4'-溴化水杨酰苯胺 | 2627-77-2
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:172 °C
-
沸点:338.3±27.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.597±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
稳定性/保质期:
如果按照规格使用和储存,则不会分解。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:2
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:49.3
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2924299090
SDS
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: 4'-Bromosalicylanilide
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 4'-溴化水杨酰苯胺
百分比: >98.0%(T)
CAS编码: 2627-77-2
俗名: 4'-Bromo-2-hydroxybenzanilide
分子式: C13H10BrNO2
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
特殊危险性: 小心,燃烧或高温下可能分解产生毒烟。
4'-溴化水杨酰苯胺
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 白色-极淡的黄红色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点:
172°C
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
4'-溴化水杨酰苯胺
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳, 氮氧化物 (NOx), 溴化氢
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
4'-溴化水杨酰苯胺
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:NAD(P)H:醌受体氧化还原酶 1 (NQO1) 可激活水杨酰胺 H+/Cl− 转运蛋白摘要:在这里,我们报告了两种酶可激活的离子转运系统,它们在被 NQO1(一种癌细胞中丰富的酶)选择性激活后,能够跨脂质双层转运 H + /Cl - 。这种转运破坏了癌细胞中的离子稳态,并通过线粒体膜去极化、溶酶体脱酸和氧化应激诱导引发细胞凋亡。DOI:10.1002/chem.202301412
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:三氟乙酸介导的 1,2,3-Benzotriazin-4(3H)-ones 的脱氮邻羟基化:一种无金属方法摘要:描述了一种有效的三氟乙酸介导的 1,2,3-benzotriazin-4(3 H )-ones 的脱氮羟基化。这种不含金属的方法与多种 1,2,3-benzotriazin-4(3 H )-one相容,可在较短的反应时间内以良好至高产率提供邻羟基化苯甲酰胺。据信该反应通过苯重氮中间体进行。该反应的合成效用通过以良好收率制备抗微生物药物利肝素 C 和苯并恶嗪-2,4(3 H )-二酮类化合物得到成功证明。DOI:10.1021/acs.joc.2c00354
文献信息
-
One-Pot Synthesis of Fused Pyridazino[4,5-b][1,4]oxazepine-diones via Smiles Rearrangement作者:Chen Ma、Yanli Liu、Ying Ma、Chunjing Zhan、Aiping HuangDOI:10.1055/s-0031-1290073日期:2012.1Fused pyridazino[4,5-b][1,4]oxazepine-diones were easily obtained in moderate to excellent yields via Smiles rearrangement. The synthetic approach is supported by a one-pot couplingSmiles rearrangement-cyclization process. This process has potential applications in the synthesis of biologically and medicinally relevant compounds.
-
New Groups of Potential Antituberculotics: 3-Aryl-2H,4H-benz[e][1,3]oxazine-2,4-diones. Comparison of the Topliss Approach with Regression Analysis作者:Karel Waisser、Lenka Kubicová、Věra Klimešová、Želmíra OdlerováDOI:10.1135/cccc19932977日期:——
3-Phenyl-2
H ,4H -benz[e ][1,3]oxazine-2,4-dione (I ) and its derivativesII - XI , substituted on the phenyl ring, can be regarded as a new group of potential antituberculotics. Their activity increases with increasing electron-accepting properties of the substituents. introduction of bromine into the position 6 also positively influences the activity. the compounds are active in vitro againstMycobacterium tuberculosis andM. kansasii . The activity of some of them (VIII, IX 0 exceeds that of commercial tuberculostatics used as standards. -
