乙二胺 | 107-15-3
中文名称
乙二胺
中文别名
乙撑二胺;1,2-二氨基乙烷;乙烯二胺;乙二胺,水合物;无水乙二胺;乙二胺(易制爆);乙亚胺;1,2-乙二胺,水合物;双酮嗪;亚胺-154;乙二胺(无水);二氨基乙烷;抗癌-161;1,2-乙二胺
英文名称
ethylenediamine
英文别名
Ethane-1,2-diamine;1,2-ethylenediamine;1,2-Diaminoethane;1,2-Ethanediamine;ethylendiamine;etylenediamine;EDA;ethanediamine;ethylene-1,2-diamine;ethyl diamine
CAS
107-15-3
化学式
C2H8N2
mdl
MFCD00008204
分子量
60.0989
InChiKey
PIICEJLVQHRZGT-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:8.5 °C
-
沸点:116-117 °C
-
密度:0.898 g/cm3(Temp: 25 °C)
-
物理描述:Ethylenediamine appears as a clear colorless liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Flash point of 91°F and a melting point of 47°F. Corrosive to tissue. Vapors are heavier than air. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen during combustion. Density 7.5 lb / gal. Used to make other chemicals and as a fungicide.
-
颜色/状态:Water-white liquid
-
气味:Ammonia-like
-
闪点:104 °F (40 °C) CLOSED CUP, 150 °F (66 °C) OPEN CUP /ANHYDROUS 76%/
-
溶解度:greater than or equal to 100 mg/mL at 63° F (NTP, 1992)
-
蒸汽密度:2.07 (EPA, 1998) (Relative to Air)
-
蒸汽压力:12.1 mm Hg @ 25 °C
-
亨利常数:1.73e-09 atm-m3/mole
-
自燃温度:385 °C (725 °F) /ANHYDROUS 76%/
-
分解:When heated to decomp it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides and ammonia/.
-
粘度:0.0154 cP @ 25 °C
-
燃烧热:-452.6 kg cal/g mol wt at 25 °C
-
汽化热:10510.5 gcal/gmole
-
电离电位:8.60 eV
-
气味阈值:Odor Threshold Low: 1.0 [mmHg]; Odor Threshold High: 11.0 [mmHg]; Odor threshold from CHEMINFO
-
折光率:Index of refraction: 1.4565 @ 20 °C/D
-
解离常数:pKa= 10.712; Ka= 1.94X10-11 at 0 °C (Step 1 in reaction)
-
相对蒸发率:0.91 (Butyl acetate= 1)
-
保留指数:600 ;612 ;625
-
稳定性/保质期:
-
化学性质:在空气中放置时吸湿,或吸收二氧化碳生成氨基甲酸盐(白色固体)。化学性质活泼,溶于水放热,水溶液呈强碱性。与无机酸反应生成结晶性和水溶性的盐。其硝酸盐加热时脱去2分子水,生成具有爆炸性的乙二硝胺。
-
与有机酸、酯、酸酐或酰卤反应,生成一取代酰胺或二取代酰胺。将一取代酰胺加热时,缩合生成2-烷基咪唑啉。与二元酸缩合生成聚酰胺树脂。与卤代烷反应得到一烷基或二烷基乙二胺。与丙烯腈反应生成腈乙基化合物。与环氧化合物反应生成加成化合物。与醛反应主要生成(Schiff)碱。与甲醛作用可得到组成复杂的混合物。与氯代乙酸反应得到乙二胺四乙酸盐(EDTA),是一种有用的螯合剂。与尿素、碳酸二乙酯、光气或二氧化碳反应,主要生成2-咪唑啉酮。在镍、钴或铜催化剂存在下加热到350℃可生成哌啶。与二硫化碳反应生成二硫代乙二氨基甲酸,加热脱去硫化氢得到聚硫脲树脂。
-
稳定性:稳定
-
禁配物:酸类、酰基氯、酸酐、强氧化剂
-
聚合危害:不聚合
-
分解产物:氨
-
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):-2
-
重原子数:4
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:0.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:1.0
-
拓扑面积:52
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:2
ADMET
代谢
雄性大鼠通过口服、气管内和静脉注射途径分别给予5、50或500毫克/千克的(14)C-乙二胺(EDA)。6到9%的管理放射性通过呼出的空气以(14)CO2的形式排出。主要代谢物n-乙酰乙二胺约占尿液放射性的半数。根据剂量水平的不同,2-49%的放射性保持为未改变的母体化合物。给药途径似乎并未改变代谢轮廓。
Male rats were dosed with (14)C-ethylenediamine (EDA) at 5, 50, or 500 mg/kg by oral, endotracheal, and iv routes. Six to 9% of the admin radioactivity was eliminated via expired air in the form of (14)CO2. n-Acetylethylenediamine, a major metabolite, accounted for approx half of the urinary radioactivity. Depending on the dosage level, 2-49% of the radioactivity was unchanged parent cmpd. The route of admin did not appear to change the metabolic profile.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
癌症分类:D组 不可归类为人类致癌性
Cancer Classification: Group D Not Classifiable as to Human Carcinogenicity
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
分类:D;无法归类为人类致癌性。分类依据:没有人类数据,动物数据不足。人类致癌性数据:无。动物致癌性数据:不足。
CLASSIFICATION: D; not classifiable as to human carcinogenicity. BASIS FOR CLASSIFICATION: Based on no human data and inadequate animal data. HUMAN CARCINOGENICITY DATA: None. ANIMAL CARCINOGENICITY DATA:Inadequate.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
A4:不能分类为人类致癌物。
A4: Not classifiable as a human carcinogen.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
毒理性
这种物质可以通过吸入、皮肤接触和摄入被身体吸收。
The substance can be absorbed into the body by inhalation, through the skin and by ingestion.
