甲基亚硝基脲 | 684-93-5
中文名称
甲基亚硝基脲
中文别名
亚硝基甲脲;N-甲基-N-亚硝基脲;1-甲基-1-亚硝基脲
英文名称
1-methyl-1-nitrosourea
英文别名
N-Methyl-N-nitrosourea;N-nitroso-N-methylurea;MNU;NMU;methyl nitrosourea
CAS
684-93-5
化学式
C2H5N3O2
mdl
MFCD00014794
分子量
103.081
InChiKey
ZRKWMRDKSOPRRS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:119-124°C
-
沸点:193.27°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.5048 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:二甲基亚砜:125 mg/mL(1212.65 mM)
-
物理描述:N-nitroso-n-methylurea appears as pale yellow crystals or light yellow moist powder. (NTP, 1992)
-
颜色/状态:Colorless or yellow plates from ethanol
-
蒸汽压力:3.0X10-2 mm Hg at 25 °C (est)
-
稳定性/保质期:
Decomposes to diazomethane in alkaline solutions; stability in aqueous solutions is pH-dependent (at 20 °C).
-
分解:Melting point: 124 °C (decomposition).
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):0
-
重原子数:7
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.5
-
拓扑面积:75.8
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:3
ADMET
代谢
生理pH下,NMU分解产生的氰酸根离子可以通过碳酰胺化反应与蛋白质发生作用。
The cyanate ion produced by decomposilion of NMU at physiological pH can react with proteins by carbanoylation.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
代谢
In vivo formation of NMU was shown by methylation of guanine at N7 after feeding of the precursors methylurea and sodium nitrite. /Species not specified/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
识别和使用:N-亚硝基-N-甲基脲(NMU)是一种固体。NMU曾被广泛用于实验室合成重氮甲烷,但现在已被其他试剂取代。NMU作为抗癌化疗药物进行了研究,单独使用或与环磷酰胺联合使用。在研究中,小剂量用于研究其对植物的诱变效应。人类研究:给患者静脉注射4 mg/kg体重的NMU后,出现了恶心和呕吐。NMU在人类淋巴母细胞系TK6中产生了突变。成年人类前列腺上皮细胞在多次暴露于NMU后,据报道发生了恶性转化。动物研究:NMU在动物中的主要毒性效应是由于对造血组织、淋巴组织和其他细胞周转率快的组织的严重损害。急性处理NMU已被证明会抑制组织和核酸的合成。NMU在猴视网膜中急性诱导了以杆细胞为主的视杆细胞变性,但视杆细胞和视锥细胞的功能都受到了损害。小鼠腹膜内应用NMU导致了中度的全身副作用,并选择了视杆细胞变性。玻璃体内注射NMU也诱导了视杆细胞变性;然而,没有观察到全身副作用。在兔中,玻璃体内注射3 mg/kg体重的MNU导致了选择性的但不均匀的视杆细胞变性。在大鼠中,每隔两周给予10 mg/kg体重,每隔四周给予20 mg/kg体重,持续9个月的剂量下,观察到了贲门癌。还观察到大脑(肉瘤、胶质瘤)和周围神经系统(称为神经肉瘤)的恶性肿瘤。在10/10的大鼠中,单次口服给药90 mg/kg体重后发现了牙源性肿瘤。小猪每隔两周接受10 mg/kg体重的NMU,持续4.5年。活了50个月的9只动物都发展出了胃的良性肿瘤和一些恶性肿瘤。三种猴类,恒河猴、猕猴和长尾猴口服NMU后,被发现有咽部和/或食道的鳞状细胞癌。对125只新生小鼠单次皮肤应用50-100 mg/kg体重,大约50%的处理动物主要诱导了淋巴白血病。将0.5%的NMU溶液每周三次,连续30周(1.75 mg/剂)应用于大鼠,产生了9/9动物的皮肤多发性鳞状细胞和基底细胞癌,第一个肿瘤出现在20周。将0.5%的NMU溶液每周三次,连续13周(0.35 mg/剂)应用于20只叙利亚金仓鼠,产生了18/18动物的皮肤鳞状细胞癌,第一个肿瘤出现在8周。在大鼠怀孕的最后三分之一期间用NMU处理的子代中观察到了神经系统和肾脏的肿瘤。处理过的母鼠也发生了乳腺肿瘤。雄性小鼠用NMU处理后,其后代出现了先天性缺陷。在小鼠中,使用NMU开发了一种视网膜变性模型。在小鼠中,怀孕第11天的治疗后,主要效应是并指畸形。怀孕第12天的治疗特别触发了双侧微指畸形。NMU的遗传活性已在细菌噬菌体、大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌、酿酒酵母、粘质沙雷菌、中国仓鼠细胞和果蝇中得到了证明,诱导了正向和反向突变以及基因转换。
