ethyl-2 naphthalene carbonitrile-1 | 103408-11-3
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
ethyl-2 naphthalene carbonitrile-1
英文别名
2-ethyl-[1]naphthonitrile;2-Aethyl-[1]naphthonitril;2-ethyl-1-naphthalenecarbonitrile;1-Cyano-2-ethyl-naphthalene;2-ethylnaphthalene-1-carbonitrile
CAS
103408-11-3
化学式
C13H11N
mdl
——
分子量
181.237
InChiKey
AFBHQTVEDHVZTB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:66.5-67.5 °C(Solv: ligroine (8032-32-4))
-
沸点:323.8±11.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.08±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.7
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.15
-
拓扑面积:23.8
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:1
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 2-甲基萘-1-甲腈 2-methyl-1-naphthonitrile 20944-85-8 C12H9N 167.21 氰基萘 1-Cyanonaphthalene 86-53-3 C11H7N 153.183 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— isopropyl-2 naphthalene carbonitrile-1 103408-20-4 C14H13N 195.264 —— trimethylsilyl-1 ethyl-2 naphthalene carbonitrile-1 103408-21-5 C16H19NSi 253.419
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:三甲基氯硅烷 、 ethyl-2 naphthalene carbonitrile-1 在 tetramethylpiperidine amide 、 甲基锂 作用下, 生成 trimethylsilyl-1 ethyl-2 naphthalene carbonitrile-1参考文献:名称:Fraser, R. R.; Savard, S., Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 1986, vol. 64, p. 621 - 625摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:THE ACTION OF GRIGNARD REAGENTS ON 2-METHOXY-1-NAPHTHONITRILE摘要:DOI:10.1021/jo01162a004
文献信息
-
Ligand properties of aromatic azines: C–H activation, metal induced disproportionation and catalytic C–C coupling reactions作者:Daniel Dönnecke、Joachim Wunderle、Wolfgang ImhofDOI:10.1016/j.jorganchem.2003.11.018日期:2004.2of the azine into a primary imine and a nitrile. So also one of the imine C–H bonds may be activated during the reaction. Depending on the aromatic substituent of the azine ligands iron carbonyl complexes of the disproportionation products are isolated and characterized by X-ray crystallography. C–C coupling reactions catalyzed by Ru3(CO)12 result in the formation of ortho-substituted azines. In addition
-
FRASER, R. R.;SAVARD, S., CAN. J. CHEM., 1986, 64, N 3, 621-625作者:FRASER, R. R.、SAVARD, S.DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
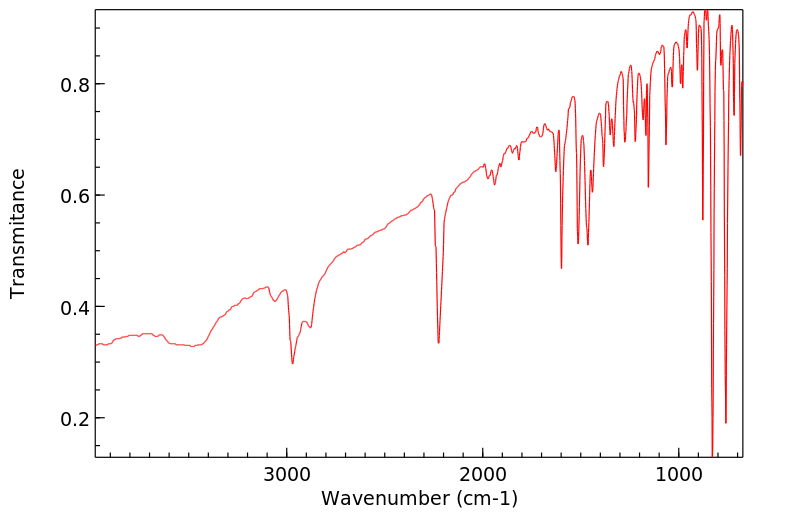
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