来源:ILO-WHO International Chemical Safety Cards (ICSCs)
毒理性
吸入,皮肤吸收,吞食,皮肤和/或眼睛接触
inhalation, skin absorption, ingestion, skin and/or eye contact
来源:The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH)
吸收、分配和排泄
口服给药后,其生物利用度约为0.34,这是由于显著的首过效应。
After oral administration its bioavailability is about 0.34, due to a substantial first-pass effect.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
肾脏对未改变物质的排泄在静脉给药后约为18%,口服给药后约为3%。
Renal excretion of the unchanged substance amounts to only about 18% after intravenous and 3% after oral administration.
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
Vd = 0.133 升/千克
Vd = 0.133 l/kg
来源:DrugBank
吸收、分配和排泄
/Diamines/ 通过皮肤吸收。 /Diamines/
/Diamines/ are absorbed through the skin. /Diamines/
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
吸收、分配和排泄
雄性大鼠通过口服、气管内和静脉注射途径给予(14)C-乙二胺(EDA),剂量为5、50或500毫克/千克。尿液排泄是消除的主要途径,占总放射性剂量的42至65%。粪便排泄量为5-32%,具体取决于给药途径。以二氧化碳的形式通过呼出空气排出的比例为6至9%。在48小时内,11-21%的放射性物质残留在各种器官和尸体中。甲状腺、骨髓、肝脏和肾脏含有相对较高的浓度。给药途径似乎没有改变代谢轮廓。随着剂量从5增加到50再到500毫克/千克,乙二胺呈现出累积模式,相应的代谢物形成减少。
Male rats were dosed with (14)C-ethylenediamine (EDA) at 5, 50, or 500 mg/kg by oral, endotracheal, and iv routes. Urinary excretion was the primary route of elimination accounting for 42 to 65% of the admin radioactivity. Fecal excretion was 5-32%, depending upon the route. Six to 9% was eliminated via expired air in the form of CO2. At 48 hr, 11-21% of radioactivity remained in the various organs & the carcass. Thyroid, bone marrow, liver, and kidney contained relatively higher concn. The route of admin did not appear to change the metabolic profile. As the dosage incr from 5 to 50 to 500 mg/kg, there was a pattern of accumulation of ethylenediamine with a corresponding decr of metabolite formation.
