啶嘧磺隆 | 104040-78-0
中文名称
啶嘧磺隆
中文别名
啶嘧黄隆;1-(4,6-二甲氧基嘧啶-2-基)-3-(3-三氟甲基-2-吡啶磺酰)脲;嘧啶磺隆
英文名称
flazasulfuron
英文别名
1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-(3-trifluoromethyl-2-pyridylsulfonyl)urea;N-[[(4,6-dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)amino]carbonyl]-3-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridine-sulfonamide;N-[(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)aminocarbonyl]-3-trifluoromethylpyridine-2-sulfonamide;1-(4,6-dimethoxypyrimidin-2-yl)-3-[3-(trifluoromethyl)pyridin-2-yl]sulfonylurea
CAS
104040-78-0
化学式
C13H12F3N5O5S
mdl
MFCD00274594
分子量
407.33
InChiKey
HWATZEJQIXKWQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:164-166°
-
密度:1.5594 (estimate)
-
颜色/状态:White, crystalline solid
-
气味:Odorless
-
溶解度:Solubility at 20 °C (w/w%): Acetone 1.2%; toluene 0.06%; at 25 °C (w/v%): acetic acid 0.67%
-
蒸汽压力:1.81X10-10 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下保持稳定,应避免与强氧化剂接触。
-
分解:When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of /sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides and F-/.
-
解离常数:pKa = 4.37
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2
-
重原子数:27
-
可旋转键数:5
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.23
-
拓扑面积:141
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:11
ADMET
代谢
一系列研究被进行以评估(14)C-SL-160(P)/flazasulfuron/在不同性别的大鼠(CRL: CD BR VAF/Plus)群体中的吸收、分布、代谢和排泄。在这些研究中,(14)C-SL-160(P)(CP-1385; 55.8 mCi/mMole; 放射性纯度报告为97.29%、97.5%、98.49%、99.2%和>98%)通过口服灌胃的方式给药,剂量为2或50 mg/kg或2 mg/kg。在/一项研究/中,大鼠在口服(14)C-SL-160(P)的第15天之前,已经连续14天接受非标记SL-160(Y-920205; 98.9%纯度)的口服灌胃剂量。在单次和重复剂量研究中,母体化合物是尿液(雄性:19-40%;雌性:51-67%的给药剂量)中的代谢物轮廓的主要成分,粪便中(雄性和雌性:2-5%的给药剂量)和胆汁中(雄性和雌性:0.6-2%的给药剂量)的量较少。在这些基质中,包括母体化合物在内,共检测到多达11个馏分。最常见的代谢物(以给药剂量的百分比表示)是HDTG+TPPG(在尿液中大约占6.5-12%,在粪便中大约占0.4-2%,在胆汁中大约占6.5-14%),其次是DTPU(N-(4,6-二甲氧基-2-嘧啶基)-N-[3-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶基]脲)、HDPU、6-甲氧基-2-[[3-(三氟甲基)-2-吡啶基]氨基]-4-嘧啶醇、TPSA(3-三氟甲基)-2-吡啶磺酰胺)和MTMG,含量较少(<5%)。单独来看,未识别的馏分在尿液和胆汁代谢物轮廓中通常占给药剂量的不到2%。粪便代谢物轮廓中有高达35%的未识别馏分。
A series of studies were conducted to evaluate the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of (14)C-SL-160(P)/flazasulfuron/ in groups of 4 or 5 rats (CRL: CD BR VAF/Plus)/sex. In these studies, (14)C-SL-160(P) (CP-1385; 55.8 mCi/mMole; radiolabel purity variously reported as 97.29%, 97.5%. 98.49%., 99.2% and >98%) was administered orally by gavage at doses of 2 or 50 mg/kg or 2 mg/kg . In /one study/, rats had received daily oral gavage doses of nonlabeled SL-160 (Y-920205; 98.9% purity) for 14 days, prior to oral dosing with (14)C-SL-160(P) on Day 15. In the single and repeated dose studies, parent compound was the primary component in the metabolite profiles for urine (males: 19-40%; females: 51-67% of administered dose), with lesser amounts in feces (males and females: 2-5% of administered dose), and bile (males and females: 0.6-2% of administered dose). Including parent compound up to 