一氧化二氮 | 97485-25-1
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
物理描述:Nitrous oxide, refrigerated liquid appears as a colorless liquid. Density 1.22 g / cm3 at its boiling point of -89°C. Boils to give a colorless gas that is sweet-smelling and moderately toxic. The gas has narcotic effects when inhaled (laughing gas). Shipped under refrigeration. Vapor pressure is at about 745 psig at 70°F. Used to freeze foods and to manufacture other chemicals.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless gas [Note: Shipped as a liquified compressed gas]
-
气味:Slightly sweetish
-
味道:Slightly sweetish
-
沸点:-88.46 °C
-
熔点:-90.81 °C
-
溶解度:At 20 °C and 2 atm one liter of the gas dissolves in 1.5 liters of water
-
密度:1.266 at -128.2 °F (USCG, 1999)
-
蒸汽密度:1.53 (Air = 1) (gas)
-
蒸汽压力:4.29X10+4 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
稳定性/保质期:
Stable under recommended storage conditions.
-
分解:This compound decomposes explosively at high temperatures.
-
粘度:0.0145 cP at 25 °C at 101.325 KPa (gas)
-
汽化热:16.54 kJ/mol at -88.48 °C
-
表面张力:1.75 dynes/cm at 20 °C in contact with vapor
-
电离电位:12.89 eV
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.000516 at 0 °C/D, 1 atmosphere, 0.5893 um
-
保留指数:182;182
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0.5
-
重原子数:3
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:19.1
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:2.2
制备方法与用途
制备方法
- 1.热解法 加热硝酸铵或加热无水硝酸钠与硫酸铵的混合物,生成的气体经精制、压缩、冷却、干燥、液化等工序,制得一氧化二氮成品。 2.催化氧化法 氨与空气在催化剂存在条件下发生催化氧化反应,生成的气体经精制得到粗一氧化二氮气体。该气体经压缩、高压水洗,再经压缩、干燥、液化工序,制得液体一氧化二氮产品。 3.市场上可以买到麻醉用一氧化二氮。实验室常用热分解NH4NO3制得。将纯硝酸铵放在烘箱中烘至160~170℃,令其完全脱水后,放入干燥器中凝固。将它研细装入带有支管的圆底烧瓶中。烧瓶颈上缠绕加热线圈,不让分解反应中生成的水冷凝回到熔融的反应物里。烧瓶支管接上一冰冷阱,使生成的水大部分冷凝下来。将烧瓶放在铁丝网上小心地加热,反应在170℃开始,温度不可超过250℃,以防止分解为N2和NO的反应发生。因为这是放热反应,应避免加热过急和反应物的量过多,否则有可能变成爆炸反应。生成的N2O用50%的KOH溶液洗涤。若有必要,微量的氧气可用连二亚硫酸盐的碱性溶液除去。 4.以纯度为95%~97%的一氧化二氮为原料,经常温吸附和低温下数次间歇抽空,可制得纯度达99.998%的高纯一氧化二氮产品。采用硝酸铵加热分解法可制取粗一氧化二氮,易分离和净化,再经提纯可得到高纯产品。反应式如下。
合成制备方法
1.热解法 加热硝酸铵或加热无水硝酸钠与硫酸铵的混合物,生成的气体经精制、压缩、冷却、干燥、液化等工序,制得一氧化二氮成品。
2.催化氧化法 氨与空气在催化剂存在条件下发生催化氧化反应,生成的气体经精制得到粗一氧化二氮气体。该气体经压缩、高压水洗,再经压缩、干燥、液化工序,制得液体一氧化二氮产品。