来源:Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB)
安全信息
-
危险品标志:C
-
安全说明:S23,S26,S36/37/39,S45
-
危险类别码:R34,R21/22,R10,R42/43
-
WGK Germany:2
-
RTECS号:KH8575000
-
海关编码:2921211000
-
包装等级:II
-
危险类别:8
-
危险标志:GHS02,GHS05,GHS06,GHS08
-
危险品运输编号:UN 1604 8/PG 2
-
危险性描述:H226,H302 + H332,H311,H315,H317,H318,H334,H412
-
危险性防范说明:P261,P273,P280,P305 + P351 + P338,P342 + P311
制备方法与用途
根据您提供的信息,乙二胺可以通过以下几种方法来制备:
-
使用Na-MOR和活性氧化铝作为催化剂,通过氨气与二氯乙烷在固定床反应器中合成:
- 首先制备NH4-MOR。将一定浓度的氯化铵溶液加入到Na型分子筛(Na-MOR)中,在回流搅拌离子交换器中加热回流4-12小时,然后抽滤、烘干,得到NH4-MOR。
- 将NH4-MOR与活性氧化铝混合,造粒并制成片状催化剂。
- 在500℃下煅烧该催化剂以获得强酸性选择性催化剂。
之后,在通用型常压固定床反应装置中进行乙二胺的合成。将氨气和惰性气体氮气预热后通入催化反应器,反应温度在320-390℃之间,氨与单乙醇胺摩尔比为36-70,压力控制在0.5-0.7MPa,主要产物为乙二胺和哌嗪(PIP)。
-
其他方法:
这些制备过程中涉及的化学反应主要包括缩合反应。通过调整原料配比、反应温度及压力等参数可以控制产物的选择性和收率。此外,根据最终产品的应用领域不同,可能还需要进行精馏或其他提纯工艺以获得高纯度的乙二胺产品。
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Age Changes and Differences in Personality Traits and States of the Old and Very Old摘要:The purpose of this study was to examine stability and change in personality, traits and states for 3 age groups: centenarians, octogenarians, and sexagenarians. One hundred seventy-nine older adults participated in the 2-wave study.. Results concerning age-group differences indicated that centenarians scored higher in Suspiciousness but lower in Intelligence and Stress when compared with the other 2 age groups. Octogenarians were lower in the personality traits Intelligence, Dominance, and Conscientiousness when compared with sexagenarians. Octogenarians were lower in the personality state Arousal, but higher on Regression. Results from the longitudinal analyses for centenarians indicated lower scores for Sensitivity, but higher scores for Radicalism (both personality traits), as well as higher scores of Fatigue and Depression (personality, states) at follow-up. For the younger 2 age groups, age changes included higher scores for Sensitivity and Suspiciousness (personality traits). Stability scores for traits and states were considerably, lower for centenarians when compared with the younger age groups.DOI:10.1093/geronb/57.2.p144
-
作为产物:参考文献:名称:Zettel, Monatshefte fur Chemie, 1893, vol. 14, p. 229摘要:DOI:
-
作为试剂:描述:2-碘-9,9-二甲基芴 在 三氟化硼乙醚 、 silver(I) acetate 、 palladium diacetate 、 乙二胺 作用下, 以 甲苯 、 叔丁醇 为溶剂, 反应 108.0h, 生成参考文献:名称:通过非对映选择性 Pd(II) 催化 sp3C−H 功能化制备芴和芴酮非天然氨基酸基序摘要:描述了外消旋和对映体纯(D-和L-)芴或基于芴酮的新型非天然氨基酸支架的构建。完成了安装具有反立体化学的氨基酸基序的芴或芴酮基序文库,包括苯丙氨酸正缬氨酸、亮氨酸、正亮氨酸和2-氨基辛酸、丙氨酸和非α-氨基酸衍生物。这项工作对富集芴或芴酮基(芴基)非天然氨基酸支架做出了贡献。DOI:10.1002/ejoc.202400272
文献信息
-
PYRAZOLO[1,5a]PYRIMIDINE DERIVATIVES AS IRAK4 MODULATORS申请人:Arora Nidhi公开号:US20120015962A1公开(公告)日:2012-01-19Compounds of the formula I or II: wherein X, m, Ar, R 1 and R 2 are as defined herein. The subject compounds are useful for treatment of IRAK-mediated conditions.式I或II的化合物: 其中X,m,Ar,R1和R2如本文所定义。所述化合物对于治疗IRAK介导的疾病是有用的。
-
Pyrrole and Pyrazole Ring Closure in Heterogeneous Media作者:F. Texier-Boullet、B. Klein、J. HamelinDOI:10.1055/s-1986-31655日期:——Pyrroles and pyrazoles may be conveniently prepared by dispersing primary amines or hydrazines and 1,4- or 1,3-diketones, respectively, on alumina or clay (montmorillonite K 10) without solvent, keeping the mixture at 20°C or higher temperatures for 1-26 h, and then eluting the product with dichloromethane.
-
Melanocortin-4 receptor binding compounds and methods of use thereof申请人:Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Inc.公开号:US20040082779A1公开(公告)日:2004-04-29Provided are MC4-R binding compounds of the formula XVII: 1 wherein L 2 is a linker group, and P 1 , P 2 , P 3 , P 4 , Z 1 , Z 2 , Z 3 , Z 4 , Z 5 , t, s, and R are as described in the specification. Methods of using the compounds to treat MC4-R associated disorders, such as disorders associated with weight loss, are also provided.
