媒介橙 1 | 2243-76-7
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:250°C
-
沸点:429.53°C (rough estimate)
-
密度:1.3681 (rough estimate)
-
溶解度:易溶于水、乙醇;微溶于丙酮
-
最大波长(λmax):385nm
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.1
-
重原子数:21
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:128
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:7
安全信息
-
危险品标志:Xn
-
安全说明:S24/25,S26
-
危险类别码:R22
-
WGK Germany:3
-
海关编码:2901100000
-
RTECS号:VO5310000
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 5-苯基叠氮水杨酸 2-hydroxy-5-phenylazo-benzoic acid 3147-53-3 C13H10N2O3 242.234 -
下游产品
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 5-[(4-氨基苯基)偶氮]-2-羟基苯甲酸 5-(4-amino-phenylazo)-2-hydroxy-benzoic acid 101-51-9 C13H11N3O3 257.249 —— 5-(4-nitrophenylazo)-2-(methacroyloxy)benzoic acid 1073928-78-5 C17H13N3O6 355.307 5-氨基水杨酸 5-Aminosalicylic Acid 89-57-6 C7H7NO3 153.137
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Grandmougin; Freimann, Journal fur praktische Chemie (Leipzig 1954), 1908, vol. <2>78, p. 402摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:Hewitt; Fox, Journal of the Chemical Society, 1901, vol. 79, p. 50摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:1-甲基-4-哌啶醇 、 4-三氟甲基苯磺酰氯 在 calcium hydride 、 媒介橙 1 作用下, 以 乙腈 为溶剂, 反应 24.0h, 以81%的产率得到(but-3-en-1-yl)-N-methyl-4-(trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonamide参考文献:名称:可见光光致电荷转移复合物促进了N-烷基-4-哌啶子醇的开环摘要:已在温和条件下实现了N-烷基-4-哌啶子醇的可见光光致开环。反应顺序涉及可见光诱导的电荷转移复合物,该复合物促进了磺酰氯的S–Cl键裂解。生成的磺酰基基团进一步与N-烷基-4-哌啶醇阳离子基团反应,实现C–N和C–C键裂解,生成高烯丙基胺产物。DOI:10.1039/d0gc00196a
文献信息
-
Synthesis and characterization of triorganotin(IV) complexes of 5-[(E)-2-(aryl)-1-diazenyl]-2-hydroxybenzoic acids.作者:Tushar S Basu Baul、Sushmita Dhar、Simon M Pyke、Edward R.T Tiekink、Eleonora Rivarola、Ray Butcher、Frank E SmithDOI:10.1016/s0022-328x(01)01024-5日期:2001.8The triphenyltin and tri-n-butyltin complexes of some 5-[(E)-2-(aryl)-1-diazenyl]-2-hydroxybenzoic acids have been synthesized and characterized by 1H-, 13C-, 119Sn-NMR, IR and 119mSn Mössbauer spectroscopic techniques in combination with elemental analysis. The crystal structures of triphenyltin 5-[(E)-2-(aryl)-1-diazenyl]-2-hydroxybenzoates (aryl=phenyl, 2-methylphenyl, 3-methylphenyl and 4-methoxyphenyl)的三苯基锡和三Ñ一些5 -butyltin络合物- [(ë)-2-(芳基)-1-二氮烯基] -2-羟基苯甲酸已经合成和表征通过1 H-,13 C-,119 Sn的NMR,IR和119m SnMössbauer光谱技术与元素分析相结合。报道了三苯基锡5-[(E)-2-(芳基)-1-二氮烯基] -2-羟基苯甲酸酯的晶体结构(芳基=苯基,2-甲基苯基,3-甲基苯基和4-甲氧基苯基)。X射线和119 SnMössbauer数据均表明三苯锡配合物采用单体扭曲的四面体构型,且羧酸盐配体以单齿模式配位。相比之下,119 SnMössbauer光谱表明,每个三丁基锡配合物都是聚合的,具有跨三角形的双锥体几何结构,具有平面的SnBu 3单元和两个双齿形的羧酸根配位体衍生而来的顶端的羧基氧原子。这是一种固态的效果,既是119 Sn-NMR的和1 Ĵ(13 C- 117分之119 Sn)的耦合常数的数据表明在溶液中四面体几何形状的三苯基-和三-
-
Alizarin Yellow-Modified β-Cyclodextrin as a Guest-Responsive Absorption Change Sensor作者:Taiyo Aoyagi、Asao Nakamura、Hiroshi Ikeda、Tsukasa Ikeda、Hisakazu Mihara、Akihiko UenoDOI:10.1021/ac960727z日期:1997.2.1Alizarin yellow-modified β-cyclodextrin (ACD), in which alizarin yellow is linked to β-cyclodextrin via an ethylenediamine spacer, was synthesized as a new absorption change indicator for molecules. Alizarin yellow is a pH indicator that exhibits absorption peaks at 360 and 480 nm in the neutral region and in the alkaline region, respectively, with pKa = 10.98 for an equilibrium between two forms. ACD has two parts to be deprotonated: one is the phenolic hydroxyl group of alizarin yellow residue and the other is the secondary amine group of the spacer. ACD exhibits pH dependency very different from that of alizarin yellow. We obtained two pKa values, 4.88 (pKa1) and 8.89 (pKa2), for ACD by pH titration of its absorption intensity. The pKa1 and pKa2 values were suggested to be the pKa values of the phenolic hydroxyl group of alizarin yellow