IDENTIFICATION AND USE: N-Nitroso-N-methylurea (NMU) is a solid. NMU was once widely used to synthesize diazomethane in the laboratory, it has been replaced by other reagents for this use. NMU has been studied as a chemotherapeutic agent in cancer treatment, either alone or in combination with cyclophosphamide. Small quantities are used in research to study its mutagenic effects on plants. HUMAN STUDIES: Nausea and vomiting were seen after iv injection of 4 mg/kg body wt NMU to patients. NMU produced mutations in human lymphoblast cell line TK6. The malignant transformation of adult human prostate epithelial cells has been reported after multiple exposures to the NMU. ANIMAL STUDIES: The major toxic effects of NMU in animals result from severe damage to hematopoietic, lymphoid and other tissues that have rapid rates of cell turnover. Acute treatment with NMU has been shown to inhibit protein and nucleic acid synthesis in tissues. NMU acutely induced rod-dominant photoreceptor degeneration in monkey retinas, but the photoreceptor function was impaired in both the rods and cones. The intraperitoneal application of NMU led to moderate systemic side effects in mice and to selective photoreceptor degeneration. Intravitreal injections of NMU also induced photoreceptor degeneration; however, no systemic side effects were observed. In rabbits, the intravitreal injection of 3 mg/kg bw MNU leads to selective but inhomogeneous photoreceptor degeneration. Carcinomas of the forestomach were seen in rats at doses of 10 mg/kg bw given once every 2 weeks and 20 mg/kg bw given once every 4 weeks over a period of 9 months. Malignant tumors of the brain (sarcomas, gliomas) and the peripheral nervous system (described as neurosarcomas) were also observed. Odontogenic neoplasms were found in 2/10 rats after a single i.g. administration of 90 mg/kg bw. Minipigs received 10 mg/kg bw NMU at fortnightly intervals for 4.5 years. All of the 9 animals that lived 50 months developed benign and some malignant tumors of the stomach. Three species of monkeys, Macaca mulatta, M. fascicularis and Cercopithecus aethiops were administered NMU orally, and were found to have squamous-cell carcinomas of the oropharynx and/or esophagus. One skin application of 50-100 mg/kg bw to 125 newborn mice induced mainly lymphatic leukemias in about 50% of treated animals. Application of a 0.5% solution of NMU 3 times/week for 30 weeks (1.75 