11 fractions were detected among these matrices. The most prevalent metabolite (expressed as percent of administered dose) were HDTG+TPPG (approximately 6.5-12% in urine, approximately 0.4-2% in feces, and approximately 6.5-14% in bile), with minor amounts < 5%) of DTPU (N-(4,6-Dimethoxy-2-pyrimidinyl)-N-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]urea), HDPU, 6-Methoxy-2-[[3-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinyl]amino]-4-pyrimidinol, TPSA (3-Trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridinesulfonamide), and MTMG. Individually, unidentified fractions generally accounted for less than 2% of the administered dose in the urine and biliary metabolite profile. The fecal metabolite profile had up to 35% unidentified of the recovered dose.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 立即急救:确保已经进行了充分的中毒物清除。如果患者停止呼吸,开始人工呼吸,最好使用需求阀复苏器、袋阀面罩装置或口袋面罩,按训练操作。如有必要,执行心肺复苏。立即用缓慢流动的水冲洗受污染的眼睛。不要催吐。如果发生呕吐,让患者前倾或置于左侧(如果可能的话,头部向下)以保持呼吸道畅通,防止吸入。保持患者安静,维持正常体温。寻求医疗帮助。 /毒物A和B/
/SRP:/ Immediate first aid: Ensure that adequate decontamination has been carried out. If patient is not breathing, start artificial respiration, preferably with a demand valve resuscitator, bag-valve-mask device, or pocket mask, as trained. Perform CPR if necessary. Immediately flush contaminated eyes with gently flowing water. Do not induce vomiting. If vomiting occurs, lean patient forward or place on the left side (head-down position, if possible) to maintain an open airway and prevent aspiration. Keep patient quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Obtain medical attention. /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 基本治疗:建立专利气道(如有需要,使用口咽或鼻咽气道)。如有必要,进行吸痰。观察呼吸不足的迹象,如有需要,辅助通气。通过非循环呼吸面罩以10至15升/分钟的速度给予氧气。监测肺水肿,如有必要,进行治疗……。监测休克,如有必要,进行治疗……。预防癫痫发作,如有必要,进行治疗……。对于眼睛污染,立即用水冲洗眼睛。在运输过程中,用0.9%的生理盐水(NS)持续冲洗每只眼睛……。不要使用催吐剂。对于摄入,如果患者能吞咽、有强烈的干呕反射且不流口水,则用温水冲洗口腔,并给予5毫升/千克,最多200毫升的水进行稀释……。在去污后,用干燥的无菌敷料覆盖皮肤烧伤……。/毒药A和B/
/SRP:/ Basic treatment: Establish a patent airway (oropharyngeal or nasopharyngeal airway, if needed). Suction if necessary. Watch for signs of respiratory insufficiency and assist ventilations if needed. Administer oxygen by nonrebreather mask at 10 to 15 L/min. Monitor for pulmonary edema and treat if necessary ... . Monitor for shock and treat if necessary ... . Anticipate seizures and treat if necessary ... . For eye contamination, flush eyes immediately with water. Irrigate each eye continuously with 0.9% saline (NS) during transport ... . Do not use emetics. For ingestion, rinse mouth and administer 5 mL/kg up to 200 mL of water for dilution if the patient can swallow, has a strong gag reflex, and does not drool ... . Cover skin burns with dry sterile dressings after decontamination ... . /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