residue and the secondary amine group, respectively. Upon addition of guest species, the pKa1 and pKa2 values shifted to 5.11 and 7.56, respectively, indicating a larger shift in the pKa for the amine group than for the hydroxyl group. The guest-induced pKa shift in the alkaline region suggests that deprotonation of the amine group of ACD occurs when the alizarin yellow moiety is excluded from the cyclodextrin cavity associated with guest accommodation and exposed to an alkaline environment. The sensitivities of this host to various guests were examined by absorption changes at 475 nm in pH 8.3 phosphate buffer, and the order of the sensitivities was found to be adamantane derivatives > borneol > bile acids. This order is not parallel with that of the binding constants, suggesting that the structural features of the host−guest complexes are important. All these results demonstrate that ACD can be used as an effective chemosensor for molecules.改性铝红黄β-环糊精(ACD)是通过乙二胺间隔物将铝红黄连接到β-环糊精上合成的新型分子吸收变化指示剂。铝红黄是一种pH指示剂,在中性区和碱性区分别在360 nm和480 nm处显示吸收峰,pKa = 10.98表示两种形式之间的平衡。ACD有两个需要去质子化的部分:一是铝红黄残基的酚羟基,另一是间隔物的二级胺基。ACD的pH依赖性与铝红黄有很大不同。通过对其吸收强度进行pH滴定,我们得到了两个pKa值,分别为4.88(pKa1)和8.89(pKa2)。pKa1和pKa2的值被认为分别是铝红黄残基的酚羟基和二级胺基的pKa值。当添加客体物种时,pKa1和pKa2值分别 shifted至5.11和7.56,表明胺基的pKa变化幅度大于羟基。碱性区域中客体引起的pKa变化暗示,当铝红黄基团从与客体适配的环糊精腔内排除并暴露于碱性环境中时,ACD的胺基发生去质子化。通过在pH 8.3的磷酸盐缓冲液中观察475 nm处的吸收变化,考察了该宿主对各种客体的敏感性,敏感性的顺序为:金刚烷衍生物 > borneol > 胆酸。这个顺序与结合常数的顺序不相符,表明宿主-客体复合物的结构特征很重要。所有这些结果表明,ACD可以作为有效的分子化学传感器。
-
Radical Arylation of Triphenyl Phosphite Catalyzed by Salicylic Acid: Mechanistic Investigations and Synthetic Applications作者:Manel Estruch-Blasco、Diego Felipe-Blanco、Irene Bosque、Jose C. Gonzalez-GomezDOI:10.1021/acs.joc.0c00795日期:2020.11.20arylphosphonates at 20 °C within 1–2 h is reported using inexpensive SA as the catalytic promoter of the reaction. Mechanistic investigations suggest that the reaction proceeds via radical–radical coupling, consistent with the so-called persistent radical effect. The reaction tolerated a wide range of functional groups and heteroaromatic moieties. The synthetic usefulness and the unique reactivity of the
-
A TEMPERATURE-JUMP STUDY OF INCLUSION REACTIONS OF<i>m</i>- AND<i>p</i>-NITROPHENYLAZOSALICYLIC ACID WITH α-CYCLODEXTRIN IN AQUEOUS SOLUTIONS作者:Noboru Yoshida、Masatoshi FujimotoDOI:10.1246/cl.1980.1377日期:1980.11.5Inclusion reactions of the title compounds with α-cyclodextrin were studied in aqueous solution by means of a temperature-jump method. The rate constants for inclusion reactions were found to be in the order of magnitude 106–107 mol−1 dm3 s−1.
-
The in situ generation and reactive quench of diazonium compounds in the synthesis of azo compounds in microreactors作者:Faith M Akwi、Paul WattsDOI:10.3762/bjoc.12.186日期:——
In this paper, a micro-fluidic optimized process for the continuous flow synthesis of azo compounds is presented. The continuous flow synthesis of Sudan II azo dye was used as a model reaction for the study. At found optimal azo coupling reaction temperature and pH an investigation of the optimum flow rates of the reactants for the diazotization and azo coupling reactions in Little Things Factory-MS microreactors was performed. A conversion of 98% was achieved in approximately 2.4 minutes and a small library of azo compounds was thus generated under these reaction conditions from couplers with aminated or hydroxylated aromatic systems. The scaled up synthesis of these compounds in PTFE tubing (i.d. 1.5 mm) was also investigated, where good reaction conversions ranging between 66–91% were attained.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
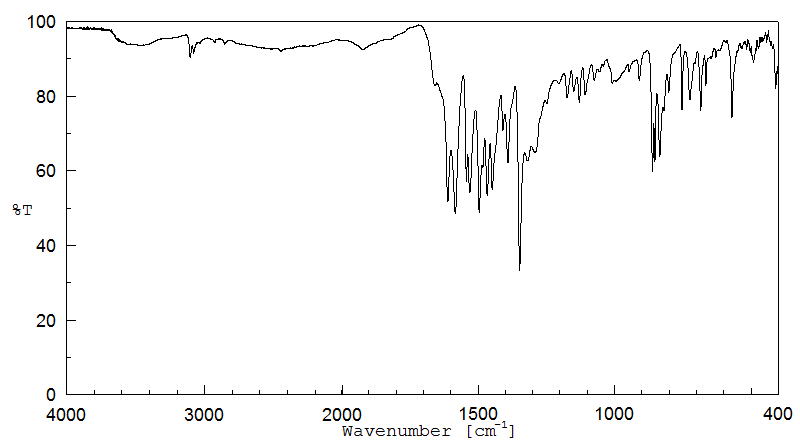
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息