mg/dose) to rats produced multiple squamous- and basal-cell carcinomas of the skin in 9/9 animals. The first tumor appeared at 20 weeks. Skin application to 20 Syrian golden hamsters with 0.5% solution of NMU 3 times/week for 13 weeks (0.35 mg/dose) produced squamous-cell carcinomas of skin in 18/18 animals, the first tumor appearing at 8 weeks. Tumors of the nervous system and kidney were observed in the offspring of rats treated with NMU during the last third of pregnancy. Mammary tumors also occurred in the treated mothers. Congenital defects in the offspring of mice following paternal treatment with NMU also occurred. A model of retinal degeneration has been developed in mice using NMU. In mice, ectrodactyly was the predominant effect after treatment on day 11 of pregnancy. Treatment on day 12 triggered especially double-sided microdactyly. The genetic activity of NMU has been demonstrated in bacterial phage, Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Serratia marcescens, Chinese hamster cells and Drosophila melanogaster, inducing forward and reverse mutations and gene conversions.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
没有关于人类的数据可用。动物中有足够的致癌性证据。总体评估:2A组:该物质很可能对人类具有致癌性。
No data are available in humans. Sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity in animals. OVERALL EVALUATION: Group 2A: The agent is probably carcinogenic to humans.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
N-亚硝基-N-甲基脲合理预期为人类致癌物,基于实验动物研究中充分的致癌性证据。
N-Nitroso-N-methylurea is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构致癌剂:N-甲基-N-亚硝基脲
IARC Carcinogenic Agent:N-Methyl-N-nitrosourea
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
毒理性
国际癌症研究机构(IARC)致癌物分类:2A组:可能对人类致癌
IARC Carcinogenic Classes:Group 2A: Probably carcinogenic to humans
来源:International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
吸收、分配和排泄
NMU的高化学反应性使得酶催化不太可能参与其分解。NMU是一种直接的烷基化剂,能够在体外和体内烷基化核酸。这种烷基化已经在包括小鼠、大鼠、仓鼠和小型猪等多种物种的多种组织中检测到,包括大脑、肺、肾、肝、肠、胸腺和脾。NMU在体内烷基化核酸后形成的甲基化核苷中,甲基团上的三个氢原子都被保留下来。
The high chemical reactivity of NMU renders it unlikely that enzymic catalysis is involved in its decomposition. NMU is a direct alkylating agent and alkylates nucleic acids both in vitro and in vivo. Such alkylation has been detected in a number of tissues, including brain, lung, kidney, liver, intestine, thymus and spleen, in a number of species, including mice, rats, hamsters and mini-pigs. All three hydrogen atoms in the methyl group of NMU are retained in the methylated nucleosides formed in nucleic acids after alkylation by NMU in vivo.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险等级:6.1(b)
