苯芴酮 | 975-17-7
中文名称
苯芴酮
中文别名
苯基荧光酮;9-苯基-2,3,7-三羟基-6-荧光酮;2,6,7-三羟基-9-苯基-3H-呫吨-3-酮;2,6,7-三羟基-9-苯基-3H-占吨-3-酮;2,6,7-三羟基-9-苯基-6-荧光酮
英文名称
fluorone black
英文别名
2,6,7-trihydroxy-9-phenyl-3H-xanthen-3-one;9-phenyl-2,6,7-trihydroxy-3H-xanthen-3-one;2,6,7-trihydroxy-9-phenylxanthen-3-one;9-phenyl-2,6,7-trihydroxyxanthen-3-one;9-phenyl 2,3,7-trihydroxyfluor-6-one
CAS
975-17-7
化学式
C19H12O5
mdl
MFCD00005048
分子量
320.301
InChiKey
YDCFOUBAMGLLKA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:300 °C
-
沸点:646.8±55.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.59±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
-
溶解度:易溶于氯仿。
-
稳定性/保质期:
- 常温常压下稳定,避免强氧化剂接触。
- 在弱酸性介质中与Ce⁴⁺、Sn⁴⁺等离子形成红色或紫色的配合物。
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):2.4
-
重原子数:24
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:4.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:87
-
氢给体数:3
-
氢受体数:5
安全信息
-
TSCA:Yes
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:29329995
-
储存条件:请将容器密封保存,并储存在阴凉干燥的地方。
SDS
苯基荧光酮
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Phenylfluorone
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 苯基荧光酮
百分比: ....
CAS编码: 975-17-7
俗名: 9-Phenyl-2,3,7-trihydroxy-6-fluorone , 2,6,7-Trihydroxy-9-phenyl-3-
isoxaNThone
分子式: C19H12O5
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
苯基荧光酮
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
光敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 浅黄色-黄红色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
苯基荧光酮
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
苯基荧光酮
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
模块 1. 化学品
产品名称: Phenylfluorone
模块 2. 危险性概述
GHS分类
物理性危害 未分类
健康危害 未分类
环境危害 未分类
GHS标签元素
图标或危害标志 无
信号词 无信号词
危险描述 无
防范说明 无
模块 3. 成分/组成信息
单一物质/混和物 单一物质
化学名(中文名): 苯基荧光酮
百分比: ....
CAS编码: 975-17-7
俗名: 9-Phenyl-2,3,7-trihydroxy-6-fluorone , 2,6,7-Trihydroxy-9-phenyl-3-
isoxaNThone
分子式: C19H12O5
模块 4. 急救措施
吸入: 将受害者移到新鲜空气处,保持呼吸通畅,休息。若感不适请求医/就诊。
皮肤接触: 立即去除/脱掉所有被污染的衣物。用水清洗皮肤/淋浴。
