甲胺 | 74-89-5
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
物理描述:Methylamine, anhydrous appears as a colorless gas or a liquid. Pungent fishy odor resembling odor of ammonia. The liquid boils at 20.3°F hence vaporizes rapidly when unconfined. Vapors are heavier than air and may collect in low-lying areas. Easily ignited under most conditions. Under prolonged exposure to intense heat the containers may rupture violently and rocket. Used for making pharmaceuticals, insecticides, paint removers, surfactants, rubber chemicals.
-
颜色/状态:Colorless gas [Note: A liquid below 21 degrees F. Shipped as a liquefied compressed gas]
-
气味:Fish or ammonia-like odor
-
沸点:-6.3 °C
-
熔点:-93.4 °C
-
闪点:-10 °C (14 °F) - closed cup /Methylamine solution 30-50%/
-
溶解度:1 volume of water at 12.5 °C dissolves 1154 volumes of gas; at 25 °C dissolves 959 volumes of gas; 10.5 g is contained in 100 mL saturated benzene solution
-
密度:0.6624 g/cu cm at 25 °C; 0.0014 g/cu cm at 101.33 kPa
-
蒸汽密度:Saturated vapor density: 0.21270 lb/cu ft at 60 °F (Methylamine, anhydrous)
-
蒸汽压力:2.65X10+3 mm Hg at 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.11e-05 atm-m3/mole
-
大气OH速率常数:2.20e-11 cm3/molecule*sec
-
稳定性/保质期:
1、甲胺水溶液或醇溶液均为易燃液体。由于闪点低,容易挥发,有毒,并能与空气形成爆炸性混合物,应避免日光直射和使用可能产生静电的设备。甲胺对铜或铜合金、铝、锡以及镀锌铁板有腐蚀作用,且具有易燃性。
- 其水溶液呈碱性,能与无机酸、有机酸及芳香族硝基化合物等物质反应生成具有一定熔点的盐类。与铜、银等重金属氯化物也能形成络合盐。
- 与酰氯或酸酐进行酰基化反应,可生成N-取代酰胺;与羧酸生成的盐再经过脱水处理也能生成N-取代酰胺。与苯磺酰氯反应,则能生成N-取代苯磺酰胺。
- 可以与卤代烃、醇、酚或胺盐等烃基化试剂作用,氮原子上的氢可被烃基所取代。
- 能够与氰酸、二硫化碳、腈类化合物及环氧化物发生加成反应。
- 在伯胺与脂肪族或芳香族物质进行反应时,脱水生成Schiff碱。
- 对于酸性高锰酸钾而言,甲胺较为稳定;然而,它容易被碱性高锰酸钾所氧化,生成醛或羧酸。在过硫酸、过氧化氢及有机过氧酸的作用下,则可得到含氧化合物的胺类化合物。
- 在与亚硝酸反应时能够定量地生成氮气。
- 加热条件下,甲胺与氯仿和氢氧化钾醇溶液共同作用可生成异腈。
- 与Grignard试剂反应可生成烃类物质。
此外,在高温(550~670℃)下发生热解,生成氨、氰化氢、甲烷、氢气以及氮气等产物。在紫外光照射下也能分解产生甲烷和氮气气体及液体。
-
自燃温度:806 °F (430 °C)
-
分解:Hazardous decomposition products formed under fire conditions: Carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides (NOx) /Methylamine solution 30-50%/
-
腐蚀性:Corrosive to copper, copper alloys, zinc alloys, aluminum, and galvanized surfaces (Methylamine solution)
-
燃烧热:-1085.6 kJ/mole at 25 °C (gas)
-
汽化热:Molar enthalpy of vaporization at 25 °C: 23.37 kJ/mol
-
表面张力:19.15 mN/m at 25 °C
-
电离电位:8.97 eV
-
气味阈值:The odor of methylamine is faint but readily detectable at less than 10 ppm, becomes strong at from 20 to 100 ppm and intolerably ammoniacal at 100 to 500 ppm.
