噻唑磷 | 98886-44-3
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:<25 °C
-
沸点:bp0.5 198°
-
密度:1.26±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:可溶于氯仿(少许)、水(少许)
-
颜色/状态:Pale yellow oil
-
蒸汽压力:4.20X10-6 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.74e-10 atm-m3/mole
-
稳定性/保质期:
在常温常压下保持稳定,应避免与强氧化剂接触。
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.5334 at 19.6 °C/D
-
保留指数:1982.2;1978.3
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2
-
重原子数:16
-
可旋转键数:6
-
环数:1.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.89
-
拓扑面积:97.2
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:5
ADMET
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:T,N
-
安全说明:S25,S26,S39,S45,S53,S60,S61
-
危险类别码:R39,R21,R43,R50/53,R23/25,R41
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29341000
-
危险品运输编号:UN 2810
-
RTECS号:TB1707000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
制备方法与用途
噻唑磷简介
噻唑磷是由日本石原产业公司开发的一种有机磷类杀线虫剂。其主要作用方式是抑制根结线虫乙酰胆碱酯酶的合成,具有强烈的触杀活性,并对传统杀虫剂已产生抗性的害虫也有很高的活性。
防治对象与应用
噻唑磷主要用于防治线虫、蚜虫等多种害虫,尤其适用于无公害蔬菜生产。它对根结线虫、根腐线虫、茎线虫和胞囊线虫等各种线虫都有很好的防效,并且具有良好的植物体传导作用,能防止侵入并对已侵入的线虫等有杀灭效果。
噻唑磷在一年生作物上的持效期为2~3个月,在多年生作物上则可达4~6个月。推荐用量为1.5~2公斤/亩,山东蔬菜区一般每季使用两次,每次施用4~6公斤,平均每季作物的生产成本约为200元。
噻唑磷在中国已取得了在黄瓜、番茄和西瓜上的登记,并可广泛应用于蔬菜、香蕉、果树、药材等作物。适用作物包括胡萝卜、茄子、萝卜、山药、马铃薯、大蒜、甘薯、西瓜、香蕉和烟草等。
毒性
噻唑磷对大鼠的急性经口LD₅₀值为57~73mg/kg,小鼠为91~104mg/kg;雄性大鼠的急性经皮LD₅₀值为2396mg/kg,雌性大鼠为861mg/kg。此外,噻唑磷对母鸡具有迟发神经毒性阴性,对兔眼睛有刺激性但无皮肤刺激性。对鲤鱼和水蚤的半数致死浓度分别为208mg/L(48小时)和2.17mg/L。
化学性质
噻唑磷为浅黄色液体,沸点为198℃/66.66Pa,蒸气压在25℃时为5.6×10⁻⁴Pa,在水中溶解度为9.85g/L(0.87%),分配系数为1.75。
用途
噻唑磷是一种杀虫剂和杀线虫剂,主要作用方式是抑制靶标害虫的乙酰胆碱酯酶,影响其神经系统功能。此外,它还可以用于防治多种作物上的线虫、蚜虫等害虫。
噻唑磷合成方法 正丁基锂法将1.5g 2-氧代噻唑烷溶解于30mL四氢呋喃中,冷却后滴加正丁基锂的正己烷溶液(1.65mol),混合物搅拌15min。再向其中加入含有5g S-仲丁基-O-乙基硫代磷酰氯的10mL四氢呋喃溶液,并继续搅拌30min,于室温下反应3d后倒入水中,用乙酸乙酯提取、水洗、干燥、脱溶得2~3g所需产品。收率在70%~90%。
金属钠法将甲苯和金属钠加入反应器中,在氮气保护下升温至回流温度。待金属钠熔融后,搅拌分散,滴加2-氧代噻唑烷的四氢呋喃溶液,继续反应2h。冷至15℃后,滴加S-仲丁基-O-乙基硫代磷酰氯,再反应1h。经后处理得噻唑硫磷纯度为96.4%,以磷酰氯计收率为91.2%。
反应信息
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:XAGA, TAKAXIRO;DOKI, TADAAKI;KOYANAGI, TORU;OKADA, XIROSI;JOSIDA, KIEMITS+摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
[EN] ACC INHIBITORS AND USES THEREOF<br/>[FR] INHIBITEURS DE L'ACC ET UTILISATIONS ASSOCIÉES
-