若皮肤刺激或发生皮疹:求医/就诊。
眼睛接触: 用水小心清洗几分钟。如果方便,易操作,摘除隐形眼镜。继续清洗。
如果眼睛刺激:求医/就诊。
食入: 若感不适,求医/就诊。漱口。
紧急救助者的防护: 救援者需要穿戴个人防护用品,比如橡胶手套和气密性护目镜。
模块 5. 消防措施
合适的灭火剂: 干粉,泡沫,雾状水,二氧化碳
苯基荧光酮
模块 5. 消防措施
特定方法: 从上风处灭火,根据周围环境选择合适的灭火方法。
非相关人员应该撤离至安全地方。
周围一旦着火:如果安全,移去可移动容器。
消防员的特殊防护用具: 灭火时,一定要穿戴个人防护用品。
模块 6. 泄漏应急处理
个人防护措施,防护用具, 使用个人防护用品。远离溢出物/泄露处并处在上风处。
紧急措施: 泄露区应该用安全带等圈起来,控制非相关人员进入。
环保措施: 防止进入下水道。
控制和清洗的方法和材料: 清扫收集粉尘,封入密闭容器。注意切勿分散。附着物或收集物应该立即根据合适的
法律法规处置。
模块 7. 操作处置与储存
处理
技术措施: 在通风良好处进行处理。穿戴合适的防护用具。防止粉尘扩散。处理后彻底清洗双手
和脸。
注意事项: 如果粉尘或浮质产生,使用局部排气。
操作处置注意事项: 避免接触皮肤、眼睛和衣物。
贮存
储存条件: 保持容器密闭。存放于凉爽、阴暗处。
远离不相容的材料比如氧化剂存放。
光敏
包装材料: 依据法律。
模块 8. 接触控制和个体防护
工程控制: 尽可能安装封闭体系或局部排风系统,操作人员切勿直接接触。同时安装淋浴器和洗
眼器。
个人防护用品
呼吸系统防护: 防尘面具。依据当地和政府法规。
手部防护: 防护手套。
眼睛防护: 安全防护镜。如果情况需要,佩戴面具。
皮肤和身体防护: 防护服。如果情况需要,穿戴防护靴。
模块 9. 理化特性
固体
外形(20°C):
外观: 晶体-粉末
颜色: 浅黄色-黄红色
气味: 无资料
pH: 无数据资料
熔点: 无资料
沸点/沸程 无资料
闪点: 无资料
爆炸特性
爆炸下限: 无资料
爆炸上限: 无资料
密度: 无资料
溶解度:
[水] 无资料
[其他溶剂] 无资料
苯基荧光酮
模块 10. 稳定性和反应性
化学稳定性: 一般情况下稳定。
危险反应的可能性: 未报道特殊反应性。
须避免接触的物质 氧化剂
危险的分解产物: 一氧化碳, 二氧化碳
模块 11. 毒理学信息
急性毒性: 无资料
对皮肤腐蚀或刺激: 无资料
对眼睛严重损害或刺激: 无资料
生殖细胞变异原性: 无资料
致癌性:
IARC = 无资料
NTP = 无资料
生殖毒性: 无资料
模块 12. 生态学信息
生态毒性:
鱼类: 无资料
甲壳类: 无资料
藻类: 无资料
残留性 / 降解性: 无资料
潜在生物累积 (BCF): 无资料
土壤中移动性
log水分配系数: 无资料
土壤吸收系数 (Koc): 无资料
亨利定律 无资料
constaNT(PaM3/mol):
模块 13. 废弃处置
如果可能,回收处理。请咨询当地管理部门。建议在可燃溶剂中溶解混合,在装有后燃和洗涤装置的化学焚烧炉中
焚烧。废弃处置时请遵守国家、地区和当地的所有法规。
模块 14. 运输信息
联合国分类: 与联合国分类标准不一致
UN编号: 未列明
模块 15. 法规信息
《危险化学品安全管理条例》(2002年1月26日国务院发布,2011年2月16日修订): 针对危险化学品的安全使用、
生产、储存、运输、装卸等方面均作了相应的规定。
苯基荧光酮
模块16 - 其他信息
N/A
制备方法与用途
概述
近年来,随着科技水平的提高,酸性显色剂在化学分析中的应用越来越广泛。酸性显色剂能够与被检测物形成红色或紫色的高灵敏度胶束络合物,利用分光光度法可测定被检测物的含量。
苯芴酮(分子式:C₁₉H₁₂O₅),又称为苯基荧光酮、锗试剂、9-苯基-2,3,7-三羟基-6-氧杂蒽酮,是一种广泛应用于化学检测的酸性显色剂。它主要用于检测冶炼产品中的硒化合物,并可作为Ge⁴⁺、Sn⁴⁺、In³⁺、MoO₄²⁻和TaO₃⁻等离子体的测定。
目前,制备苯芴酮的方法是将苯三酚三醋酸酯溶于酸化乙醇水溶液中后与苯甲醛反应。然而,由于对酸化乙醇水溶液的酸碱度控制不佳,导致苯芴酮的制备周期较长,一般需要15~20天;同时所制备的苯芴酮纯度较低,在分光光度法检测过程中灵敏度较差。
