三甲基(2-萘基)硅烷 | 18052-85-2
中文名称
三甲基(2-萘基)硅烷
中文别名
2-(三甲硅基)萘
英文名称
2-naphthyltrimethylsilane
英文别名
trimethyl(naphthalen-2-yl)silane;2-(trimethylsilyl)naphthalene
CAS
18052-85-2
化学式
C13H16Si
mdl
——
分子量
200.356
InChiKey
FSTJPXXIHGWZIV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.39
-
重原子数:14
-
可旋转键数:1
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.23
-
拓扑面积:0
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:0
SDS
上下游信息
-
上游原料
中文名称 英文名称 CAS号 化学式 分子量 —— (6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)trimethylsilane 18410-39-4 C14H18OSi 230.382
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:Palladium-Catalyzed Desilylative Acyloxylation of Silicon–Carbon Bonds on (Trimethylsilyl)arenes: Synthesis of Phenol Derivatives from Trimethylsilylarenes摘要:A strategy for desilylative acetoxylation of (trimethylsilyl)-arenes has been developed in which (trimethylsilyl)arenes are converted into acetoxyarenes. The direct acetoxylation is performed in the presence of 5 mol % of Pd(OAc)(2) and PhI(OCOCF3)(2) (1.5 equiv) in AcOH at 80 degrees C for 17 h. The acetoxyarenes are obtained in good to high yields (67-98%). The synthetic utility is demonstrated with a one-pot transformation of (trimethylsilyearenes to phenols by successive acetoxylation and hydrolysis. Furthermore, desilylative acyloxylation of 2-(trimethylsilyl)-naphthalene using several carboxylic acids has been conducted.DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02336
-
作为产物:描述:alkaline earth salt of/the/ methylsulfuric acid 在 copper(l) chloride 作用下, 以 四氢呋喃 为溶剂, 反应 2.0h, 以89%的产率得到三甲基(2-萘基)硅烷参考文献:名称:锆茂,铜介导的苯并环丁二烯与腈和炔烃的偶联反应中的萘,异喹啉和苯并唑嗪。摘要:[反应:见正文]市售的1-溴苯并环丁烯是一种潜在有用的合成子,尤其是在有机金属方法学的应用中。在这里我们表明,它很容易转化为Cp(2)Zr(苯并环丁二烯),它与炔烃或腈类偶联形成五元氧化锆环。用CuCl处理这些炔烃或腈衍生的氧化锆环可生成取代的萘,异喹啉或在MeO(2)C-CC-CO(2)Me(含有八元环的3-benzazocine)存在下进行[校正] 。DOI:10.1021/ol034040u
文献信息
-
Rhodium-Catalyzed Reductive Cleavage of Aryl Carbamates Using Isopropanol as a Reductant作者:Naoto Chatani、Mamoru Tobisu、Kosuke Yasui、Masaya HigashinoDOI:10.1055/s-0036-1589093日期:2017.12directing group in C–H bond-functionalization reactions, reductive removal of this directing group is not straightforward. Currently available methods are limited to nickel-catalyzed reactions using i PrMgX or hydrosilane as a reductant, leaving the functional group compatibility issue to be solved. Herein, we report rhodium-catalyzed reductive cleavage of aryl carbamates using i PrOH as a milder reductant
-
Gold-Catalysed Oxyarylation of Styrenes and Mono- and<i>gem</i>-Disubstituted Olefins Facilitated by an Iodine(III) Oxidant作者:Liam T. Ball、Guy C. Lloyd-Jones、Christopher A. RussellDOI:10.1002/chem.201103061日期:2012.3.51‐Hydroxy‐1,2‐benziodoxol‐3(1H)‐one (IBA) is an efficient terminal oxidant for gold‐catalysed, three‐component oxyarylation reactions. The use of this iodine(III) reagent expands the scope of oxyarylation to include styrenes and gem‐disubstituted olefins, substrates that are incompatible with the previously reported Selectfluor‐based methodology. Diverse arylsilane coupling partners can be employed
-
Silyloxyarenes as Versatile Coupling Substrates Enabled by Nickel-Catalyzed C–O Bond Cleavage作者:Eric M. Wiensch、David P. Todd、John MontgomeryDOI:10.1021/acscatal.7b02025日期:2017.9.1coupling processes. The C(sp2)–O bond of aryl silyl ethers is directly transformed into C–H or C–Si bonds using Ti(O-i-Pr)4 or trialkylsilanes as reagents using nickel catalysts with N-heterocyclic carbene (NHC) ligands. Paired with the useful characteristics of silyl protecting groups, these methods enable protected hydroxyls to directly participate in high-value bond-forming steps rather than requiring
-
Addition and Cyclization Reactions in the Thermal Conversion of Hydrocarbons with an Enyne Structure, 5. High-Temperature Ring Closures of 1,3-Hexadien-5-ynes to Naphthalenes – Competing Reactions via Isoaromatics, Alkenylidene Carbenes, and Vinyl-type Radicals作者:Jörg Hofmann、Kathrin Schulz、Annett Altmann、Matthias Findeisen、Gerhard ZimmermannDOI:10.1002/jlac.199719971218日期:1997.122-ethynylstyrenes 7a–c were subjected to high-temperature pyrolysis. The cycloisomerization products isolated suggest that these are formed by three competing processes: by (i) an electrocyclic or a molecule-induced, (ii) an alkenylidene carbene controlled, and (iii) a radical-controlled ring-closure process. To estimate the relative importance of these three reactions here mentioned, the substrates have
-
Sodium silylsilanolate enables nickel-catalysed silylation of aryl chlorides作者:Kenshiro Hitoshio、Hiroki Yamagishi、Jun Shimokawa、Hideki YorimitsuDOI:10.1039/d1cc02683f日期:——Structurally diverse aryl chlorides were silylated with sodium silylsilanolate reagents in the presence of a Ni(cod)2 catalyst complexed with a phosphine ligand; PMe2Ph for electron-rich substrates, and PCy2Ph for electron-deficient ones. The mild reaction conditions allowed the silylation of various aryl chlorides including functionalised drug molecules.
表征谱图
-
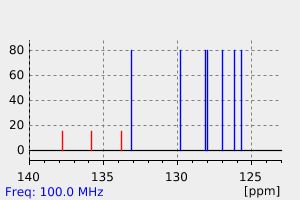
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