3.市场上可以买到麻醉用一氧化二氮。实验室常用热分解NH4NO3制得。将纯硝酸铵放在烘箱中烘至160~170℃,令其完全脱水后,放入干燥器中凝固。将它研细装入带有支管的圆底烧瓶中。烧瓶颈上缠绕加热线圈,不让分解反应中生成的水冷凝回到熔融的反应物里。烧瓶支管接上一冰冷阱,使生成的水大部分冷凝下来。将烧瓶放在铁丝网上小心地加热,反应在170℃开始,温度不可超过250℃,以防止分解为N2和NO的反应发生。因为这是放热反应,应避免加热过急和反应物的量过多,否则有可能变成爆炸反应。生成的N2O用50%的KOH溶液洗涤。若有必要,微量的氧气可用连二亚硫酸盐的碱性溶液除去。
4.以纯度为95%~97%的一氧化二氮为原料,经常温吸附和低温下数次间歇抽空,可制得纯度达99.998%的高纯一氧化二氮产品。采用硝酸铵加热分解法可制取粗一氧化二氮,易分离和净化,再经提纯可得到高纯产品。反应式如下。
用途简介
- 1.超临界溶剂。单独或与氧气混合用作牙科、外科和妇产科的麻醉剂。也可用作防腐剂、制冷剂、助燃剂、烟雾喷射剂。食品工业作为发泡剂和食品的密封剂。电子工业用于二氧化硅的化学气相沉积等离子工艺。军火工业用作推进剂。还可用于气密性检查、原子吸收光谱的载体等。检漏剂、制冷剂,以及用作原子吸收光谱用的助燃剂。 2.本产品用作医用麻醉剂、制冷剂、助燃剂、防腐剂、烟雾喷射剂、标准气和平衡气等,也用于半导体制造中的乳化CVD工序及气相淀积氮化硅的氮源。还可作为原子吸收光谱的氧化气体。 3.用于电子工业中二氧化硅的化学气相淀积等离子工艺。 4.用作医药麻醉剂、防腐剂,以及用于气密性检查。
用途
1.超临界溶剂。单独或与氧气混合用作牙科、外科和妇产科的麻醉剂。也可用作防腐剂、制冷剂、助燃剂、烟雾喷射剂。食品工业作为发泡剂和食品的密封剂。电子工业用于二氧化硅的化学气相沉积等离子工艺。军火工业用作推进剂。还可用于气密性检查、原子吸收光谱的载体等。检漏剂、制冷剂,以及用作原子吸收光谱用的助燃剂。
2.本产品用作医用麻醉剂、制冷剂、助燃剂、防腐剂、烟雾喷射剂、标准气和平衡气等,也用于半导体制造中的乳化CVD工序及气相淀积氮化硅的氮源。还可作为原子吸收光谱的氧化气体。
3.用于电子工业中二氧化硅的化学气相淀积等离子工艺。
4.用作医药麻醉剂、防腐剂,以及用于气密性检查。 [17]
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Fe-MCM-41和Fe-ZSM-5的室温,N 2 O转化为吸附式NO的化学计量转换摘要:一氧化二氮(N 2 O)在室温和低压(> 10 -5 mbar)下与Fe-MCM-41和Fe-ZSM-5中的Fe(II)物种相互作用,形成吸附的一氧化氮。吸附的产物通过其特性但在这两种材料上的N = O拉伸频率不同而鉴定,并且还通过在T > 420 K下解吸后的化学发光分析来鉴定。提出了N 2 O分解的另一产物是氮。该分解在热力学上是有利的,这不仅是由于所形成的被吸附的NO的吸附热。直到T > 770 K时,才可能发生催化N 2 O分解,形成氮和氧,这可能是通过不同的机理引起的。DOI:10.1006/jcat.2000.3005
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:REMARKABLE CATALYTIC ACTIVITY OF THERMALLY MODIFIED CoTPP SUPPORTED ON TiO2FOR NO-CO REACTION摘要:在250°C下经过真空预处理的精细TiO2-120s支撑的CoTPP表现出卓越的活性,即在100°C下用CO还原NO时,活性达到每摩尔钴每分钟2.2摩尔NO。预处理改变了CoTPP的结构,使其在苯中不溶,但在喹啉中仍可溶解。这种活性被认为源自热改性的二聚体CoTPP形式,该形式失去了大部分与适度脱水载体更良好相互作用的苯基。DOI:10.1246/cl.1984.217
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:环糊精封装 (NHC)Cu-FeCp(CO)2 配合物中金属-金属键合的超分子扰动摘要:尽管二次配位层对催化活性位点的影响已被广泛认识,但这种相互作用对(异)双核活性位点的影响尚未得到全面研究。在这里,详细分析了环糊精封装对 (NHC)Cu-FeCp(CO) 2 部分的影响,已知该部分在多种转化中具有催化活性。与游离的 (NHC)CuFp 配合物 (Fp = FeCp(CO) 2 ) 相比,根据穆斯堡尔 (Mössbauer) 的理论,封装的 (NHC)CuFp 配合物被发现从类似 Fe(0) 转变为具有 Fe(II) 特征和红外光谱。根据 DFT 建模,电子结构的这种变化与 Fp 片段远离平面方向的金字塔化以及 (NHC)CuFp 复合物中常见的半桥 CO 相互作用的破坏相关。后一种变化部分归因于反静电 C-H·Cu 抑制相互作用的存在,由于几何限制,这种相互作用胜过半桥联的 Cu·CO 相互作用。这些综合因素导致其中一种 CO 配体产生类似 Fe(II) 的取代反应性,而DOI:10.1021/acs.organomet.4c00105
文献信息
-