用途反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Crystallographic studies on a series of salts of 2,3,7-trihydroxy-9-phenyl-fluorone摘要:2,3,7-Trihydroxy-9-phenyl-fluorone (hereafter H(3)Z) has been synthesised in its H(4)Z(+), H(3)Z, H(2)Z(-) and Z(3)-protonation states. X-ray crystal structure determinations have been carried out for (H(4)Z)(HSO4), H(3)Z, [(EtPr2NH)-Pr-i]H(2)Z, solvated (PPh4)H(2)Z and solvated K(3)Z. In each of these salts the 9-phenyl group adopts a different orientation so as to be involved in intermolecular aromatic interactions. The 3- and 6-phenolic carbon-oxygen bond lengths show that double bond character can be delocalised from the ketone to the deprotonated phenoxide across the conjugated pi system of the fluorone. (C) 2009 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.DOI:10.1016/j.molstruc.2008.12.020
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Reliable Synthesis of 9-Aryl-Substituted 2,6,7-Trihydroxyxanthen-3-ones摘要:2,6,7-三羟基xanthen-3-酮是通过在关键步骤中使用碱金属过氧硫酸盐的一锅法可靠制备的。氘代氢氧化钠中的核磁共振谱证实了预期的结构,并允许通过内标测定染料含量。DOI:10.1055/s-2008-1078447
-
作为试剂:参考文献:名称:Colorimetric and fluorometric determination of homocysteine and cysteine摘要:揭示了用于快速、准确、选择性和廉价检测同型半胱氨酸,或同型半胱氨酸和半胱氨酸,或半胱氨酸的比色法和荧光法。这些方法可以与商业上易获得的材料一起使用。这些新颖的方法对同型半胱氨酸、半胱氨酸或总同型半胱氨酸和半胱氨酸具有选择性,并且不会与谷胱甘肽等化学相关物质发生明显的交叉反应。同型半胱氨酸选择性方法对与之非常密切相关的半胱氨酸没有重大的交叉反应。半胱氨酸选择性方法对与之非常密切相关的同型半胱氨酸没有重大的交叉反应。这些方法可以用于直接检测人类血浆中的同型半胱氨酸水平,例如。公开号:US09201075B2
文献信息
-
Synthesis, Structure and Cation-Binding Properties of Some [4 + 4] Metallocyclic MO<sub>2</sub><sup>2+</sup> (M = Mo or W) Derivatives of 9-Phenyl-2,3,7-trihydroxyfluor-6-one作者:Laura J. McCormick、Brendan F. Abrahams、Berin A. Boughton、Martin J. Grannas、Timothy A. Hudson、Richard RobsonDOI:10.1021/ic402860r日期:2014.2.3The trianion Z3– obtained from 9-phenyl 2,3,7-trihydroxyfluor-6-one, ZH3, affords dioxomolybdenum and dioxotungsten derivatives which contain [4 + 4] metallocycles of composition [(MO2)4Z4]4– (M = Mo, W) in combination with a variety of counter cations. The syntheses, structures and ESMS of the following compounds are presented: compound 1, (MePPh3)3(NBu4)[(MoO2)4Z4]; compound 2, (MePPh3)3(NBu4)[(WO2)4Z4];由9-苯基2,3,7-三羟基氟-6-一(ZH 3)获得的三阴离子Z 3–得到二氧钼和二氧钨衍生物,它们包含[4 + 4]组成为[(MO 2)4 Z 4 ] 4的金属环。 –(M = MO,W)与各种抗衡阳离子组合。给出了以下化合物的合成,结构和ESMS:化合物1,(MePPh 3)3(NBu 4)[(MOO 2)4 Z 4 ];化合物2,(MePPh 3)3(NBu 4)[(WO2)4 Z 4 ]; 化合物3,(MePPh 3)4 [(WO 2)4 Z 4 ];化合物4,(PPh 4)2(NBu 4)2 [(MOO 2)4 Z 4 ];化合物5,(AsPh 4)3(NBu 4)[(MOO 2)4 Z 4 ];化合物6,(AsPh 4)2(NBu 4)2 [(WO 2)4 Z 4 ]; 化合物7,(Ph 3 PNPPh 3)(NBu 4)3 [(MOO 2)4 Z 4 ];化合物8,(Ph 3
-
Synthesis and Characterization of Dianionic Hexacoordinate Silicon(IV) Complexes of Substituted Catechols, Flavones, and Fluorone: X-Ray Crystal Structures of [(<i>n</i>-C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>7</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>]<sub>2</sub>[(Cl<sub>4</sub>C<sub>6</sub>O<sub>2</sub>)<sub>3</sub>Si] · 3 CH<sub>3</sub>CN and [(<i>n</i>-C<sub>3</sub>H<sub>7</sub>)<sub>2</sub>NH<sub>2</sub>]<sub>2</sub>[(Br<sub>4</sub>C<sub>6</sub>O<sub>2</sub>)<sub>3</sub>Si] · 2 (CH<sub>3</sub>)<sub>2</sub>SO作者:Adinarayana Doddi、J. V. Kingston、V. Ramkumar、Mika Suzuki、Masashi Hojo、M. N. Sudheendra RaoDOI:10.1080/10426507.2011.613078日期:2012.3.1state structures of compounds [(n-C3H7)2NH2]2[Cl4C6O2}3Si] (1) and [(n-C3H7)2NH2]2[Br4C6O2}3Si] (2) were determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction. Both 1 and 2 crystallize in the monoclinic space group C2/c and reveal (i) bidentate mode of ligation, (ii) octahedral coordination around silicon, and (iii) hydrogen bonding features. Supplemental materials are available for this article. Go to the摘要 四乙氧基硅烷 (TEOS) 与取代的儿茶酚 (IX)、7,8-二羟基黄酮 (XI)、3,3',4'-三羟基黄酮 (XII)、3',4',5,7-四羟基黄酮 (XIII) 的反应和 9-苯基-2,3,7-三羟基-6-氟酮 (XIV) 在乙腈中的胺(摩尔比 1:3:2)存在下得到相应的双阴离子六配位硅 (IV) 配合物 1-15具有“SiO6”结构片段。双阴离子硅酸盐被分离为二正丙基铵/三乙基铵/二正丁基铵盐,并通过元素分析和各种光谱数据(IR、1H、13C 和 29Si NMR)进行表征。化合物[(n-C3H7)2NH2]2[Cl4C6O2}3Si](1)和[(n- )2NH2]2[Br4C6O2}3Si](2)的固态结构由单晶X-射线衍射。1 和 2 在单斜空间群 C2/c 中结晶并揭示 (i) 双齿连接模式,(ii) 硅周围的八面体配位,以及 (iii) 氢键特征。补充材
-