-
解离常数:pKa = 10.66 at 25 °C
-
保留指数:305 ;380 ;328
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.7
-
重原子数:2
-
可旋转键数:0
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:26
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:1
ADMET
安全信息
-
安全说明:S16,S26,S29,S3,S3/7,S33,S36/37,S36/37/39,S39,S45,S7
-
危险品运输编号:UN 3286 3/PG 2
-
WGK Germany:2
-
海关编码:2921110090
-
危险类别:3
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
危险类别码:R37/38,R12,R41,R20
-
RTECS号:PF6300000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05,GHS07
-
危险性描述:H225,H314,H335
-
危险性防范说明:P210,P280,P303 + P361 + P353,P304 + P340 + P310,P305 + P351 + P338,P403 + P235
制备方法与用途
制备方法: 在工业生产中,甲胺是通过将甲醇和氨在高温下通入装有活性氧化铝催化剂的转化器来合成的。虽然甲基化反应不会仅限于一甲胺阶段,但所得产物是一甲胺、二甲胺和三甲胺的混合物。为增加一甲胺和二甲胺的比例,需使氨过量并加入水进行循环。当氨是甲醇的2.5倍,且反应温度控制在425℃、压力保持在2.45MPa时,可得到10-12%的一甲胺、8-9%的二甲胺和11-13%的三甲胺混合物。由于三甲胺与氨及其他甲胺在常压下形成共沸物,分离方法通常采用加压精馏和萃取精馏相结合的方式。据文献报道,改变甲醇和氨的比例是获得理想产品的有效手段,其中甲醇与氨的比例为1:1.5时适合生成三甲胺,而比例为1:4时适合生成一甲胺。
精制方法: 甲胺中通常会含有二甲胺、三甲胺、甲醇及氨等杂质。首先可将甲胺水溶液进行萃取蒸馏以去除三甲胺,随后通过分馏除去二甲胺。另外,也可以采用以下步骤:将甲胺盐酸盐用干燥的氯仿萃取30小时以上,以去除高级胺,并使用乙醇进行重结晶(熔点225~226℃)精制。另一方法是先将甲胺与甲醛生成的缩合物进行分馏,然后在丁醇中用盐酸分解所得盐酸盐并再次用乙醇重结晶。此过程中的精制甲胺盐酸盐需使用过量的氢氧化钾或氢氧化钠分解以得到气态甲胺,并通过固体氢氧化钾脱水后,利用氧化银去除微量氨。最后,使用干冰-乙醚冷却液化,再用芴酮钠干燥即可获得纯净的甲胺。其他精制方法包括将甲胺盐酸盐用丁醇、无水乙醇或甲醇与氯仿混合物进行重结晶,并用氯仿洗涤以除去微量二甲胺盐酸盐,最后在真空干燥器中干燥。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:HCN 在 14 μm 区域的傅里叶变换光谱摘要:摘要 使用美国国家太阳天文台傅里叶变换光谱仪以约 0.005 cm -1 的分辨率测量了 HCN 各种同位素的 710-cm -1 谱带。分析了六个 HCN 波段、一个 H 13 CN 波段和一个 HC 15 N 波段以获得准确的波段原点和旋转常数。对于大多数波段,计算的波段原点的精度优于 0.0003 cm -1。通过与模拟的比较,已经从这些光谱中导出了相对积分强度,并给出了所用方法的示例。DOI:10.1016/0022-2852(89)90018-0
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Wertheim, Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie, 1850, vol. 73, p. 210摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:一系列新型三唑和2,4-噻唑烷二酮杂化酰胺衍生物的合成及生物学评价摘要:一系列具有通过连接体连接的三唑和噻唑烷核的杂化化合物已被合成并进行了广泛的研究。已经测试了目标化合物的各种合成方法。对所获得的化合物进行了病原真菌白色念珠菌、非白色念珠菌、多重耐药念珠菌、根霉、曲霉属菌株的微生物学评估。以及一些皮肤癣菌和其他酵母菌。目标化合物的最低 MIC 值在 0.003 µg/mL 至 0.5 µg/mL 之间,因此这些化合物不比商业唑类药物差或好几倍。酰基哌嗪接头的长度对抗真菌活性的影响有限。一些生物等排类似物在微生物分析中进行了测试,但结果证明其活性弱于先导物质。噻唑烷片段中具有对氯亚苄基取代基的化合物表现出最高的活性。分子模型用于预测合成分子的结合模式并合理化实验观察到的 SAR。与伏立康唑相比,前导化合物在抑制白色念珠菌酵母细胞形成芽管方面的效果高出两倍。观察到吡咯类药物外排泵 Pdr5 水平增加,但增加幅度低于唑类引起的水平。研究结果可用于进一步开发更强大、更安全的抗真菌药物。DOI:10.3390/ph17060723
文献信息
-
Alkyl 1-Chloroalkyl Carbonates: Reagents for the Synthesis of Carbamates and Protection of Amino Groups作者:Gérard Barcelo、Jean-Pierre Senet、Gérard Sennyey、Jean Bensoam、Albert LoffetDOI:10.1055/s-1986-31724日期:——The synthesis of 1-chloroalkyl carbonates and their reaction with various type of amines are described. This reaction is useful for the synthesis of carbamate pesticides and for the protection of various amino groups, including amino acids.