/SRP:/ 高级治疗:对于无意识、严重肺水肿或严重呼吸困难的病人,考虑进行口咽或鼻咽气管插管以控制气道。使用气囊面罩装置的正压通气技术可能有益。考虑使用药物治疗肺水肿……。对于严重的支气管痉挛,考虑给予β激动剂,如沙丁胺醇……。监测心率和必要时治疗心律失常……。开始静脉输注D5W /SRP: "保持开放",最低流量/。如果出现低血容量的迹象,使用0.9%生理盐水(NS)或乳酸林格氏液。对于伴有低血容量迹象的低血压,谨慎给予液体。注意液体过载的迹象……。使用地西泮或劳拉西泮治疗癫痫……。使用丙美卡因氢氯化物协助眼部冲洗……。 /Poisons A and B/
/SRP:/ Advanced treatment: Consider orotracheal or nasotracheal intubation for airway control in the patient who is unconscious, has severe pulmonary edema, or is in severe respiratory distress. Positive-pressure ventilation techniques with a bag valve mask device may be beneficial. Consider drug therapy for pulmonary edema ... . Consider administering a beta agonist such as albuterol for severe bronchospasm ... . Monitor cardiac rhythm and treat arrhythmias as necessary ... . Start IV administration of D5W /SRP: "To keep open", minimal flow rate/. Use 0.9% saline (NS) or lactated Ringer's if signs of hypovolemia are present. For hypotension with signs of hypovolemia, administer fluid cautiously. Watch for signs of fluid overload ... . Treat seizures with diazepam or lorazepam ... . Use proparacaine hydrochloride to assist eye irrigation ... . /Poisons A and B/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
实验室动物:急性暴露/研究类型:兔急性皮肤刺激性;结果:在涂抹部位未观察到红斑、水肿或皮肤效应。
/LABORATORY ANIMALS: Acute Exposure/ Study Type: Acute dermal irritation (rabbit); Results: No erythema, edema, or dermal effects observed at application site.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
实验室动物:急性暴露/研究类型:兔急性眼刺激;结果:48小时内出现最小程度的结膜炎。72小时后恢复正常。
/LABORATORY ANIMALS: Acute Exposure/ Study Type: Acute eye irriation (rabbit); Results: Minimal conjunctivitis through 48 hours. Free by 72 hours.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
迅速且广泛吸收(90%),广泛分布并在7天内几乎完全排泄(高达90%),主要在尿液中。
Rapidly and extensively absorbed(90%), widely distributed and almost completely excreted (up to 90%) within 7 days, mainly in urine.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
一系列研究被进行以评估(14)C-SL-160(P)/flazasulfuron/在不同性别的大鼠(CRL: CD BR VAF/Plus)群体中的吸收、分布、代谢和排泄。在这些研究中,(14)C-SL-160(P)(CP-1385; 55.8 mCi/mMole; 放射性纯度报告为97.29%、97.5%、98.49%、99.2%和>98%)通过口服灌胃给药,剂量为2或50 mg/kg或2 mg/kg。在一项研究中,大鼠在口服(14)C-SL-160(P)之前,连续14天每天口服非标记的SL-160(Y-920205; 98.9%纯度)... 不同剂量水平之间或单次与重复剂量给药之间通常没有差异,但在雄性和雌性之间有差异。研究表明,在单次口服2或50 mg/kg剂量后,14C SL-160(P)迅速被吸收。在暴露后48小时,雄性和雌性分别吸收了低剂量的94%和93%,高剂量的86%和93%。在跟踪低剂量和高剂量动物至168小时时,观察到类似的模式,单次与重复暴露之间几乎没有差异。通过尿液排泄是主要的排泄途径,在低剂量和高剂量以及单次和重复剂量给药后,雄性和雌性分别占74-80%和90-94%。时间过程数据显示,暴露后48-72小时内,尿液中大部分放射性物质被排泄。粪便为次要排泄途径,在低剂量和高剂量以及单次和重复剂量给药后,雄性和雌性分别占21-24%和9-10%。胆汁排泄研究确定,在低剂量雄性和雌性以及高剂量雌性中,大约9.5%的给药剂量在48小时内出现在胆汁中,高剂量雄性中大约为16.5%。组织分布研究表明,14C-SL-160(P)迅速从系统中排出,在给药后七天内,不到4%(雄性)和1%(雌性)的给药放射性物质残留在组织中。在单次口服剂量研究中,低剂量和高剂量组之间以及单次和重复剂量低剂量组之间的组织放射性分布模式通常是相似的。药代动力学研究证实了14C-SL-160(P)的快速吸收和消除。在单次口服(14)C-SL-160(P)后,tmax值(仅提供个体动物;未提供数学确定值)在2 mg/kg时为30分钟(3/5动物/性别)或4小时(2/5动物/性别),而在50 mg/kg剂量时,雄性中位数为6小时,雌性为4小时。在2和50 mg/kg剂量下,雄性在血液中的消除半衰期略长于雌性(雄性:27和36小时,分别为;雌性:18.8和33.8小时,分别为)。同样,雄性的AUC(304和4440 ug-eq/g hr,分别为)高于雌性(189和3080 ug-eq/g hr,分别为)。