Onium ions. 34. The methoxydiazonium ion: preparation, proton, carbon-13, and nitrogen-15 NMR and IR structural studies, theoretical calculations, and reaction with aromatics. Attempted preparation and the intermediacy of the hydroxydiazonium ion作者:George A. Olah、Rainer. Herges、Khosrow. Laali、Gerald A. SegalDOI:10.1021/ja00268a054日期:1986.4Nitrous oxide is methylated with CH/sub 3/F ..-->.. SbF/sub 5/F/sub 2/ or with CH/sub 3/O/sup +/SOClF in SO/sub 2/ClF to give the stable methoxydiazonium ion CH/sub 3/ON/sub 2//sup +/ (1), which was characterized by NMR (/sup 15/N, /sup 13/C, /sup 1/H) and FT IR spectroscopic studies. It is stable below -30 /sup 0/C, above which it decomposes, regenerating N/sub 2/O. When reacted with aromatics, such一氧化二氮用 CH/sub 3/F ..-->.. SbF/sub 5/F/sub 2/ 或用 CH/sub 3/O/sup +/SOClF 在 SO/sub 2/ClF 中甲基化得到稳定的甲氧基重氮离子 CH/sub 3/ON/sub 2//sup +/ (1),通过 NMR (/sup 15/N, /sup 13/C, /sup 1/H) 和 FT IR 光谱表征学习。它在低于 -30 /sup 0/C 时稳定,高于此温度会分解,再生 N/sub 2/O。当与芳烃(如甲苯)反应时,1 仅产生甲基化产物,不形成甲氧基衍生物。光谱和化学数据表明,中间体形式 CH/sub 3/ON=N/sup +/ 是 1. 考虑计算的电荷分布(4-31 G 与全几何优化和 4-31 G*) 也支持这个结论。还通过甲基偶氮氧基三氟甲磺酸酯的溶剂分解和甲氧基胺与 NO/sup +/BF/sub 4//sup -/
-
Selenols are resistant to irreversible modification by HNO作者:Christopher L. Bianco、Cathy D. Moore、Jon M. Fukuto、John P. ToscanoDOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2016.07.008日期:2016.10to be additional potential targets of HNO. Indeed, as determined in the current work, selenols are targeted by HNO. Such reactions appear to result only in formation of diselenide products, which can be easily reverted back to the free selenol. This characteristic is distinct from the reaction of HNO with thiols/thiolproteins. These findings suggest that, unlike thiolproteins, selenoproteins are resistant
-
Investigation of the silicon beading phenomena during zone‐melting recrystallization作者:Z. A. Weinberg、V. R. Deline、T. O. Sedgwick、S. A. Cohen、C. F. Aliotta、G. J. Clark、W. A. LanfordDOI:10.1063/1.94242日期:1983.12.15During recrystallization of encapsulated silicon films on SiO2, by the graphite strip heater technique, the silicon sometimes breaks apart and agglomerates into small beads or stripes. By secondary ion mass spectroscopy analysis, it was found that a high concentration of nitrogen at the interface between the silicon and the top SiO2 capping layer is needed to prevent this from occurring. Incorporation