-
危险品标志:F
-
安全说明:S22,S24/25,S45,S53
-
危险类别码:R61,R45,R11,R25,R46
-
WGK Germany:-
-
海关编码:29241990
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1325 4.1/PG 2
-
RTECS号:YT7875000
-
包装等级:III
-
危险类别:6.1(b)
-
储存条件:| 温度范围:2-8℃ |
SDS
| 第一部分:化学品名称 |
| 化学品中文名称: | 亚硝基甲脲;1-甲基-1-亚硝基脲 |
| 化学品英文名称: | N-Nitroso-N-methylurea;1-Methyl-1-nitrosourea |
| 中文俗名或商品名: | |
| Synonyms: | |
| CAS No.: | 684-93-5 |
| 分子式: | C 2 H 5 N 3 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 103.10 |
| 第二部分:成分/组成信息 |
| 纯化学品 混合物 | |||
| 化学品名称:亚硝基甲脲;1-甲基-1-亚硝基脲 | |||
|
| 第三部分:危险性概述 |
| 危险性类别: | |
| 侵入途径: | 吸入 食入 经皮吸收 |
| 健康危害: | 吸入、摄入或经皮肤吸收后对身体有害。且有致癌作用。接触本品可致皮炎。蒸气对眼睛、皮肤和呼吸道有强烈刺激作用。 |
| 环境危害: | 对环境有危害。 |
| 燃爆危险: | 本品属自燃物品,有毒,具强刺激性。 |
| 第四部分:急救措施 |
| 皮肤接触: | 用肥皂水及清水彻底冲洗。就医。 |
| 眼睛接触: | 拉开眼睑,用流动清水冲洗15分钟。就医。 |
| 吸入: | 脱离现场至空气新鲜处。呼吸困难时给输氧。呼吸停止时,立即进行人工呼吸。就医。 |
| 食入: | 误服者,饮适量温水,催吐。洗胃。就医。 |
| 第五部分:消防措施 |
| 危险特性: | 遇明火、高热可燃。长期储存可引起爆炸。受高热分解,放出有毒的烟气。 |
| 有害燃烧产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物。 |
| 灭火方法及灭火剂: | 消防人员须戴好防毒面具,在安全距离以外,在上风向灭火。灭火剂:雾状水、抗溶性泡沫、二氧化碳、干粉。 |
| 消防员的个体防护: | |
| 禁止使用的灭火剂: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 自燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸下限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 爆炸上限[%(V/V)]: | |
| 最小点火能(mJ): | |
| 爆燃点: | |
| 爆速: | |
| 最大燃爆压力(MPa): | |
| 建规火险分级: |
| 第六部分:泄漏应急处理 |
| 应急处理: | 隔离泄漏污染区,周围设警告标志,切断火源。建议应急处理人员戴自给式呼吸器,穿化学防护服。不要直接接触泄漏物,小心扫起,避免扬尘,置于袋中转移至安全场所。用水刷洗泄漏污染区,经稀释的污水放入废水系统。如大量泄漏,收集回收或无害处理后废弃。 |
| 第七部分:操作处置与储存 |
| 操作注意事项: | 密闭操作,提供充分的局部排风。防止粉尘释放到车间空气中。操作人员必须经过专门培训,严格遵守操作规程。建议操作人员佩戴防尘面具(全面罩),穿胶布防毒衣,戴橡胶手套。远离火种、热源,工作场所严禁吸烟。使用防爆型的通风系统和设备。避免产生粉尘。避免与氧化剂接触。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材及泄漏应急处理设备。倒空的容器可能残留有害物。 |
| 储存注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、干燥、通风良好的库房。远离火种、热源。防止阳光直射。包装密封。应与氧化剂、食用化学品等分开存放,切忌混储。不宜久存。配备相应品种和数量的消防器材。储区应备有合适的材料收容泄漏物。 |
| 第八部分:接触控制/个体防护 |
| 最高容许浓度: | 中 国 MAC:未制订标准前苏联 MAC:未制订标准美国TLV—TWA:未制订标准 |
| 监测方法: | |
| 工程控制: | 密闭操作,局部排风。 |
| 呼吸系统防护: | 可能接触毒物时,应该佩戴防毒口罩。紧急事态抢救或逃生时,建议佩戴自给式呼吸器。 |
| 眼睛防护: | 戴化学安全防护眼镜。 |
| 身体防护: | 穿防静电工作服。 |
| 手防护: | 戴防化学品手套。 |
| 其他防护: | 工作现场禁止吸烟、进食和饮水。工作后,淋浴更衣。注意个人清洁卫生。定期体检。 |
| 第九部分:理化特性 |
| 外观与性状: | 淡黄色晶体。 |
| pH: | |
| 熔点(℃): | 124(分解) |
| 沸点(℃): | |
| 相对密度(水=1): | |
| 相对蒸气密度(空气=1): | |
| 饱和蒸气压(kPa): | |
| 燃烧热(kJ/mol): | |
| 临界温度(℃): | |
| 临界压力(MPa): | |
| 辛醇/水分配系数的对数值: | |
| 闪点(℃): | |
