物的碳水化合物代谢、蛋白质合成和肝脏解毒功能中出现了干扰。甲萘威是肝脏微粒体药物代谢活性的弱诱导剂。据报道,甲萘威增加了大鼠垂体促性腺激素的功能。甲萘威是胆碱酯酶活性的抑制剂。这种效应与剂量有关,并且可以迅速逆转。所有识别的甲萘威代谢物作为胆碱酯酶抑制剂的活性明显低于甲萘威本身。甲萘威通过吸入和口服途径在人类中很容易被吸收,通过皮肤途径吸收较少。由于胆碱酯酶的抑制是甲萘威作用的主要机制,中毒的临床表现主要是由症状主导,如:支气管分泌增加、过度出汗、流涎和流泪;瞳孔缩小、支气管收缩、腹部绞痛(呕吐和腹泻);心动过缓;细小肌肉的震颤(在严重情况下,横膈膜和呼吸肌也参与);心动过速;头痛、眩晕、焦虑、精神混乱、抽搐和昏迷;以及呼吸中枢的抑制。中毒症状在吸收后迅速出现,在暴露结束后迅速消失。在职业过度暴露于甲萘威的情况下,轻度症状在吸收危险剂量之前就已经观察到,这就是为什么甲萘威职业中毒的严重病例很少见。在农业应用中,皮肤暴露可能扮演重要角色。已经描述了在意外溅到甲萘威配方后出现皮疹的情况。甲萘威暴露的最敏感的生物指标是尿液中出现1-萘酚和血液中胆碱酯酶活性的下降。由于甲萘威的蒸汽压低、快速降解、被抑制的胆碱酯酶快速自发恢复,以及症状通常在危险剂量积累在体内之前出现,因此甲萘威对人类的风险被认为是低的。
Food represents the major source of carbaryl intake for the general population. ... The general population can be exposed to carbaryl during pest control operations in both the home & recreation areas. Workers can be exposed to carbaryl during its manufacture, formulation, packing, transportation, storage, & during & after application. ... Significant dermal exposure may occur in industrial & agricultural workers if protective measures are inadequate. Carbaryl is rapidly absorbed in the lungs & digestive tract. ... The principal metabolic pathways of carbaryl are ring hydroxylation & hydrolysis. As a result, numerous metabolites are formed & subjected to conjugation with the formation of water-soluble sulfates, glucuronides, & mercapturates, excreted in the urine. Hydrolysis results in the formation of 1-naphthol, carbon dioxide & methylamine. Hydroxylation produces 4-hydroxycarbaryl, 5-hydroxycarbaryl, N-hydroxymethylcarbaryl, 5-6-dihydro-5-6-dihydroxycarbaryl & 1,4-naphthalendiol. The principal metabolite in humans is 1-naphthol. Under normal exposure conditions, the accumulation of carbaryl in animals is unlikely. Carbaryl is excreted primarily via the urine, since the product of its hydrolysis, 1-naphthol, is mainly detoxified to water-soluble conjugates. Enterohepatic cycling of carbaryl metabolites is also considerable, especially after oral administration. ... Carbaryl metabolites are also present in a small percentage of the absorbed doses in saliva & milk. ... The acute toxicity for birds is low. ... Carbaryl is very toxic for honey-bees & earthworms. ... The acute toxicity ... varies considerably according to species, formulation & vehicle. ... Carbaryl is a mild eye irritant & has little or no sensitizing potential. ... Carbaryl has a low cumulative potential. Carbaryl has been shown to affect mammalian reproduction & perinatal development adversely in a number of species. Effects on reproduction include impairment of fertility, decreased litter size, & reduced postnatal viability. Developmental toxicity is seen as increased in utero death, reduced fetal weight, & the occurrence of malformation. With the exception of a small number of studies, all adverse reproductive & developmental effects were noted only at doses that caused overt maternal toxicity, &, in a number of cases, the maternal animal was more sensitive to carbaryl than the conceptus. The maternal toxic effects included lethality, decreased growth, & dystocia. ...The available evidence indicates that carbaryl does not have any DNA-damaging properties. ... Negative results were obtained in tests for gene mutations in a large number of bacterial assays ... The available database does not support the presumption that carbaryl poses a risk of inducing genetic changes in ... humans. Carbaryl has been