A series of studies were conducted to evaluate the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of (14)C-SL-160(P)/flazasulfuron/ in groups of 4 or 5 rats (CRL: CD BR VAF/Plus)/sex. In these studies, (14)C-SL-160(P) (CP-1385; 55.8 mCi/mMole; radiolabel purity variously reported as 97.29%, 97.5%. 98.49%., 99.2% and >98%) was administered orally by gavage at doses of 2 or 50 mg/kg or 2 mg/kg . In /one study/, rats had received daily oral gavage doses of nonlabeled SL-160 (Y-920205; 98.9% purity) for 14 days, prior to oral dosing with (14)C-SL-160(P) on Day 15. ... Differences were generally not noted between dose levels or between single versus repeated dose administration, but were noted between males and females. The studies demonstrated that 14C SL-160(P) is rapidly absorbed following a single oral dose of 2 or 50 mg/kg. By 48 hours post exposure, males and females absorbed 94% and 93% of the low dose, respectively, and 86% and 93% of the high dose, respectively. A similar pattern was observed when low- and high-dose animals were followed up to 168 hours with little difference noted between a single or repeated exposure. Elimination via the urine was the major route of excretion, accounting for 74-80% and 90-94% in males and females, respectively, following both low- and high-dose and single and repeated dose administration. Time course data revealed that a significant portion of the radioactivity in urine was excreted by 48-72 hours post exposure. Feces were the secondary route of elimination, accounting for 21-24% and 9-10% in males and females, respectively, following both low- and high-dose and single and repeated dose administration. The biliary excretion study determined that approximately 9.5% of the administered dose appeared in bile by 48 hours in low-dose males and females and high-dose females, with approximately 16.5% in high-dose males. Tissue distribution studies indicated that 14C-SL-160(P) is rapidly excreted from the system, with less than 4% (males) and 1% (females) of the administered radioactivity remaining in the tissues seven days after dosing. In general, the pattern of the radiolabel distribution in tissues was similar between the low- and high-dose groups in the single oral dose study and between the low-dose groups in the single and repeated dose groups. Pharmacokinetic studies confirmed the rapid absorption and elimination of 14C-SL-160(P). Following a single oral dose of (14)C-SL-160(P), tmax values (provided only for individual animals; mathematically determined value not provided) ranged from 30 minutes (3/5 animals/sex) or 4 hours (2/5 animals/sex) at 2 mg/kg, while the median tmax was 6 hours in males and 4 hours in females at the 50 mg/kg dose. At 2 and 50 mg/kg, males had slightly longer elimination half times for the blood than females (males: 27 and 36 hours, respectively; females: 18.8 and 33.8 hours, respectively). Likewise, males had a greater AUC (304 and 4440 ug-eq/g hr, respectively) than females (189 and 3080 ug-eq/g hr, respectively).