| 引燃温度(℃): | |
| 爆炸上限%(V/V): | |
| 爆炸下限%(V/V): | |
| 分子式: | C 2 H 5 N 3 O 2 |
| 分子量: | 103.10 |
| 蒸发速率: | |
| 粘性: | |
| 溶解性: | 微溶于水,溶于多数有机溶剂。 |
| 主要用途: | 用于制造重氮甲烷和供实验用。 |
| 第十部分:稳定性和反应活性 |
| 稳定性: | 在常温常压下 不稳定 |
| 禁配物: | 强氧化剂、水。 |
| 避免接触的条件: | 光照。 |
| 聚合危害: | 不能出现 |
| 分解产物: | 一氧化碳、二氧化碳、氮氧化物。 |
| 第十一部分:毒理学资料 |
| 急性毒性: | LD50:110mg/kg(大鼠经口) LC50: |
| 急性中毒: | |
| 慢性中毒: | |
| 亚急性和慢性毒性: | |
| 刺激性: | |
| 致敏性: | |
| 致突变性: | |
| 致畸性: | |
| 致癌性: |
| 第十二部分:生态学资料 |
| 生态毒理毒性: | |
| 生物降解性: | |
| 非生物降解性: | |
| 生物富集或生物积累性: |
| 第十三部分:废弃处置 |
| 废弃物性质: | |
| 废弃处置方法: | 建议用焚烧法处置。在能利用的地方重复使用容器或在规定场所掩埋。 |
| 废弃注意事项: |
| 第十四部分:运输信息 |
| |
| 危险货物编号: | |
| UN编号: | |
| 包装标志: | |
| 包装类别: | |
| 包装方法: | |
| 运输注意事项: | 储存于阴凉、低温、通风良好的不燃库房。远离火种、热源。包装密封。避光保存。防止受潮和雨淋。防止阳光曝晒。应与氧化剂、潮湿物品、食用化工原料等分开存放。不宜久存。操作现场不得吸烟、饮水、进食。搬运时轻装 |
| RETCS号: | |
| IMDG规则页码: |
| 第十五部分:法规信息 |
| 国内化学品安全管理法规: | 化学危险物品安全管理条例 (1987年2月17日国务院发布),化学危险物品安全管理条例实施细则 (化劳发[1992] 677号),工作场所安全使用化学品规定 ([1996]劳部发423号)等法规,针对化学危险品的安全使用、生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应规定。 |
| 国际化学品安全管理法规: |
| 第十六部分:其他信息 |
| 参考文献: | 1.周国泰,化学危险品安全技术全书,化学工业出版社,1997 2.国家环保局有毒化学品管理办公室、北京化工研究院合编,化学品毒性法规环境数据手册,中国环境科学出版社.1992 3.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety,CHEMINFO Database.1998 4.Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety, RTECS Database, 1989 |
| 填表时间: | 年月日 |
| 填表部门: | |
| 数据审核单位: | |
| 修改说明: | |
| 其他信息: | 6 |
| MSDS修改日期: | 年月日 |
制备方法与用途
用途
1-甲基-1-亚硝基脲是重氮甲烷的前体。它具有细胞毒性作用,并且该产品含有不确定量的水分。
生物活性N-Nitroso-N-methylurea(NMU;MNU;NMH)是一种有效的致癌剂、诱变剂和致畸剂。这是一种直接作用的烷基化剂,能与DNA相互作用。N-Nitroso-N-methylurea能够靶向多种动物器官,引起各种癌症或/和其他疾病,并且也是重氮甲烷合成中的前体物质。
体外研究N-Nitroso-N-methylurea(NMU;5 μM)处理人类恶性角质细胞时,会增加细胞内NF-κB的活性。同时也会增加I-κBα的磷酸化水平。
体内研究将N-Nitroso-N-methylurea(NMU)静脉注射给龄期为50天的大鼠后,在89%的 BUF/N、73% 的Sprague-Dawley 和89% 的F344雌性大鼠中诱发了乳腺癌。潜伏期分别为77天、86天和94天。NMU诱导的原发性和移植性肿瘤的加倍时间相似,大约为7天。在第五周开始出现第一个肿瘤时,通常会引发恶病质现象。当肿瘤质量超过15克时,还会观察到高钙血症。
化学性质黄色片状结晶(溶于乙醇),熔点124℃(分解)。在室温下存放时有可能因分解而引起爆炸。
用途 生产方法上下游信息
-
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 1-氨基-1-甲基脲 2-methyl semicarbazide 22718-48-5 C2H7N3O 89.0971
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Et2AlX/CH2N2 试剂用于空间位阻烯烃以及含氧和含氮不饱和化合物的环丙烷化反应摘要:在有机卤化铝存在下,使用重氮甲烷开发了空间位阻烯烃、取代烯丙醇、烯丙胺和乙烯基甲硅烷基醚的无过渡金属环丙烷化方法。DOI:10.1007/s11172-019-2638-5