studied for its carcinogenic potential in numerous studies on rats & mice. The results of most of these studies were negative ... The effects of carbaryl on the nervous system are primarily related to cholinesterase inhibition & are usually transitory. ... Carbaryl has been reported to affect coagulation ... Carbaryl binds free blood amino acids. Disturbances have been reported in the carbohydrate metabolism & protein synthesis & detoxification function of the liver in mammals. Carbaryl is a weak inducer of hepatic microsomal drug-metabolizing activity. ... Carbaryl has been reported to incr the gonadotropic function of the hypophysis of rats. Carbaryl is an inhibitor of cholinesterase activity. This effect is dose-related & quickly reversible. ... All identified metabolites of carbaryl are appreciably less active cholinesterase inhibitors than carbaryl itself. Carbaryl is easily absorbed /in humans/ through inhalation & via the oral route & less readily by the dermal route. Since the inhibition of cholinesterase is the principal mechanism of carbaryl action, the clinical picture of intoxication is dominated by ... symptoms, such as: increased bronchial secretion, excessive sweating, salivation, & lacrimation; pinpoint pupils, bronchoconstriction, abdominal cramps (vomiting & diarrhea); bradycardia; fasciculation of fine muscles (in severe cases, diaphragm & respiratory muscles also involved); tachycardia; headache, dizziness, anxiety, mental confusion, convulsions, & coma; & depression of the respiratory center. Signs of intoxication develop quickly after absorption & disappear rapidly after exposure ends.... In cases of occupational overexposure to carbaryl, mild symptoms are observed long before a dangerous dose is absorbed, which is why severe cases of occupational intoxication with carbaryl are rare. During agricultural application, dermal exposure may play an important role. ... The appearance of a skin rash after accidental splashing with carbaryl formulations has been described. ... The most sensitive biological indicator of carbaryl exposure is the appearance of 1-naphthol in the urine & the decr of cholinesterase activity in the blood. ... The hazards of carbaryl for human beings are judged to be low, because of its low vapor pressure, rapid degradation , rapid spontaneous recovery of inhibited cholinesterase, & the fact that symptoms usually appear well before a dangerous dose has accumulated in the body. ...
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
卡巴立尔是一种胆碱酯酶或乙酰胆碱酯酶(AChE)抑制剂。碳酰胺通过使酶的活性部位碳酰胺化,与胆碱酯酶形成不稳定的络合物。这种抑制作用是可逆的。胆碱酯酶抑制剂抑制乙酰胆碱酯酶的作用。由于其基本功能,干扰乙酰胆碱酯酶作用的化学物质是强效的神经毒素,即使在低剂量下也会导致过度流涎和流泪。在更高水平的暴露下,头痛、流涎、恶心、呕吐、腹痛和腹泻常常很明显。乙酰胆碱酯酶分解神经递质乙酰胆碱,后者在神经和肌肉接头处释放,以便让肌肉或器官放松。乙酰胆碱酯酶抑制的结果是乙酰胆碱积聚并继续发挥作用,使得任何神经冲动持续传递,肌肉收缩不会停止。
Carbaril is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. Carbamates form unstable complexes with chlolinesterases by carbamoylation of the active sites of the enzymes. This inhibition is reversible. A cholinesterase inhibitor suppresses the action of acetylcholine esterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholine esterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses. Headache, salivation, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diarrhea are often prominent at higher levels of exposure. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop.