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险品标志:N
-
安全说明:S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R50/53
-
WGK Germany:2
-
危险品运输编号:UN3077 9/PG 3
-
RTECS号:UT7930000
SDS
制备方法与用途
概述
啶嘧磺隆是由日本石原产业株式会社(Ishihara Sangyo Kaisha)于20世纪80年代中期开发的一种含氟磺酰脲类除草剂。纯品为无嗅白色结晶粉末,熔点为166~170℃,蒸汽压小于0.013MPa。其在水中的溶解度为2.1g/L(pH=7)、甲醇4.2g/L、乙腈8.7g/L、丙酮22.7g/L、甲苯0.56g/L、己烷0.0005g/L。水中DT50值为11天,而田间土壤的DT50小于7天。
用途啶嘧磺隆是一种苗前和苗后除草剂,主要用于暖季草坪控制阔叶杂草及莎草,特别有效于莎草属和香附子。此外,它也用于葡萄、甘蔗、柑橘、橄榄等非耕作地的杂草防除。使用该药后,可能会出现新叶褪色以及草坪萎缩的情况,但通常这些症状会很快消失。
作用机理啶嘧磺隆是通过抑制支链氨基酸(ALS或AHAS)合成起作用的一种乙酰乳酸合成酶(ALS)抑制剂。这种药物能够阻止必需氨基酸如缬氨酸、异亮氨酸的生成,从而停止细胞分裂和植物生长,并根据代谢速率的不同产生选择性效应。啶嘧磺隆是一种系统除草剂,能迅速被叶片吸收并传导至整个植株。它主要通过抑制乙酰乳酸合成酶的反应来阻止侧链氨基酸(如亮氨酸、异亮氨酸和缬氨酸)的生成。通常在施药后4~7天杂草逐渐失色,之后枯死;部分杂草则可能需要20~30天才会完全死亡。
名称商品名称:Katana、Shibagen。 其他名称:Aikido、Chikara、Epsilon、Mission、Palma、Parandol、啶密黄隆、秀百宫。
用途上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— N-phenoxycarbonyl-3-trifluoromethylpyridine-2-sulfonamide —— C13H9F3N2O4S 346.287 3-三氟甲基-2-吡啶磺酰胺 3-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-sulfonamide 104040-76-8 C6H5F3N2O2S 226.179 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— 3-(trifluoromethyl)-2-pyridylsulfonylmethylcarbamate 181313-25-7 C8H7F3N2O4S 284.216 3-三氟甲基-2-吡啶磺酰胺 3-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-2-sulfonamide 104040-76-8 C6H5F3N2O2S 226.179
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Flazasulfuron:酒精分解,化学水解和对各种矿物质的降解。摘要:除草剂黄酮磺隆会快速醇解。在醇解过程(甲醇或乙醇)于30摄氏度下获得高产率的相应氨基甲酸酯和氨基嘧啶,在此过程中伴随的重排反应仍然很小。在30摄氏度下,flazasulfuron的水解(pH范围为5至11)主要涉及消除SO(2)后尿素的重排,并可能导致氨基嘧啶和吡啶磺酰胺中的一小部分。一级动力学正确地描述了醇解和水解的速率。用一阶动力学假设评估了磺酰脲桥的收缩和最终转化为相应的胺。水性介质中胺和尿素的转化取决于pH。在30摄氏度下研究了氟磺隆在各种干燥矿物(钙膨润土,高岭石,二氧化硅,蒙脱土和氧化铝)上的化学降解。重排反应是在高岭石和氧化铝存在下唯一观察到的重排反应。然而,在二氧化硅的存在下,水解和重排具有相同的反应速率。Flazasulfuron的水解路径与关于rimsulfuron的水解路径相当。DOI:10.1021/jf0347970