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:来自Clusia burle-marxii的新型聚异戊二烯基二苯甲酮衍生物摘要:三个新的笼polyprenylated二苯甲酮命名burlemarxiones DF(衍生物1 - 3)购自的己烷提取物中分离Clusia布雷-marxii中继线。Burlemarxione D(1)含有四环[8.3.1.0 3,11 .0 5,10十四烷核心骨架还观察到了可能的直接前体burlemarxioneA。但是,形成了两个额外的环以产生空前的复杂笼核核心骨架。这些额外的环可通过C-5上一个异戊二烯基与C-1和C-33的自由基环化反应,随后的氧化脱氢(再芳构化)或分子内[4 + 2]自由基环加成反应形成(Diels-Alder反应),然后进行烯醇化反应(芳构化)。用重氮甲烷甲基化后分离出Burlemarxiones E和F,这对于避免互变异构平衡中的β-二酮对的相互转化是必要的。burlemarxiones DF的拟议的生物合成途径涉及将草酰焦磷酸或2-(1-甲基乙烯基)-六-5-DOI:10.1016/j.fitote.2020.104760
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:INDOLE COMPOUNDS AS AN INHIBITOR OF CELLULAR NECROSIS摘要:本发明涉及新的吲哚化合物,其药学上可接受的盐或异构体,用于预防或治疗细胞坏死和坏死相关疾病。本发明还涉及一种预防或治疗细胞坏死和坏死相关疾病的方法和组合物,该组合物包括所述吲哚化合物作为活性成分。公开号:US20100210647A1
文献信息
-
[EN] BIS-HETEROARYL DERIVATIVES AS MODULATORS OF PROTEIN AGGREGATION<br/>[FR] DÉRIVÉS BIS-HÉTÉROARYLIQUES EN TANT QUE MODULATEURS DE L'AGRÉGATION DES PROTÉINES申请人:NEUROPORE THERAPIES INC公开号:WO2017020010A1公开(公告)日:2017-02-02The present invention relates to certain bis-heteroaryl compounds, pharmaceutical compositions containing them, and methods of using them, including methods for preventing, reversing, slowing, or inhibiting protein aggregation, and methods of treating diseases that are associated with protein aggregation, including neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, Lewy body disease, Parkinson's disease with dementia, fronto- temporal dementia, Huntington's Disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple system atrophy, and cancer including melanoma.
-
Noncanonical RNA Nucleosides as Molecular Fossils of an Early Earth-Generation by Prebiotic Methylations and Carbamoylations作者:Christina Schneider、Sidney Becker、Hidenori Okamura、Antony Crisp、Tynchtyk Amatov、Michael Stadlmeier、Thomas CarellDOI:10.1002/anie.201801919日期:2018.5.14prebiotic routes towards RNA. Contemporary RNA, however, is not only constructed from the four canonical nucleobases (A, C, G, and U), it also contains many chemically modified (noncanonical) bases. A still open question is whether these noncanonical bases were formed in parallel to the canonical bases (chemical origin) or later, when life demanded higher functional diversity (biological origin). Here
-
SULFONAMIDE DERIVATIVE AND MEDICINAL USE THEREOF申请人:AJINOMOTO CO., LTD.公开号:US20150051395A1公开(公告)日:2015-02-19Provided are sulfonamide derivatives of a specific chemical structure in which a sulfonamide group having, as a substituent, a phenyl group or a heterocyclic group having a hetero atom(s) as a constituent element(s) is present at its terminal, and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof. These compounds are novel compounds having excellent α4 integrin-inhibitory action.