-
Reversible covalent linkage of functional molecules申请人:Smith Mark公开号:US09295729B2公开(公告)日:2016-03-29The present invention relates to the use of a compound containing a moiety of formula (I) as a reagent for linking a compound of formula R1—H which comprises a first functional moiety of formula F1 to a second functional moiety of formula F2 wherein X, X′, Y, R1, F1 and F2 are as defined herein. The present invention also provides related processes and products. The present invention is useful for creating functional conjugate compounds, and specifically conjugates in which at least one of the constituent molecules carries a thiol group.本发明涉及使用含有式(I)的基团的化合物作为将具有式F1的第一功能基团的化合物R1-H与具有式F2的第二功能基团连接的试剂 其中X、X'、Y、R1、F1和F2如本文所定义。本发明还提供相关的工艺和产品。本发明适用于制备功能共轭化合物,特别是至少一种组分分子携带硫醇基团的共轭物。
-
Biphenylenes-xxxi作者:John W. Barton、Michael C. Goodland、Ken J. Gould、John F.W. Mcomie、W.Roderick Mound、Sadiq A. SalehDOI:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)99488-8日期:1979.1As possible routes to 1,4-diazabiphenylene and its 2,3-disubstituted derivatives we have studied the condensation of benzocyclobutene-1,2-dione (BBD) with various 1,2-diamines. Instead of giving the 1,4-diazabiphenylene ring system, BBD reacted with ethylenediamine, diaminomaleonitrile, 4,5-diaminopyrimidine, 2-aminopyridine, also 2,3- and 3,4-diaminopyridine to give, respectively, 2-o-carboxyphenylimidazolidinium作为制备1,4-二氮杂联苯及其2,3-二取代衍生物的可能途径,我们研究了苯并环丁烯1,2-二酮(BBD)与各种1,2-二胺的缩合反应。