来源:Toxin and Toxin Target Database (T3DB)
毒理性
癌症分类:可能对人类致癌
Cancer Classification: Likely to be Carcinogenic to Humans
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A4;不可归类为人类致癌物。
A4; Not classifiable as a human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌物:卡巴立尔
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:Carbaryl
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
进行了一项体外皮肤渗透研究,同时使用了大鼠和人类的皮肤。这项研究表明,大鼠皮肤对 carbaryl(甲萘威)的渗透性是人类皮肤的2.8倍。
An in vitro dermal penetration study was conducted using both rat and human skin . This study showed that rat skin was 2.8 times more permeable to carbaryl than human skin.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
分泌--在大鼠腹腔注射给药后48小时研究了对不同位置标记的西维因的保留情况。65%的碳基-(14)C-西维因以尿液形式排出,25%通过呼出气体排出,2%通过粪便排出,还有10%被保留……(14)C的最高水平出现在肝脏、肾脏、心脏和细胞(红细胞和白细胞)中。58%的N-甲基-(14)C-西维因以尿液形式排出,12%通过呼出气体排出,4%通过粪便排出,还有13%被保留……(14)C在肝脏、肾脏、心脏、肺和脾脏中的含量最高,这些器官具有高血流。77%的萘基-(14)C-西维因以尿液形式排出,9%通过粪便排出,还有7%被保留……组织中(14)C的水平在肾脏、脾脏、骨骼和脂肪中最高……大约50%的(14)C在4小时内被排出……。
Excretion--retention of ... carbaryl labeled in 3 different positions ... studied 48 hr after ip admin to rats. 65% of (14)C of carbonyl-(14)C-carbaryl was excreted in urine, 25% in expired air, 2% in feces, & 10% was retained ... highest levels of (14)C were present in liver, kidneys, heart, & corpuscles (erythrocytes & leukocytes). 58% of (14)C of n-methyl-(14)C-carbaryl was excreted in urine, 12% in expired air, 4% in feces, & 13% was retained ... (14)C was maximal in liver, kidneys, heart, lungs, & spleen, organs with high blood flow. 77% of (14)C of naphthyl-(14)C-carbaryl was excreted in urine, 9% in feces, & 7% was retained ... levels of (14)C in tissue were highest in kidneys, spleen, bone, & fat ... about 50% of (14)C had been excreted in 4 hr ... .
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
Of oral dose of (1-naphthyl-1-(14)C)-N-methylcarbamate given to rats, 53% & 82% were absorbed after 20 min & 1 hr, respectively. Carbaryl is absorbed very rapidly from lung, 2.5 times faster than from small intestine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
(14)C-carbaryl labeled in n-methyl group has been found in fetuses of pregnant rats, & mice. ... Autoradiographic study of (14)C-methyl-carbaryl in pregnant rat has shown that radiolabel was localized in eye, liver, & brain of fetus.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