-
Synthetic studies aimed at the elucidation of the stereostructure of the aggregation pheromone, 2-methyl-6-(4′-methylenebicyclo[3.1.0]hexyl)hept-2-en-1-ol, produced by the male stink bug Erysarcoris lewisi作者:Kenji MoriDOI:10.1016/j.tetasy.2007.03.019日期:2007.4The male-produced aggregation pheromone of the stink bug Erysarcoris lewisi Distant was shown to be one of the two diastereomers of (2Z,6R)-2-methyl-6-(4′-methylenebicyclo[3.1.0]hexyl)hept-2-en-1-ol by synthesizing and bioassaying (2E,6R)-, (2E,6S)-, (2Z,6R)-, and (2Z,6S)-isomers. These were synthesized from the enantiomers of citronellal by employing an intramolecular α-ketocarbene addition to a double
-
7-Methyl- and 7-phenylcyclohepta-1, 3, 5-trienes from benzvalene via 3, 3a, 4, 5, 6, 6a-hexahydro-4, 5, 6-methenocyclopentapyrazoles and tetracyclo[4. 1. 0. 0.0] heptanes作者:Manfred Christl、Erich Brunn、Wolfgang R. Roth、Hans-Werner LennartzDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)80119-8日期:1989.1norbornene with both diazoalkanes cannot be rationalized on the basis of frontier orbital energies. On direct photolysis, the pyrazolines 2a-g were converted into the tetracyclo[4. 1. 0. 02,4. 