-
BENZOTHIOPHENE INHIBITORS OF RHO KINASE申请人:Kahraman Mehmet公开号:US20080021026A1公开(公告)日:2008-01-24The present invention relates to compounds and methods which may be useful as inhibitors of Rho kinase for the treatment or prevention of disease.本发明涉及化合物和方法,这些化合物和方法可能作为Rho激酶的抑制剂在治疗或预防疾病方面有用。
-
Enantioselective Transfer Hydrogenation of Aliphatic Ketones Catalyzed by Ruthenium Complexes Linked to the Secondary Face of β-Cyclodextrin作者:Alain Schlatter、Wolf-D. WoggonDOI:10.1002/adsc.200700558日期:2008.5.5Ruthenium-η-arene complexes attached to the secondary face of β-cyclodextrin catalyze the enantioselective reduction (ee up to 98%) of aliphatic and aromatic ketones in aqueous medium in the presence of sodium formate (HCOONa).
-
Ammonia–dimethylchloramine system: Kinetic approach in an aqueous medium and comparison with the mechanism involving liquid ammonia作者:J. Stephan、V. Pasquet、M. Elkhatib、V. Goutelle、H. DelaluDOI:10.1002/kin.20312日期:2008.6medium. Dimethylchloramine prepared in a pure state undergoes dehydrohalogenation in an alkaline medium: the principal products formed are N-methylmethanimine, 1,3,5-trimethylhexahydrotriazine, formaldehyde, and methylamine. The kinetics of this reaction was studied by UV, GC, and HPLC as a function of temperature, initial concentrations of sodium hydroxide, and chlorinated derivative. The reaction is of在对液氨中的氨-二甲基氯胺系统进行了详尽的研究之后,比较该系统在液氨中的反应性与相同系统在水性介质中的反应性是很有趣的。以纯态制备的二甲基氯胺在碱性介质中进行脱卤化氢:形成的主要产物是 N-甲基甲亚胺、1,3,5-三甲基六氢三嗪、甲醛和甲胺。该反应的动力学通过 UV、GC 和 HPLC 作为温度、氢氧化钠初始浓度和氯化衍生物的函数进行了研究。该反应是二级反应,遵循 E2 机理(k1 = 4.2 × 10-5 M-1 s-1,ΔH○# = 82 kJ mol-1,ΔS○# = -59 J mol-1 K-1 )。二甲基氯胺氧化不对称二甲基肼涉及两个连续的过程。第一步遵循关于卤胺和肼的一级定律,导致形成氨基氮烯中间体 (k2 = 150 × 10-5 M-1 s-1)。第二步对应于在 pH 13) 下将氨基氮烯转化为甲醛二甲腙。该反应遵循一阶定律 (k3 = 23.5 × 10-5 s-1)。二甲基氯胺-氨相互作用对应于