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:(杂)芳基羧酸肟酯的可见光诱导脱羧氨基磺酰化摘要:磺酰胺是药物、农用化学品和有机催化剂中的重要结构,但这些化合物的快速、良性合成仍然是一个巨大的挑战。在此,我们报道了一种从(杂)芳基羧酸肟酯合成磺酰胺的光诱导方法。该反应通过能量转移介导的光催化作用,通过一锅级联自由基-自由基交叉偶联进行。广泛的底物范围,包括(杂)芳基底物和药物分子实体的后期修饰揭示了其普遍性。DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.3c04142
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(TETRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE AND 3-[(HYDRAZONO)METHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE DERIVATIVES AS HERBICIDES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO))MÉTHYL]-N-(TÉTRAZOL-5-YL)-BENZAMIDE ET DE 3-[(HYDRAZONO)MÉTHYL]-N-(1,3,4-OXADIAZOL-2-YL)-BENZAMIDE UTILISÉS EN TANT QU'HERBICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA CROP PROTECTION AG公开号:WO2021013969A1公开(公告)日:2021-01-28The present invention related to compounds of Formula (I): or an agronomically acceptable salt thereof, wherein Q, R2, R3, R4, R5 and R6 are as described herein. The invention further relates to compositions comprising said compounds, to methods of controlling weeds using said compositions, and to the use of compounds of Formula (I) as a herbicide.本发明涉及以下式(I)的化合物或其农业上可接受的盐,其中Q、R2、R3、R4、R5和R6如本文所述。该发明还涉及包含所述化合物的组合物,使用这些组合物控制杂草的方法,以及将式(I)的化合物用作除草剂的用途。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
-
[EN] HERBICIDALLY ACTIVE HETEROARYL-S?BSTIT?TED CYCLIC DIONES OR DERIVATIVES THEREOF<br/>[FR] DIONES CYCLIQUES SUBSTITUÉES PAR HÉTÉROARYLE À ACTIVITÉ HERBICIDE OU DÉRIVÉS DE CELLES-CI申请人:SYNGENTA LTD公开号:WO2011012862A1公开(公告)日:2011-02-03The invention relates to a compound of formula (I), which is suitable for use as a herbicide wherein G is hydrogen or an agriculturally acceptable