03,5] heptanes 4a-g exclusively. These compounds gave the 1, 3, 5-cycloheptatrienes 5a, b, d, e, g in high yields on treatment with silver ions, thus providing better access to 7, 7-dimethyl-(5d) and 7, 7-diphenylcycloheptatriene向重氮甲烷,重氮乙烷,2-重氮丙烷,苯基重氮甲烷和二苯基重氮甲烷中添加苯并戊烯(1)以良好的收率得到1-吡唑啉2a-g。通过竞争实验,已经确定了苯并戊烯(1)和降冰片烯相对于重氮甲烷和2-重氮丙烷的相对反应性。苯并戊烯与两种重氮烷烃的反应速度约为降冰片烯的两倍,这不能基于前沿轨道能量来合理化。直接光解后,吡唑啉2a-g转化为四环[4]。1. 0. 0 2,4。0 3,5 ]庚烷4a-g只。在用银离子处理后,这些化合物可高收率地产生1,3,5-环庚烯5a,b,d,e,g,从而提供了更好的7、7-二甲基-(5d)和7,7-二苯基环庚三烯(5克)。出人意料的是,后一种化合物与大量的正十八碳烯形式处于平衡状态。-已经确定了4a至5a重排的反应热,这可以导出四环[4]的形成热。1. 0. 0 2,4。0 3,5 ]庚烷(4a)。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
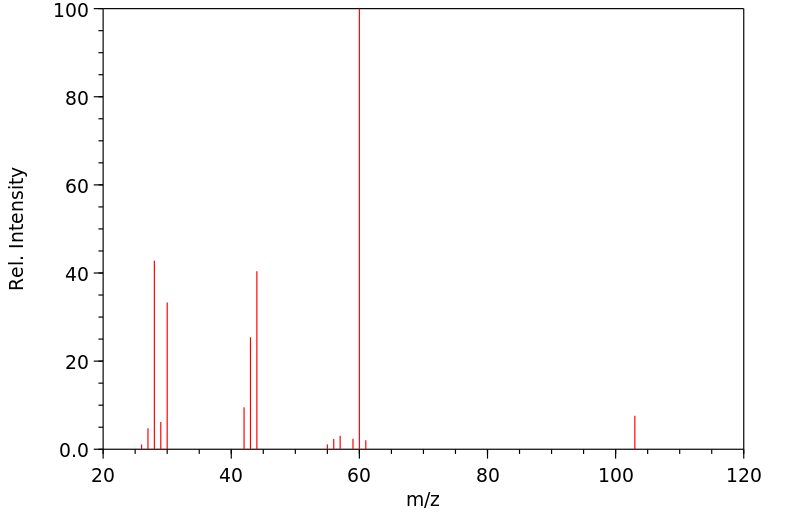
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
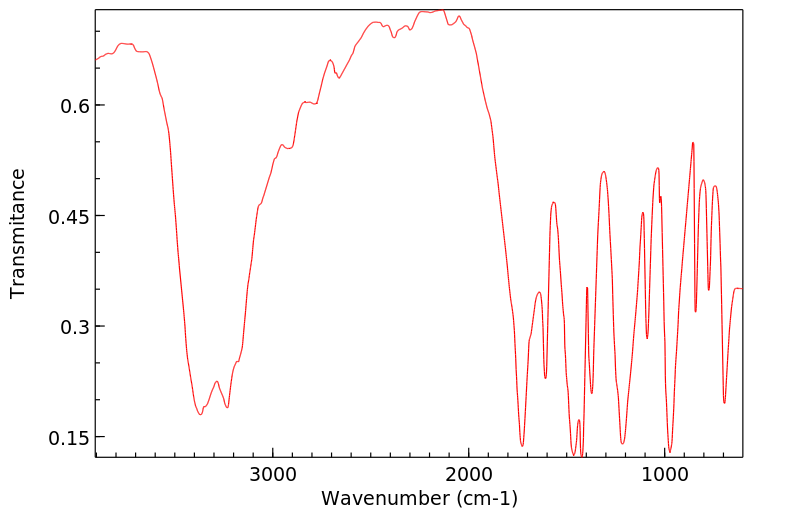
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
顺式-4-[(甲基氨基甲酰)氨基]环己烷羧酸
顺式-3-己烯醇碳酸甲酯
镏碳酸盐二水
镍,[碳酸(2-)-κO]-
镁(1-甲基-3-氧代-丁-1-烯基)碳酸氢酯
锌氮烷碳酸盐
锆碳酸盐氧化物
锂(1-羧基环丙基)锂
铵铜碳酸盐
铯碳酸氢钠
铝镁加
铝镁加
铝碳酸镁
铝碳酸镁
钠脲氯酸盐
钠甲基碳酸酯
钙钠碳酸氢盐氟化物
钙四镁钠碳酸氢盐三碳酸盐四氢氧化物
钐(+3)阳离子碳酸酯
重质碳酸镁
重碳酸钠-13C
酸氧(-2)阴离子铅杂亚酸碳
酮羧酸
邻苯二甲酸氢壬酯
过氧碳酸钠
过氧碳酸二钠盐
过氧碳酸,O,O'-1,6-亚己基-OO,OO'-二叔丁基酯
过氧化脲素
过氧化二碳酸双十四酯
过氧化二碳酸双十六酯
过氧化二碳酸二硬脂酰酯
过氧化二碳酸二环己酯
过氧化二碳酸二正丁酯
过氧化二碳酸二异丙酯
过氧化二碳酸二仲丁酯
过氧化二碳酸二乙酯
过氧化二碳酸二-3-甲氧基丁酯
过氧化二碳酸二(2-乙基己)酯
过氧化(2-乙基己基)碳酸叔戊酯
过氧二碳酸二十三烷酯
过氧二碳酸二丙基酯
达比加群酯杂质41
达比加群酯杂质22
达比加群杂质36
达比加群杂质19
辛酰脲
辛基辛氧基甲基碳酸酯
辛基脲
轻质碳酸镁
起始原料2杂质B