职业暴露等级:B
-
职业暴露限值:TWA: 5 mg/m3
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
立即威胁生命和健康浓度:100 mg/m3
-
危险品标志:Xn,F,N
-
安全说明:S2,S22,S24,S36/37,S46,S60,S61,S62
-
危险类别码:R67,R38,R40,R43,R22,R20/22,R50/53,R11,R50,R65,R20
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2922499916
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2811 6.1/PG 3
-
RTECS号:FC5950000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
储存条件:本品应密封存放在阴凉干燥处,并在运输过程中避免与碱性物质接触。
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 西维因粉剂;1-萘基-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯 |
| 化学品英文名称: | Sevin powder;1-Naphthyl-N-methyl carbamate |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 63-25-2 |
| 分子式: | C 12 H 11 NO 2 |
| 分子量: | 201.22 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | ||||||
| 化学品名称:西维因粉剂;1-萘基-N-甲基氨基甲酸酯 | ||||||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | 第6.1类 毒害品 |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 主要是抑制胆碱酯酶,使乙酰胆碱在组织中蓄积。主要症状为流涎、恶心、流泪、瞳孔缩小、视力模糊、痉挛等。其抑制胆碱酯酶的作用持续时间较短,停止接触后,胆碱酯酶恢复较快。 |
| 环境危害: | |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品可燃,有毒。 |
| 危险特性: | 5.12 遇明火、高热易引起燃烧。 |
| 5.71 受热分解放出有毒气体。 | |
| 5.108 有毒,遇明火能燃烧。 | |
| 危险性概述: | A198 有毒、可燃 |
| 安全措施: | B04 远离热源、火种,贮于阴凉通风处 |
| B09 贮于阴凉、通风、干燥处 | |
| B51 应与氧化剂、碱类、食用化学品分储 | |
| B77 眼睛接触,用流动清水彻底冲洗 | |
| B82 误食,饮水,催吐,洗胃,导泄,就医 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 立即脱去污染的衣着,用肥皂水及流动清水彻底冲洗污染的皮肤、头发、指甲等。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 立即提起眼睑,用流动清水冲洗10分钟或用2%碳酸氢钠溶液冲洗。 |
| 吸入: | 迅速脱离现场至空气新鲜处。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 饮足量温水,催吐。洗胃,导泄。就医。。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。与强氧化剂可发生反应。受热分解放出有毒的氧化氮烟气。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化氮。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 雾状水、泡沫、二氧化碳、砂土。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | 消防人员须佩戴防毒面具、穿全身消防服,在上风向灭火。 |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | 无资料 |
