沙林 | 107-44-8
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.8
-
重原子数:8
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:26.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
安全信息
-
储存条件:库房应保持低温、通风和干燥,并与食品原料分开存放。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Measurement of gas phase reactions using automated headspace gaschromatography摘要:DOI:10.1007/bf00811273
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Lorquet; Vassart, Bulletin des Societes Chimiques Belges, 1959, vol. 68, p. 336,338,341.摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:(E)-pyrene-1-carbaldehyde O-tert-butyldimethylsilyl oxime 在 四丁基氟化铵 、 沙林 作用下, 以 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 0.18h, 以99%的产率得到1-芘甲腈参考文献:名称:Detection of Chemical Warfare Nerve Agents via a Beckmann Fragmentation of Aldoxime摘要:A new (E)-pyrene-1-carbaldehyde O-tert-butyldimethylsilyl oxime 3 was synthesized for the detection of chemical warfare nerve agents, O-isopropyl methylphosphonofluoridate (GB) and O-pinacolyl methylphosphonofluoridate (GD). H-1 NMR spectrum showed that the tert-butyldimethylsilyl (TBDMS) group was deprotected using TBAF and the oximate supernucleophile was made. Upon addition of chemical warfare agents (GB and GD) (50 mol%), the reaction was completely finished within 5 min and also the color change of reaction mixture was observed under a hand-held UV lamp with the naked eye.DOI:10.1080/10426507.2011.636110
文献信息
-
Hydrolysis of toxic organophosphorus compounds by o-iodosobenzoic acid and its derivatives作者:Philip S. Hammond、Jeffry S. Forster、Claire N. Lieske、H. Dupont DurstDOI:10.1021/ja00202a029日期:1989.9Hydrolyse des esters trimethyl-1,2,2 propyle et isopropyle de l'acide methyl phosphonofluoridique (soman et sarin respectivement), du N,N-dimethyl phosphoramidocyanidate d'ethyle (tabum) et du (diethyl nitro-4 phenyl) phosphate dans des solutions aqueuses micellaires de chlorure de (palmityl trimethyl) ammonium, en presence d'acide iodosyl-«2» benzoique
-
Synthesis and analysis of phosphorylated nonapeptide adducts by LC/Q-TOF MS作者:Yu Huilan、Dong Junjun、Hu Zhen、Pei Chengxin、Liu Shilei、Xiang YuDOI:10.1080/10426507.2015.1035378日期:2016.1.2GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT Abstract A new method for the synthesis of organophosphorylated adducts of the nonapeptide FGESAGAAS is presented. The adducts were obtained by using sarin (GB) or soman (GD) as the organophosphorylating reagents and cesium carbonate as the acid scavenger. Greater than 50% of the peptide was modified on serine 4. MS/MS spectra acquired on an Agilent 6520 quadrupole time of flight
-
Reversed Enantioselectivity of Diisopropyl Fluorophosphatase against Organophosphorus Nerve Agents by Rational Design作者:Marco Melzer、Julian C.-H. Chen、Anne Heidenreich、Jürgen Gäb、Marianne Koller、Kai Kehe、Marc-Michael BlumDOI:10.1021/ja905444g日期:2009.12.2which leads to slower detoxification despite rapid hydrolysis. Enzyme engineering efforts based on rational design yielded two quadruple enzyme mutants with reversed enantioselectivity and overall enhanced activity against tested nerve agents. The reversed stereochemical preference is explained through modeling studies and the crystal structures of the two mutants. Using the engineered mutants in combination来自 Loligo vulgaris 的二异丙基氟磷酸酶 (DFPase) 是一种高效且稳定的生物催化剂,可用于水解一系列剧毒有机磷化合物,包括神经毒剂沙林、梭曼和环沙林。与底物氟代磷酸二异丙酯 (DFP) 相比,神经毒剂具有不对称的磷原子,这导致成对的对映异构体表现出明显不同的毒性。野生型 DFPase 更喜欢底物的毒性较小的立体异构体,尽管水解速度较快,但解毒速度较慢。基于合理设计的酶工程工作产生了两个四重酶突变体,它们具有反向对映选择性和对测试神经毒剂的整体增强活性。通过建模研究和两个突变体的晶体结构来解释反向立体化学偏好。将工程突变体与野生型 DFPase 结合使用可显着增强活性和解毒能力,这对于个人净化尤为重要。我们的发现也可能与结构相关的人类对氧磷酶 (PON) 相关,PON 作为一种潜在的体内催化清除剂在有机磷中毒的情况下具有相当大的意义。
-
Inhibition of Plasma Cholinesterase by O-Alkylfluorophosphonates作者:Jiří Cabal、Jiří Kassa、Jiří PatočkaDOI:10.1135/cccc19970521日期:——
Inhibition of plasma cholinesterase by three methylfluorophosphonates (MFF), sarin, soman and cyclosin, and by the products of their hydrolysis and alcoholysis was examined. Inhibition by phosphonic acids and by methyl esters derived from MFF was purely competitive while that by MFF was irreversible. The rate of phosphorylation of cholinesterase by MFF differs, depending on the structure of the alkoxy group in the MFF and decreases in the sequence soman-sarin-cyclosin. The affinity values of MFF, phosphonic acids and methyl esters of phosphonic acid for cholinesterase are comparable. The
in vitro kinetic parameters suggest that plasma cholinesterase might act as a natural detoxicating agent in cases of poisoning with the above inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. -
Group 13 chelates in nerve gas agent and pesticide dealkylation作者:Amitabha Mitra、David A. Atwood、Jeffrey Struss、Daniel J. Williams、Bradley J. McKinney、William R. Creasy、David J. McGarvey、H. Dupont Durst、Roderick FryDOI:10.1039/b717041f日期:——Schiff base boron and aluminium bromides have been used to cleave organophosphate nerve agents and pesticides and their simulants: salben(tBu)[BBr2]2 was very effective in cleaving the VX simulants EMPPT and DEPPT and nerve agent VX; salen(tBu)AlBr was effective in cleaving the nerve agents VX and Soman and the pesticideDiazinon.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
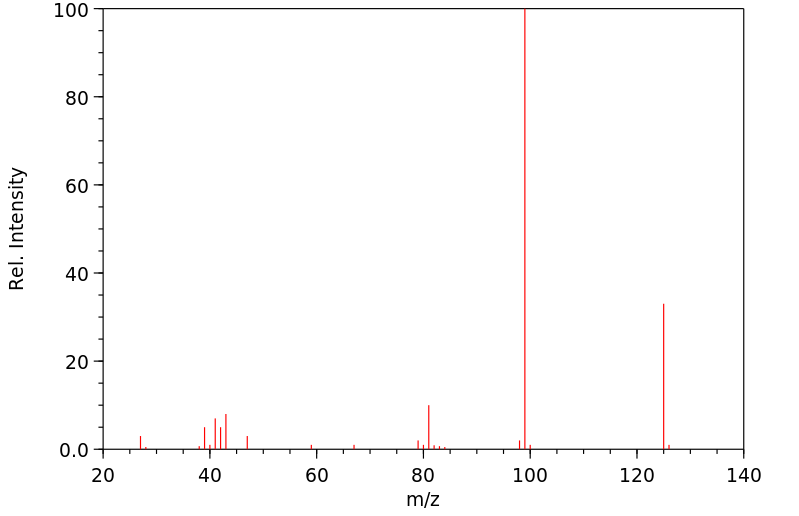
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息