Mono- and Dinuclear Ruthenium Carbonyl Complexes with Redox-Active Dioxolene Ligands: Electrochemical and Spectroscopic Studies and the Properties of the Mixed-Valence Complexes作者:Andrew P. Meacham、Kathryn L. Druce、Zöe R. Bell、Michael D. Ward、Jerome B. Keister、A. B. P. LeverDOI:10.1021/ic034579o日期:2003.12.1and accordingly the complexes were studied by electrochemistry and UV/vis/NIR, IR, and EPR spectroscopy in their accessible oxidation states. Oxidation of 1 to [1](+) generates a ligand-centered semiquinone radical with some metal character as shown by the IR and EPR spectra. Dinuclear complexes [2](+) and 3 show two reversible ligand-centered couples (one associated with each dioxolene terminus) which单核络合物[Ru(PPh(3))(2)(CO)(2)(L(1))](1; H(2)L(1)= 7,8-二羟基-6-甲氧基香豆素)和双核络合物[[Ru(PPh(3))(2)(CO)(2)](2)(L(2))] [PF(6)] [[2] [PF(6)];H(3)L(2)= 9-苯基-2,3,7-三羟基-6-芴]和[[Ru(PBu(3))(2)(CO)(2)](2)(L (3))](3; H(4)L(3)= 1,2,3,5,6,7-六羟基蒽-9,10-二酮);所有配合物均包含一个或两个反式,顺-[Ru(PR(3))(2)(CO)(2)]单元,每个单元均与螯合二氧戊烯型配体连接。在所有情况下,二氧戊烯配体均表现出可逆的氧化还原活性,因此通过电化学和UV / vis / NIR,IR和EPR光谱研究了络合物的可氧化态。将1氧化为[1](+)会生成以配体为中心的半醌自由基,该自由基具有某些金属特性,如
-
Un réactif spécifique du germanium: la phénylfluorone作者:J Gillis、J. Hoste、lA. ClaeysDOI:10.1016/s0003-2670(00)89745-7日期:——ce reactif pour la recherche du germanium. Il s'agit d'eluer par HCl 6N pour rendre cette reaction specifique. Toutefois un autre derive de la fluorone, a savoir la phenylfluorone, convient mieux encore pour identifier le Ge(IV). Il suffit de porter une goutte de la solution fortement acide (de 3N a 6N en HCl) a analyser, sur un papier-reactif porteur de phenylfluorone et d'eiuer par 2 ou 3 gouttes deResume En nous basant sur l'action de lamethylfluorone sur le Ge(IV), nous avons decrit la possibilite d'employer ce reactif pour la recherche du Germanium。Il s'agit d'eluer par HCl 6N pour rendre cette 反应特异性。Toutefois un autre 衍生出 de la fluorone,a savoir la phenylfluorone,convient mieux encore pour identifier le Ge(IV)。Il suffit de porter une goutte de la solution fortement acide (de 3N a 6N en HCl)
-