| 自燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | 无资料 |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,建议应急处理人员戴好防毒面具,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,避免扬尘,用清洁的铲子收集于干燥净洁有盖的容器中,运至废物处理场所。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,提供充分的局部排风。操作尽可能机械化、自动化。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴自吸过滤式防尘口罩,戴化学安全防护眼镜,穿防毒物渗透工作服,戴乳胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与氧化剂、碱类接触。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风的库房。远离火种、热源。应与氧化剂、碱类、食用化学品分开存放,切忌混储。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中国MAC:未制定标准苏联MAC:1mg/m3美国TWA:ACGIH 5mg/m3美国S |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 严加密闭,提供充分的局部排风。尽可能机械化、自动化。提供安全淋浴和洗眼设备。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 生产操作或农业使用时,佩带防毒口罩。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,应该佩带自给式呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿相应的防护服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防护手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,彻底清洗。工作服不要带到非作业场所,单独存放被毒物污染的衣服, |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 白色结晶,工业品略带灰色或粉红色。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 145 |
| 沸点(℃): | 无资料 |
| 相对密度(水=1): | 1.23 |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | 无资料 |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | 无资料 |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | 无资料 |
| 闪点(℃): | 无资料 |
| 引燃温度(℃): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | 无资料 |
| 分子式: | C 12 H 11 NO 2 |
| 分子量: | 201.22 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 不溶于水,溶于乙醇、苯、丙酮等多数有机溶剂。 |
| 主要用途: | 用作杀虫剂。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、强碱。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氧化氮。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | 属中等毒类 LD50:250~560mg/kg(大鼠经口);4000mg/kg(大鼠经皮) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 根据国家和地方有关法规的要求处置。或与厂商或制造商联系,确定处置方法。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | 61888 |
| UN编号: | 2757 |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | Ⅲ |
| 包装方法: | 塑料袋或二层牛皮纸袋外全开口或中开口钢桶;两层塑料袋或一层塑料袋外麻袋、塑料编织袋、乳胶布袋;塑料袋外复合塑料编织袋(聚丙烯三合一袋、聚乙烯三合一袋、聚丙烯二合一袋、聚乙烯二合一袋);塑料袋或二层牛皮纸袋外普通木箱;螺纹口玻璃瓶、塑料瓶、复合塑料瓶或铝瓶外普通木箱;塑料瓶、两层塑料袋或两层牛皮纸袋(内或外套以塑料袋)外瓦楞纸箱。 |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、通风仓间内。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。保持容器密封。应与氧化剂、碱类、食用化工原料分开存放。不可混储混运。搬运时要轻装轻卸,防止包装及容器损坏。分装和搬运作业要注意个人防护。 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 2 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