[EN] BICYCLYL-SUBSTITUTED ISOTHIAZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS ISOTHIAZOLINE SUBSTITUÉS PAR UN BICYCLYLE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2014206910A1公开(公告)日:2014-12-31The present invention relates to bicyclyl-substituted isothiazoline compounds of formula (I) wherein the variables are as defined in the claims and description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及公式(I)中变量如索权和说明中所定义的自行车基取代异噻唑啉化合物。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种通过使用这些化合物来控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包含所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] AZOLINE COMPOUNDS<br/>[FR] COMPOSÉS AZOLINE申请人:BASF SE公开号:WO2015128358A1公开(公告)日:2015-09-03The present invention relates to azoline compounds of formula (I) wherein A, B1, B2, B3, G1, G2, X1, R1, R3a, R3b, Rg1 and Rg2 are as defined in the claims and the description. The compounds are useful for combating or controlling invertebrate pests, in particular arthropod pests and nematodes. The invention also relates to a method for controlling invertebrate pests by using these compounds and to plant propagation material and to an agricultural and a veterinary composition comprising said compounds.本发明涉及式(I)的噁唑啉化合物,其中A、B1、B2、B3、G1、G2、X1、R1、R3a、R3b、Rg1和Rg2如权利要求和描述中所定义。这些化合物对抗或控制无脊椎动物害虫,特别是节肢动物害虫和线虫方面具有用途。该发明还涉及一种利用这些化合物控制无脊椎动物害虫的方法,以及包括所述化合物的植物繁殖材料、农业和兽医组合物。
-
[EN] MICROBIOCIDAL OXADIAZOLE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS D'OXADIAZOLE MICROBIOCIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2017157962A1公开(公告)日:2017-09-21Compounds of the formula (I) wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, useful as a pesticides, especially fungicides.式(I)的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义,作为杀虫剂特别是杀菌剂有用。
-
[EN] INSECTICIDAL TRIAZINONE DERIVATIVES<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS DE TRIAZINONE INSECTICIDES申请人:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG公开号:WO2013079350A1公开(公告)日:2013-06-06Compounds of the formula (I) or (I'), wherein the substituents are as defined in claim 1, are useful as pesticides.式(I)或(I')的化合物,其中取代基如权利要求1所定义的那样,可用作杀虫剂。
表征谱图
-
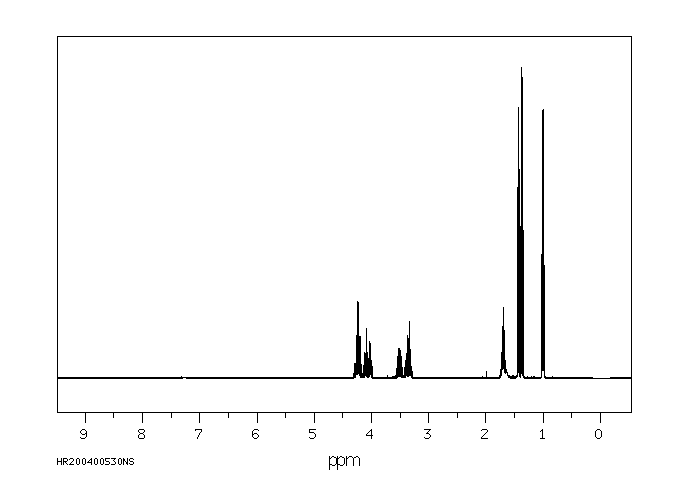
氢谱1HNMR
-
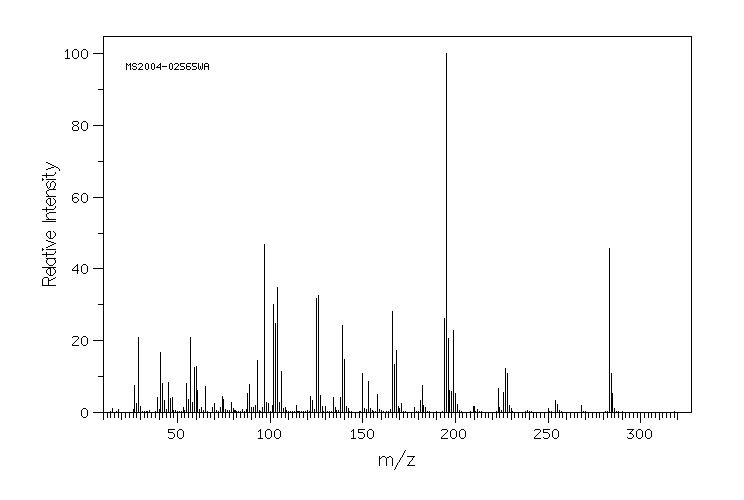
质谱MS
-
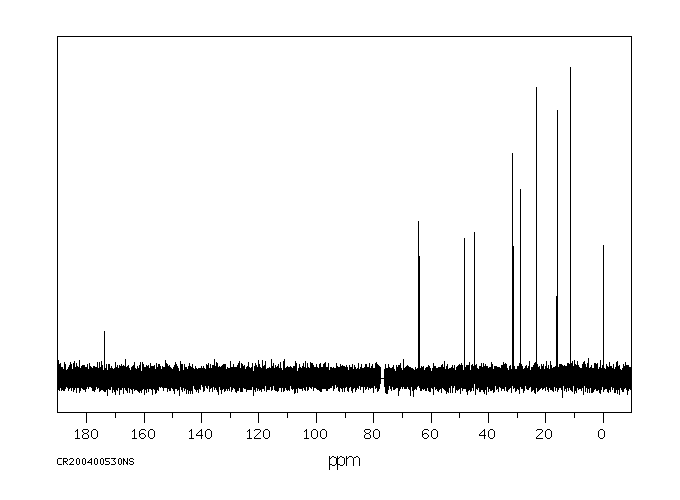
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息