7-肼-N,N-二-4-苯并呋咱磺 | 131467-86-2
中文名称
7-肼-N,N-二-4-苯并呋咱磺
中文别名
4-(N,N-二甲基氨基磺酰)-7-苯并恶二唑肼;4-(N,N-二甲氨基磺酰)-7-肼基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑;4-(N,N-二甲基氨磺酰)-7-肼-苯并呋咱;4-(N,N-二甲氨基磺酰)-7-肼基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑[用于高效液相色谱标记]
英文名称
4-(N,N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-7-hydrazino-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole
英文别名
4-(N,N-Dimethylsulfamoyl)-7-hydrazino-benzofurazan;7-hydrazinyl-N,N-dimethyl-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole-4-sulfonamide
CAS
131467-86-2
化学式
C8H11N5O3S
mdl
——
分子量
257.273
InChiKey
VPDDJYGQJSTHTA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:467.5±55.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.559±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-0.4
-
重原子数:17
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.25
-
拓扑面积:123
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:8
安全信息
-
危险等级:4.1
-
危险品标志:Xi
-
安全说明:S26,S36
-
危险类别码:R36/37/38
-
海关编码:2935009090
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 4-(N,N-二甲基胺磺酰基)-7-氟苯并呋喃 4-(N,N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-7-fluoro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole 98358-90-8 C8H8FN3O3S 245.234
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:7-肼-N,N-二-4-苯并呋咱磺 、 丙酮 生成 N,N-dimethyl-7-(2-propan-2-ylidenehydrazinyl)-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole-4-sulfonamide参考文献:名称:UZU, SONOKO;KANDA, SUSUMU;IMAI, KAZUHIRO;NAKASHIMA, KENICHIRO;AKIYAMA, SH+, ANALYST, 115,(1990) N1, C. 1477-1482摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:UZU, SONOKO;KANDA, SUSUMU;IMAI, KAZUHIRO;NAKASHIMA, KENICHIRO;AKIYAMA, SH+, ANALYST, 115,(1990) N1, C. 1477-1482摘要:DOI:
文献信息
-
A tetraester derivative of fluorescent calix[4]arene bearing a proton-ionizable moiety for highly sensitive extraction-fluorometric determination of sodium ion作者:Yoshio Nakahara、Yuta Furuno、Hitoshi Iwamoto、Setsuko Yajima、Keiichi KimuraDOI:10.1080/10610278.2018.1447110日期:2018.8.3Abstract In this study, we report the highly sensitive extraction-fluorometric detection system of Na+ using flow injection analysis with a tetraester derivative of fluorescent calix[4]arene. In liquid-liquid extraction experiments, the fluorescent intensity of calix[4]arene derivative 1 bearing a p-nitrophenol moiety was highly dependent on pH and the Na+ concentration in the aqueous phase. On the