Multivariate Regression with Substituent Shift Increments. IV. 2-(4-X-Phenyl)-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindole-1,3-diones and 3-(4-X-Phenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1,3-benzoxazine-2,4-diones作者:Miroslav Holík、Zdeněk Friedl、Karel Waisser、Jiří GregorDOI:10.1135/cccc19991709日期:——
Two series of
para disubstituted benzenes were studied: 2-(4-X-phenyl)-1,3-dihydro- 2H -isoindole-1,3-diones (1 ) and 3-(4-X-phenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H -1,3-benzoxazine-2,4-diones (2 ). Their 1H and 13C chemical shifts were correlated with substituent shift increments (SSI)aj andzj , respectively. For 13C chemical shifts, all fourzj values,zi ,zo ,zm , andzp , were used to check the assignment and to find out possible variables for improvement of regression equations. Significant deviations from plain additivity were observed in the case of δH3 and δC3 chemical shifts. This can be explained by changes in diamagnetic anisotropy contribution induced by different twist of 4-substituent from the benzene plane caused by variable substituent in position 1. -
Analogues of the active metabolite of leflunomide申请人:Italfarmaco S.p.A.公开号:US05905090A1公开(公告)日:1999-05-18Analogues of the active metabolite of leflunomide, and to the use thereof as immunosuppressive and/or antinflammatory agents.Leflunomide的活性代谢物的类似物,以及将其用作免疫抑制和/或抗炎剂的用途。
-
Potential salicylamide antiplaque agents: in vitro antibacterial activity against Actinomyces viscosus作者:Robert A. Coburn、Armando J. Batista、Richard T. Evans、Robert J. GencoDOI:10.1021/jm00142a023日期:1981.10A series of 55 salicylamides, including 3,5-dibromo-, 5-n-alkyl-, and 5-n-acylsalicyloyl derivatives of various anilines, heterocyclic amines, benzylamines, and alkylamines, was synthesized and evaluated for in vitro antibacterial activity against Actinomyces viscosus, an adherent oral microorganism implicated in periodontal disease. The in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations of 15 4'-bromosalicylanilides were found to correlate (r = 0.92) with estimated log D values. Several nonhalogenated salicylanilides, such as 5-n-hexyl- (40) and 5-n-decanoyl-4'-nitrosalicylanilide (47), were found to exhibit higher levels of in vitro antibacterial activity against a number of Actinomycetes than did tribromsalan (1) or fluorophene (2).
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
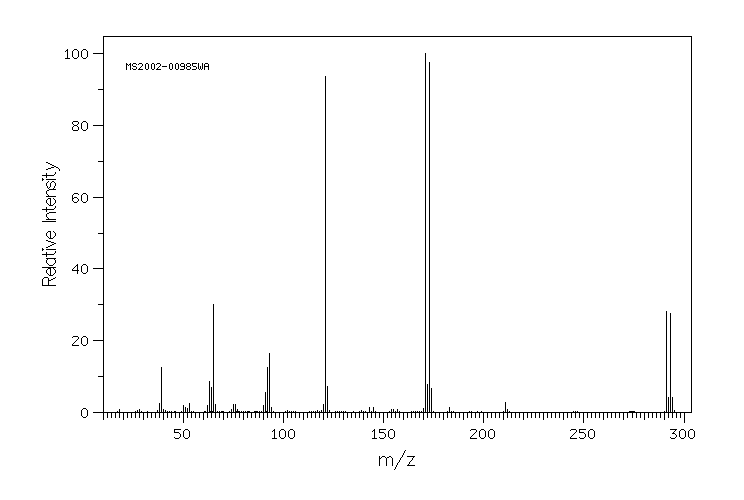
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
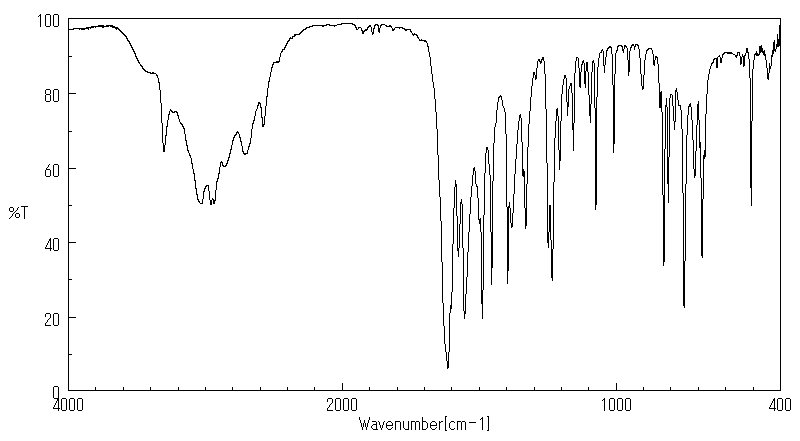
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息