BBD与提供1,4-二氮杂联苯环体系不同的是,它与乙二胺,二氨基马来腈,4,5-二氨基嘧啶,2-氨基吡啶,2,3-和3,4-二氨基吡啶反应分别生成2-邻-羧基苯基咪唑啉乙酸甲酯4,3,4-二氰基-2,5-二氢[2,5] benzodiazocine -1,6-二酮10,4-氨基-5A,9B二氢-5-,9B二羟基苯并[3' ,4' ] cyclobuta [1' ,2'-4,5]咪唑并[1,2 ç ]嘧啶14,图5A,图9b二氢5α,9B二羟基苯并[3' ,4 '] cyclobuta [1',2'- 4,5]咪唑[1,中,4-氨基衍生物16,后者的,和两性离子18的4 -氨基-3-(2-羧基亚苄基)。然而,BBD与4,5- diaminobenzotriazole反应,得到预期的1
表征谱图
-
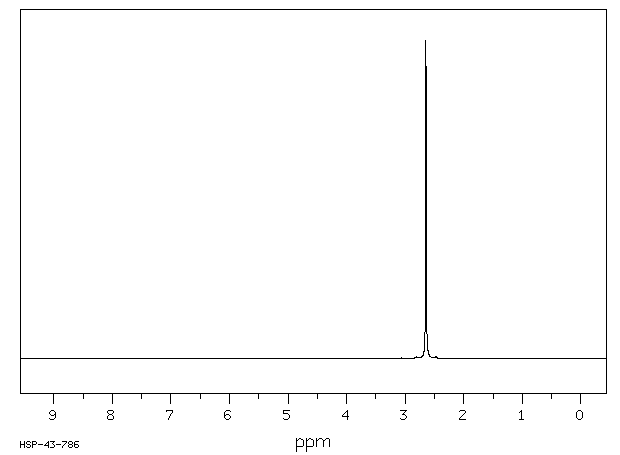
氢谱1HNMR
-
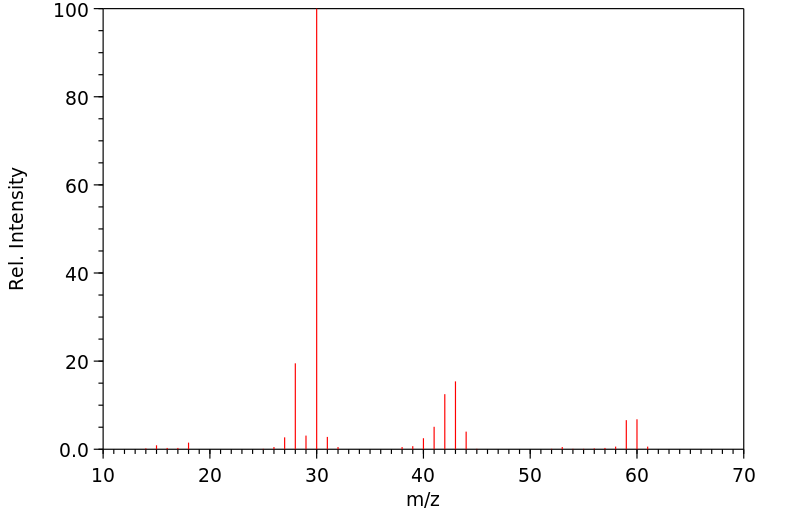
质谱MS
-
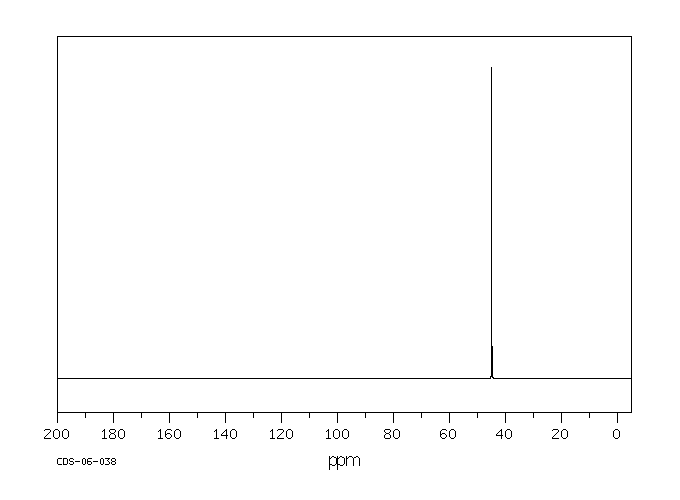
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(乙腈)二氯镍(II)
(R)-(-)-α-甲基组胺二氢溴化物
(N-(2-甲基丙-2-烯-1-基)乙烷-1,2-二胺)
(4-(苄氧基)-2-(哌啶-1-基)吡啶咪丁-5-基)硼酸
(11-巯基十一烷基)-,,-三甲基溴化铵
鼠立死
鹿花菌素
鲸蜡醇硫酸酯DEA盐
鲸蜡硬脂基二甲基氯化铵
鲸蜡基胺氢氟酸盐
鲸蜡基二甲胺盐酸盐
高苯丙氨醇
高箱鲀毒素
高氯酸5-(二甲氨基)-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-2-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-氯-1-({(E)-[4-(二甲氨基)苯基]甲亚基}氨基)-6-甲基吡啶正离子
高氯酸2-(丙烯酰基氧基)-N,N,N-三甲基乙铵
马诺地尔
马来酸氢十八烷酯
马来酸噻吗洛尔EP杂质C
马来酸噻吗洛尔
马来酸倍他司汀
顺式环己烷-1,3-二胺盐酸盐
顺式氯化锆二乙腈
顺式吡咯烷-3,4-二醇盐酸盐
顺式双(3-甲氧基丙腈)二氯铂(II)
顺式3,4-二氟吡咯烷盐酸盐
顺式1-甲基环丙烷1,2-二腈
顺式-二氯-反式-二乙酸-氨-环己胺合铂
顺式-二抗坏血酸(外消旋-1,2-二氨基环己烷)铂(II)水合物
顺式-N,2-二甲基环己胺
顺式-4-甲氧基-环己胺盐酸盐
顺式-4-环己烯-1.2-二胺
顺式-4-氨基-2,2,2-三氟乙酸环己酯
顺式-3-氨基环丁烷甲腈盐酸盐
顺式-2-羟基甲基-1-甲基-1-环己胺
顺式-2-甲基环己胺
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(苯基氨基)环己醇
顺式-2-(氨基甲基)-1-苯基环丙烷羧酸盐酸盐
顺式-1,3-二氨基环戊烷
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺二盐酸盐
顺式-1,2-环戊烷二胺
顺式-1,2-环丁腈
顺式-1,2-双氨甲基环己烷
顺式--N,N'-二甲基-1,2-环己二胺
顺式-(R,S)-1,2-二氨基环己烷铂硫酸盐
顺式-(2-氨基-环戊基)-甲醇
顺-2-戊烯腈
顺-1,3-环己烷二胺
顺-1,3-双(氨甲基)环己烷