-
Effect of Oxidants on the Oxidative Coupling of Methane over a Lead Oxide Catalyst作者:Kenji Asami、Tsutomu Shikada、Kaoru FujimotoDOI:10.1246/bcsj.64.266日期:1991.1Oxidative coupling of methane was studied over a PbO/MgO catalyst using a variety of oxidants such as N2O, NO, CO2, and SO2. While N2O showed both high activity and selectivity for the title reaction, NO produced CO2, exclusively. The coupling reaction was assumed to proceed via the redox cycle of Pb and PbO on each oxidant mentioned above. Carbon dioxide produced small amounts of C2 hydrocarbons and使用各种氧化剂(如 N2O、NO、CO2 和 SO2)在 PbO/MgO 催化剂上研究了甲烷的氧化偶联。虽然 对标题反应显示出高活性和选择性,但 NO 仅产生 。假设偶联反应通过 Pb 和 PbO 在上述每种氧化剂上的氧化还原循环进行。二氧化碳产生少量的 C2 碳氢化合物和 CO,而 SO2 对反应没有活性。氧气、 、 可以氧化 PbO/MgO 与甲烷在 1023 K 下反应形成的 Pb/MgO。这样制备的 PbO/MgO 可以从甲烷中生成 C2 烃。即使在 CH4-NO 共进料反应中没有产生 C2 烃的 NO,也将 Pb/MgO 转化为 PbO/MgO,而 PbO/MgO 仅在与 反应时产生 C2 烃。NO似乎氧化甲基自由基,它是与 偶联反应的中间体。SO2 作为氧化剂的无效性归因于 PbS 的形成,而 PbS 在甲烷活化中是无活性的。
-
Group 8 and 10 hyponitrite and dinitrosyl complexes作者:Navamoney Arulsamy、D. Scott Bohle、Jerome A. Imonigie、Raecca C. MooreDOI:10.1016/j.poly.2007.05.009日期:2007.10(PPh3)2M(NO)2. The structures of Ru(dppf)(NO)2 and Os(dppe)(NO)2 have been determined. These two analogous families of cis-hyponitrite and dinitrosyl complexes illustrate the balance of metal dn electron count and nitrosyl redox state with one having linear nitrosyls bound to low valent metal centers, and the former having coupled N 2 O 2 2 - ligands bound to a higher oxidation state metal center.先前已证明,通过用钠-(-处理相应的LnMCl2衍生物很容易制得二价10号金属的顺式-半锂盐络合物LnM(N2O2)(M = Ni,Pt; Ln = PPh3,PPh2Me,dppe和dppf)。 Z)-1- 4-(2,6-二叔丁基-4-甲氧基环己二壬基)}重氮-1-1,2-二醇酸酯。这些络合物采用具有氧结合的螯合平面顺-亚硝酸盐配体的抗磁性正方形平面几何形状。它们易于在室温下制备,但在90°C以上会热分解并释放出一氧化二氮。亲电子试剂(例如碘,三氟甲磺酸甲酯和盐酸)也与顺-亚锂盐配合物迅速反应,生成一氧化二氮。这些先前制备的配合物之一(PPh3)2Pt( )的结构已在-100°C下重新确定为二氯甲烷溶剂化物,具有更高的精密度。相关的四面体第8组二亚硝酰基配合物(PPh3)2M(NO)2(M = Ru,Os; Ln = PPh3,dppe和dppf)已被重新检查,并通过在相应的配体
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
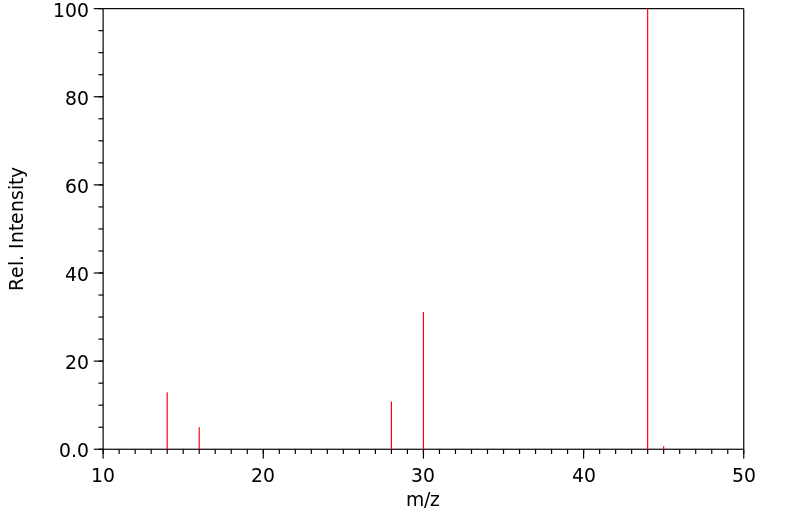
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
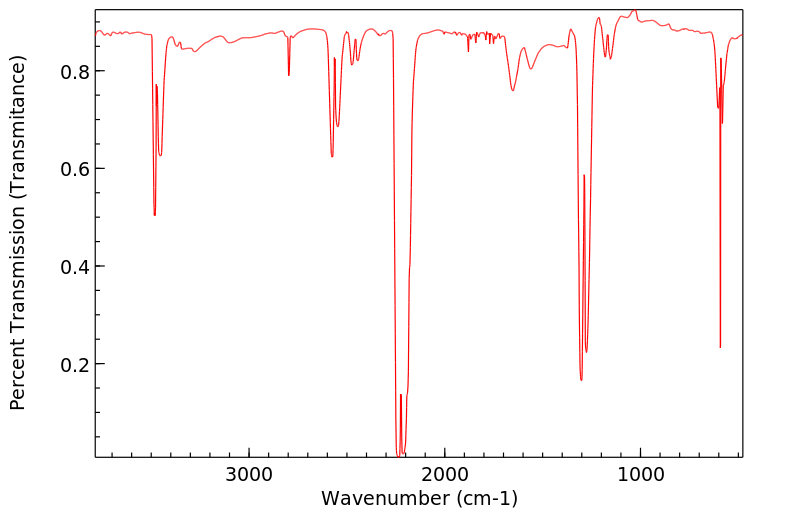
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息