Polynuclear osmium–dioxolene complexes: comparison of electrochemical and spectroelectrochemical properties with those of their ruthenium analogues作者:Anita M. Barthram、Zöe R. Reeves、John C. Jeffery、Michael D. WardDOI:10.1039/b004858p日期:——(where OO denotes a dioxolene binding site in any oxidation state). The complexes exhibit rich electrochemical behaviour, displaying a combination of metal-centred OsIII–OsII couples (as reductions) and ligand-centred couples (as oxidations). UV/VIS/NIR spectroelectrochemical analysis was carried out on all three complexes in all accessible oxidation states, and the spectra were assigned with reference[OS(bipy)2 Cl 2 ](比比 = 2,2'-联吡啶)与poly-二氧戊环 配体 3,4,3',4'-四羟基联苯(H 4 L 1),2,3,6,7-三羟基-9-苯基黄嘌呤-3-一(H 3 L 2)或2,3,6,7,10,11-六羟基联苯(H 6大号3)得到配合物[OS(联吡啶)2 } 2(μ-L 1)] [PF 6 ] 2,[OS(联吡啶)2 } 2(μ-L 2)] [PF 6 ] 3,和三核配合物[OS(联吡啶)2 } 3(μ-L 3)] [PF 6 ] 3缩写为[ O的2(L 1)] 2+,[ O的2(L 2)] 3 +和[ OS 2(L 3)] 3+。在这些复合物中,两个或三个OS III(bipy)2(OO)}片段通过共轭桥接连接配体(其中OO表示处于任何氧化态的二氧戊环结合位点)。该配合物表现出丰富的电化学行为,表现出以金属为中心的OS III –OS II对(
表征谱图
-
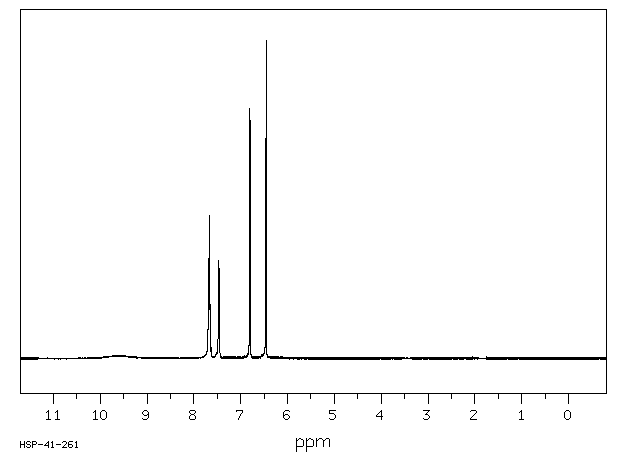
氢谱1HNMR
-
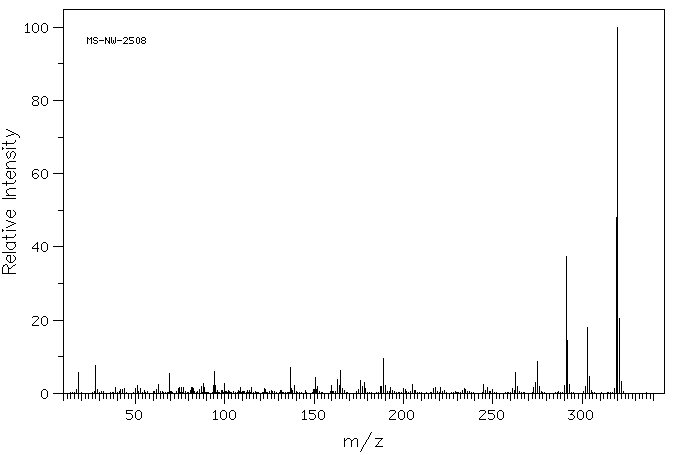
质谱MS
-
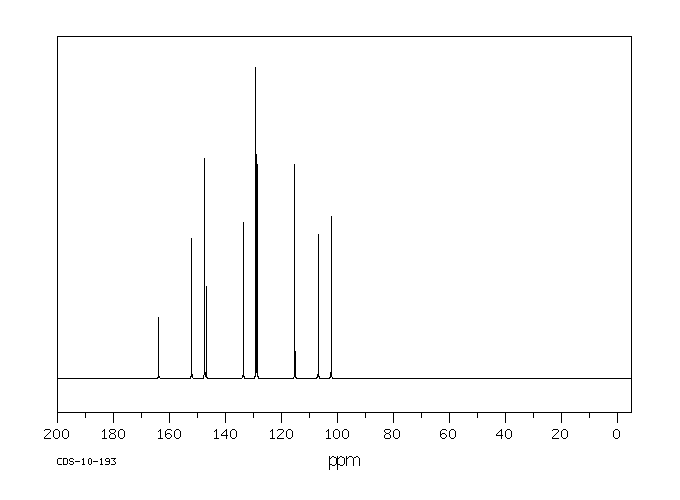
碳谱13CNMR
-
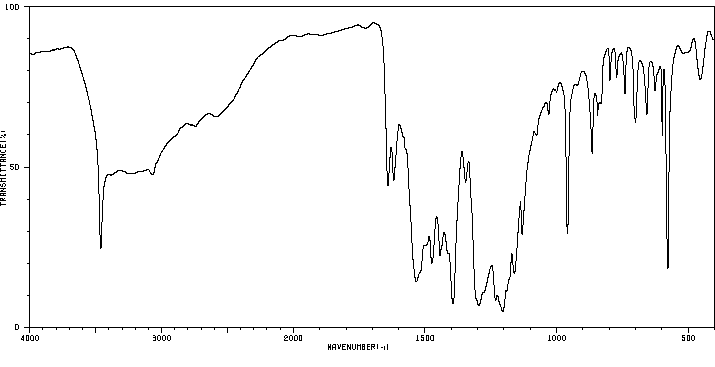
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-8-氟苯并二氢吡喃-4-胺
(2S)-6-氟-3,4-二氢-4-氧代-2H-1-苯并吡喃-2-甲酸
(2R)-6-氟-3,4-二氢-4-氧代-2H-1-苯并吡喃-2-甲酸
龙胆根素
龙胆SHAN酮
齿阿米素
黑色素-1
黄天精
麥角黃酮酸
鲍迪木醌
高邻苯二甲酸酐
高芒果苷
高氯酸罗丹明640
马佐卡林
香豆素-340
香豆素 339
食用色素红色105号
颜料红90:1铝色淀[CI45380:3]
颜料红172铝色淀[CI45430:1]
雏菊叶龙胆酮
降阿赛里奥; 1,3,6,7-四羟基氧杂蒽酮
阿米醇
阿米凯林
阿米凯林
阿扎那托
阿巴哌酮
阿尼地坦
阿尼地坦
阿匹氯铵
锌离子荧光探针-4
锆(2+)二[2-(2,4,5,7-四溴-3,6-二羟基氧杂蒽-9-基)-3,4,5,6-四氯苯甲酸酯]
铁力木呫吨酮-B
铁力木吨酮A
钠6'-羟基-5-[2-[4-(2-甲基-3-氧代-7H-咪唑并[1,2-d]吡嗪-6-基)苯氧基]乙基硫代氨基甲酰氨基]-3-氧代螺[2-苯并呋喃-1,9'-氧杂蒽]-3'-醇
钠4-{[6'-(二乙基氨基)-3'-羟基-3-氧代-3H-螺[2-苯并呋喃-1,9'-氧杂蒽]-2'-基]偶氮}-3-羟基-1-萘磺酸酯
钠2-(2,7-二氯-9H-氧杂蒽-9-基)苯甲酸酯
钙黄绿素乙酰甲酯
钙荧光探针Fluo-8,AM
钙荧光探针Fluo-4,AM
钙离子荧光探针
钙柑子
采木(HAEMATOXYLONCAMPECHIANUM)木质提取物
酸性媒介桃红3BM
邻苯三酚红
远志山酮III
转移核糖核酸(面包酵母)
赤藓红B异硫氰酸酯异构体II
赤藓红
诺大麻
西伯尔链接剂