metal, sulfonium, ammonium or latentiating group; Q is a unsubstituted or substituted C3-C8 saturated or mono-unsaturated heterocyclyl containing at least one heteroatom selected from O, N and S, or Q is heteroaryl or substituted heteroaryl; m is 1, 2 or 3; and Het is an optionally substituted monocyclic or bicyclic heteroaromatic ring; and wherein the compound is optionally an agronomically acceptable salt thereof.
-
TRIAZOLE ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF
表征谱图
-
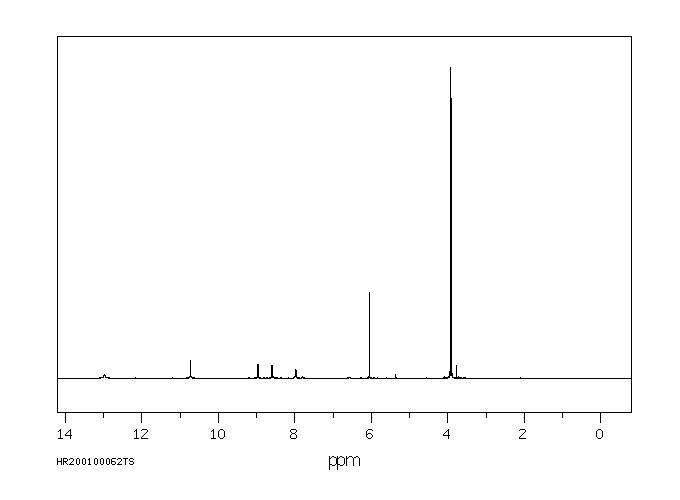
氢谱1HNMR
-
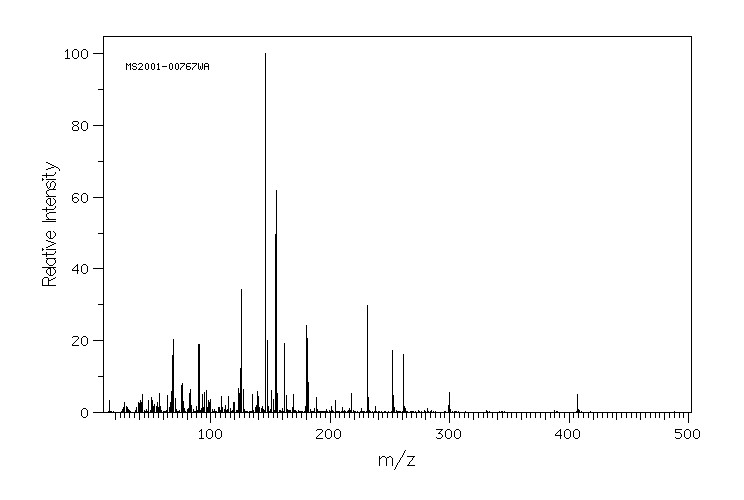
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
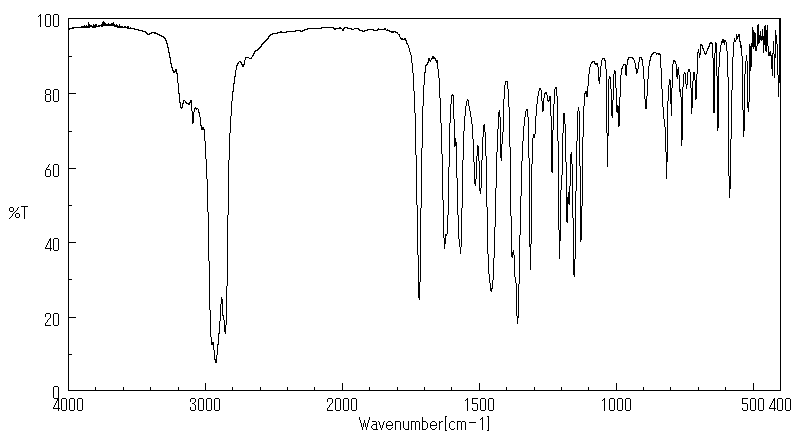
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-氨氯地平-d4
(R,S)-可替宁N-氧化物-甲基-d3
(R)-(+)-2,2'',6,6''-四甲氧基-4,4''-双(二苯基膦基)-3,3''-联吡啶(1,5-环辛二烯)铑(I)四氟硼酸盐
(R)-N'-亚硝基尼古丁
(R)-DRF053二盐酸盐
(5E)-5-[(2,5-二甲基-1-吡啶-3-基-吡咯-3-基)亚甲基]-2-亚磺酰基-1,3-噻唑烷-4-酮
(5-溴-3-吡啶基)[4-(1-吡咯烷基)-1-哌啶基]甲酮
(5-氨基-6-氰基-7-甲基[1,2]噻唑并[4,5-b]吡啶-3-甲酰胺)
(2S,2'S)-(-)-[N,N'-双(2-吡啶基甲基]-2,2'-联吡咯烷双(乙腈)铁(II)六氟锑酸盐
(2S)-2-[[[9-丙-2-基-6-[(4-吡啶-2-基苯基)甲基氨基]嘌呤-2-基]氨基]丁-1-醇
(2R,2''R)-(+)-[N,N''-双(2-吡啶基甲基)]-2,2''-联吡咯烷四盐酸盐
(1'R,2'S)-尼古丁1,1'-Di-N-氧化物
黄色素-37
麦斯明-D4
麦司明
麝香吡啶
鲁非罗尼
鲁卡他胺
高氯酸N-甲基甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸,吡啶
高奎宁酸
马来酸溴苯那敏
马来酸氯苯那敏-D6
马来酸左氨氯地平
顺式-双(异硫氰基)(2,2'-联吡啶基-4,4'-二羧基)(4,4'-二-壬基-2'-联吡啶基)钌(II)
顺式-二氯二(4-氯吡啶)铂
顺式-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯铬氯化物
顺式-1-(4-甲氧基苄基)-3-羟基-5-(3-吡啶)-2-吡咯烷酮
顺-双(2,2-二吡啶)二氯化钌(II) 水合物
顺-双(2,2'-二吡啶基)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
顺-二氯二(吡啶)铂(II)
顺-二(2,2'-联吡啶)二氯化钌(II)二水合物
韦德伊斯试剂
非那吡啶
非洛地平杂质C
非洛地平
非戈替尼
非布索坦杂质66
非尼拉朵
非尼拉敏
雷索替丁
阿雷地平
阿瑞洛莫
阿扎那韦中间体
阿培利司N-6
阿伐曲波帕杂质40
间硝苯地平
间-硝苯地平
镉,二碘四(4-甲基吡啶)-
锌,二溴二[4-吡啶羧硫代酸(2-吡啶基亚甲基)酰肼]-