-
Identification of Pyridine Synthase Recognition Sequences Allows a Modular Solid-Phase Route to Thiopeptide Variants作者:Walter J. Wever、Jonathan W. Bogart、Albert A. BowersDOI:10.1021/jacs.6b05389日期:2016.10.19Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579. Through a series of truncations, we define a minimum recognition sequence (RS) that is necessary and sufficient for TclM activity. This RS can be readily synthesized and ligated to linear thiopeptide cores prepared via solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS), giving an efficient and modular route to thiopeptide variants. We exploit this strategy to define C-terminal core peptide requirements硫肽是结构复杂、具有生物活性的天然产物,来源于核糖体合成和翻译后修饰的肽。最近发现一组显着的酶通过正式的 [4 + 2] 环加成催化硫肽核心三噻唑基吡啶的形成。这些吡啶合酶通常在硫肽生物合成的后期作用以影响 N 末端前导肽的大环化和切割,使其成为制备新硫肽变体的潜在有用的生物催化剂。在这里,我们研究了蜡样芽孢杆菌 ATCC 14579 中硫西林生物合成对 TclM 的前导肽要求。通过一系列截断,我们定义了 TclM 活性所必需和充分的最小识别序列 (RS)。这种 RS 可以很容易地合成并连接到通过固相肽合成 (SPPS) 制备的线性硫肽核心,从而为硫肽变体提供高效和模块化的途径。我们利用这种策略来定义 C 末端核心肽的要求,并探索两种吡啶合酶 TclM 和 TbtD 的混杂性差异,最终检查它们获得新结构变体的能力。
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
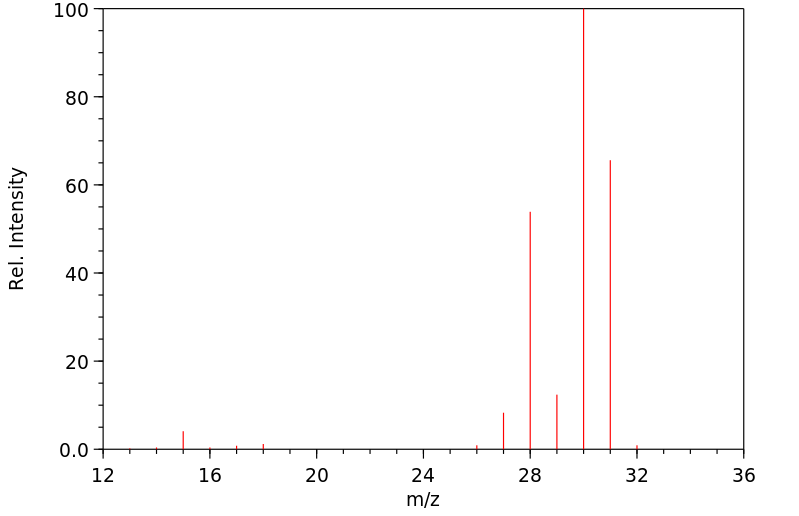
质谱MS
-
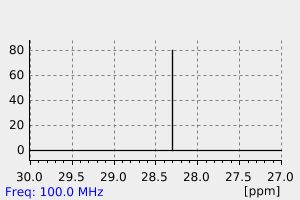
碳谱13CNMR
-
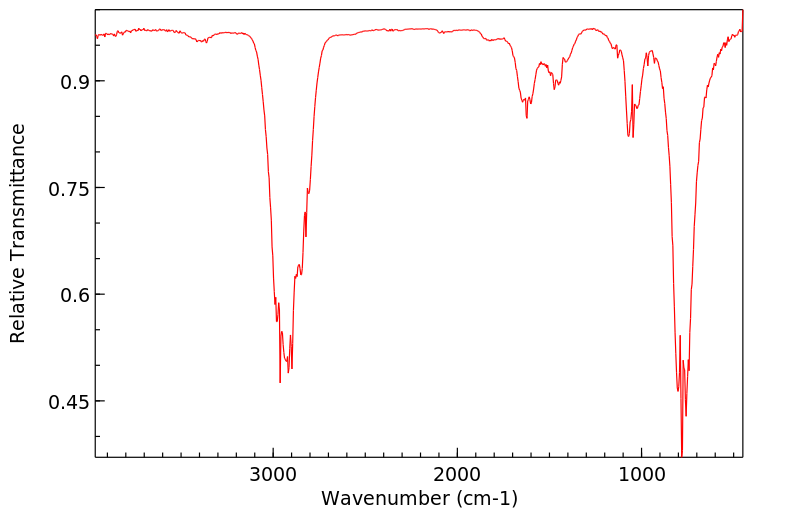
红外IR
-
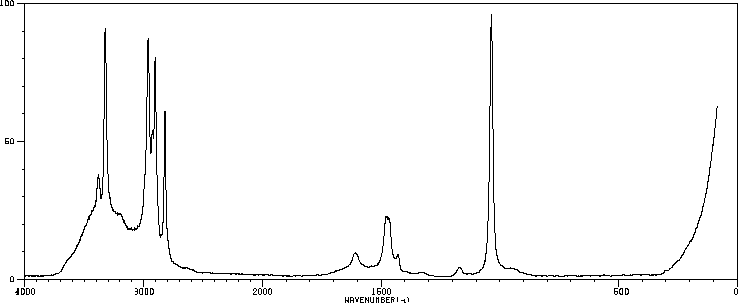
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息