-
JPH03258772A申请人:——公开号:JPH03258772A公开(公告)日:1991-11-19
表征谱图
-
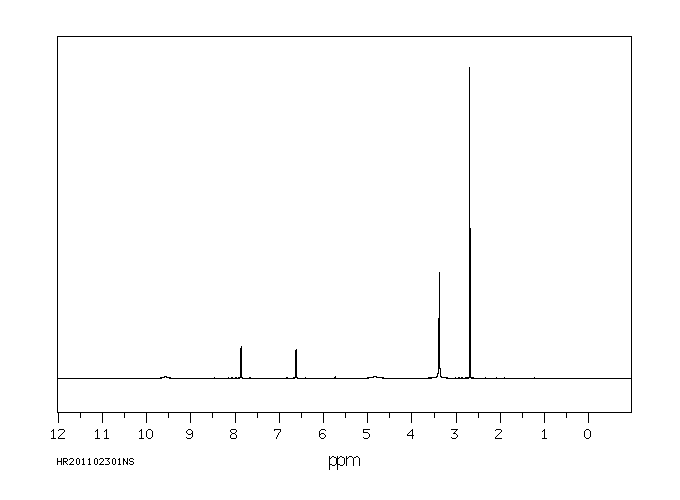
氢谱1HNMR
-
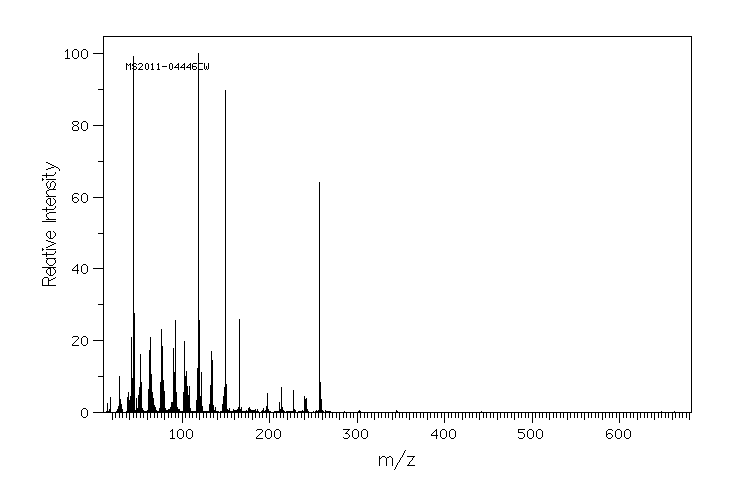
质谱MS
-
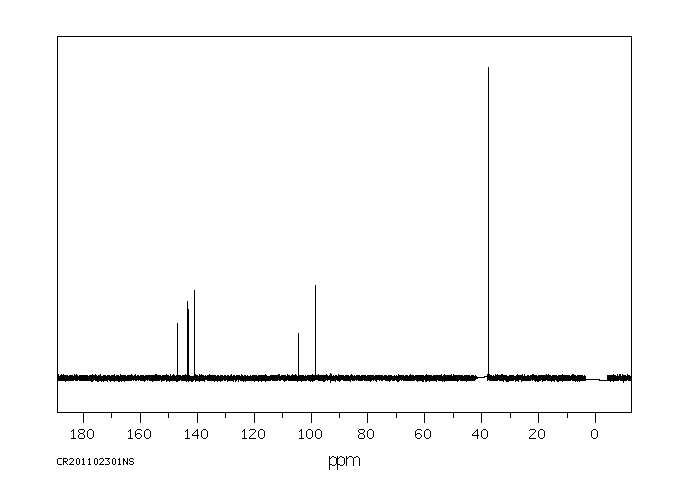
碳谱13CNMR
-
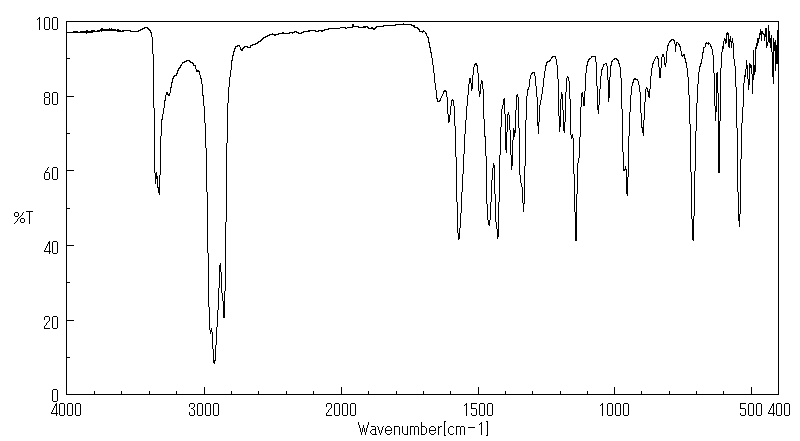
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
重氮二硝基苯酚
达罗地平
苯并芙咱-5-硼酸频那醇酯
苯并氧化呋咱-5-羧酸
苯并呋扎-5-甲腈
苯并呋喃-5-磺酰氯
苯并呋喃-5-甲酸乙酯
苯并呋喃
苯并呋咱-5-羧酸乙酯
苯并呋咱-5-羧酸
苯并呋咱-5-碳酰氯
苯并呋咱
苯并二唑-4-甲醛
苯呋咱-5-三氟硼酸钾
硝基氨基吡咯烷苯并恶嗪
哌嗪酮,6-甲基-5-硫代-,(R)-(9CI)
去甲基伊拉地平
伊拉地平内酯
伊拉地平EP杂质A
伊拉地平
乙酮,1-[5-(丁基氨基)-2-羟基苯基]-
NBD-双十六胺
N-[12-[((7-硝基-2-1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-基)氨基]十二烷酰基]-D-赤型-鞘氨醇
N-7-(4-硝基苯并-2-氧代-1,3-二氮唑)-omega-氨基己酸beta-(N-三甲基铵)乙酯
N-(7-硝基苯并-2-氧杂-1,3-二氮唑-4-基)磷脂酰乙醇胺
N-(3-氯-5-氟苯基)-4-硝基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-5-胺
N-(2-吗啉基乙基)-7-硝基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-胺
N,N-二甲基-7-硝基苯并呋咱-4-胺
N,N-二丁基-7-硝基-4-苯并呋咱胺
N'-[5-[[4-[5-(乙酰基-羟基氨基)戊基氨基]-4-氧代丁酰基]-羟基氨基]戊基]-N-羟基-N-[5-[(4-硝基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-7-基)氨基]戊基]丁二酰胺
EAM-1试剂
8-异米索前列醇
7-肼-N,N-二-4-苯并呋咱磺
7-硝基-N-[2-(2-吡啶基二硫代)乙基]-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-胺
7-硝基-1-氧代-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-1-鎓
7-甲氧基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-磺酰氯
7-氯苯并[c][1,2,5]噁二唑-4-胺
7-氯-N,N-二乙基-4-硝基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-5-胺
7-氯-4-硝基-5-哌啶基-2,1,3-苯并噁二唑
7-氯-4-硝基-2,1,3-苯并噁二唑1-氧化
7-氯-2,1,3-苯并噁二唑-4-磺酸
7-氟苯呋咱-4-磺酰胺
7-氟苯呋咱-4-硫氨
7-氟-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-磺酰氯
7-哌啶-1-基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-胺
7-吗啉-4-基苯并[1,2,5]恶二唑-4-基胺
6-溴苯并[c][1,2,5]噁二唑1-氧化物
6-氟-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-5-胺
6-[[7-(N,N-二甲氨基磺酰)-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-基]氨基]己酸琥珀酰亚胺酯
6-[(7-硝基-2,1,3-苯并恶二唑-4-基)氨基]己酸