化学性质
纯品为白色结晶,熔点(m.p.)145℃,相对密度1.232(20℃),蒸气压在25℃时为0.666 Pa。溶解度如下:二甲基甲酰胺>45%,丙酮>20%,环己酮>20%,甲乙酮>15%,氯仿>10%,乙醇>5%,甲苯>1%,水40mg/L(30℃)。对光和热较为稳定,遇碱性物质会迅速分解失效。对金属无腐蚀作用。
用途西维因是一种高效、低毒、低残留且具有长残效的广谱氨基甲酸酯类杀虫剂。它不仅有强烈的触杀作用,还有一定的胃毒作用和微弱的内吸作用。适用于防治棉铃虫、卷叶虫、棉蚜、造桥虫、蓟马和稻叶蝉、稻纵卷叶螟、稻苞虫、稻蓟马及多种果树害虫,也可用于防治菜园蜗牛、蛞蝓等软体动物。常用剂量为2.6~20g/100 m²。
用途该产品还适用于防治稻飞虱、叶蝉、蓟马、豆蚜、大豆食心虫、棉铃虫及多种果树害虫、林业害虫,如松毛虫等。
用途作为氨基甲酸酯类杀虫剂的一种,西维因具有高效和低毒的特点。适用于多种作物的害虫防治,通常在农业上应用广泛。急性毒性方面,口服-大鼠LD50为590毫克/公斤;皮肤接触-兔LD50为2000毫克/公斤。
爆炸物危险特性所装容器密闭时遇火可爆炸。
可燃性危险特性燃烧时会产生有毒的氮氧化物气体。
储运特性需存放在通风、低温和干燥的地方,避免与氧化剂、碱类及食品添加剂接触存放。
灭火方法 职业健康标准短时间暴露限值(STEL)为10毫克/立方米;时间加权平均浓度(TWA)为5毫克/立方米。
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 氯甲酸-1-萘酯 1-naphthyl chloroformate 3759-61-3 C11H7ClO2 206.628 氯甲基萘-1-基碳酸酯 Chloromethyl naphthalen-1-yl carbonate 132905-86-3 C12H9ClO3 236.655 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 N-(羟基甲基)甲萘威 Carbaryl methylol 5266-96-6 C12H11NO3 217.224 萘-2-基N-甲基氨基甲酸酯 naphthalen-2-yl methylcarbamate 4089-04-7 C12H11NO2 201.225
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:基于新型PAN @ Ru @ PEI @ Nafion纳米纤维垫的超灵敏自增强电化学发光传感器。摘要:在本工作中,首次通过简单地电纺聚丙烯腈(PAN),Ru(bpy)32+,聚(乙烯亚胺)(PEI)和Nafion的混合物,首次制备了一种新型的自增强电致发光(ECL)复合材料。定义为PAN @ Ru @ PEI @ Nafion纳米纤维垫(PAN @ Ru @ PEI @ Nafionnfm)。在此,Ru(bpy)32+被用作ECL试剂,并且由于其骨架中的叔胺基团丰富,因此选择PEI作为共反应物。为了进一步提高Ru(bpy)32 + -PEI系统的ECL效率,我们通过一步电纺技术将Ru(bpy)32+和PEI创新地同时加载到PAN纳米纤维中。结果,它们之间的电子传输距离大大缩短了。同时,借助带正电的Ru(bpy)32+或PEI与带负电的Nafion之间的静电相互作用,有效避免了PAN纳米纤维毡中Ru(bpy)32+和PEI的剥落。如预期的那样,发光纳米纤维表现出优异的ECL性能,包括高效率和DOI:10.1039/c9tb02287b
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Patonay, Tamas; Patonay-Peli, Erzsebet; Mogyorodi, Ferenc, Synthetic Communications, 1990, vol. 20, # 18, p. 2865 - 2885摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Preparation of carbamates摘要:卡巴酯可以在无酸清除剂的情况下通过醇、光气和胺的反应一步制备。公开号:US04272441A1
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
Thieno-pyrimidine compounds having fungicidal activity
表征谱图
-
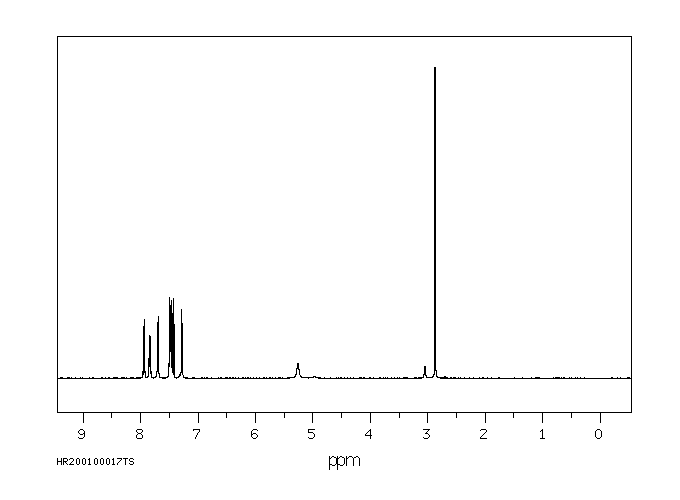
氢谱1HNMR
-
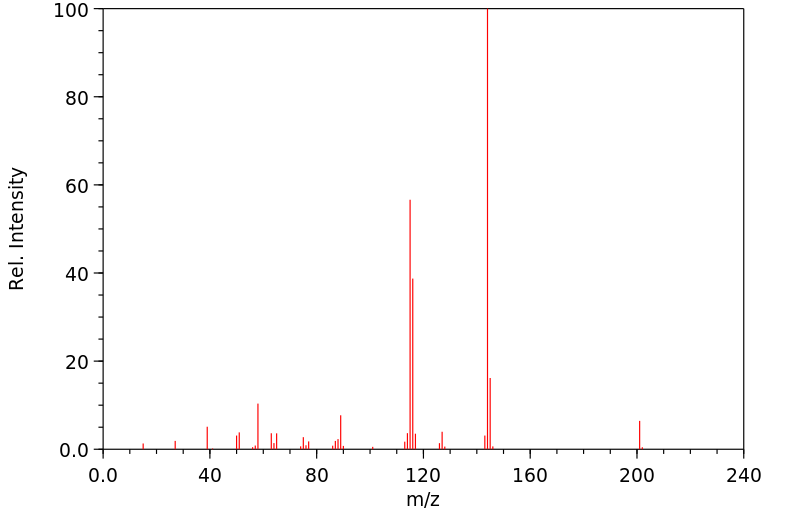
质谱MS
-
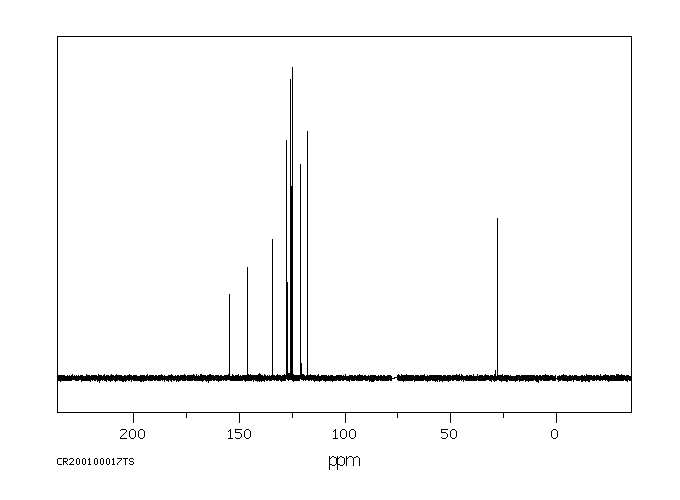
碳谱13CNMR
-
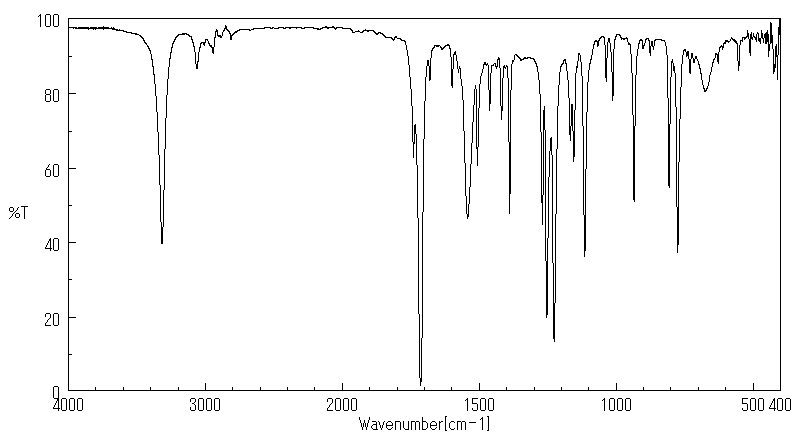
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