1-(4-methoxyphenylazo)naphthalen-2-ol | 13411-91-1
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
1-(4-methoxyphenylazo)naphthalen-2-ol
英文别名
1-((4-methoxyphenyl)azo)-2-naphthol;1-({4-methoxyphenyl}diazenyl)naphthalen-2-ol;1-(4'-methoxybenzeneazo)-2-naphthol;Anisol-(4 azo 1)-naphthol-(2);1-(4-Methoxyphenylazo)-2-naphthol;1-[(4-methoxyphenyl)diazenyl]naphthalen-2-ol
CAS
13411-91-1
化学式
C17H14N2O2
mdl
MFCD00417049
分子量
278.31
InChiKey
XYVPTQBXFHRJJR-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:134-135 °C
-
沸点:482.2±25.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.19±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.1
-
重原子数:21
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.06
-
拓扑面积:54.2
-
氢给体数:1
-
氢受体数:4
SDS
上下游信息
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Charrier; Pellegrini, Gazzetta Chimica Italiana, 1913, vol. 43 II, p. 564摘要:DOI:
-
作为产物:描述:1,3-双(4-甲氧基苯基)脲 在 sodium hydroxide 、 亚硝酰氯 作用下, 以 乙醇 、 N,N-二甲基甲酰胺 为溶剂, 反应 2.08h, 生成 1-(4-methoxyphenylazo)naphthalen-2-ol参考文献:名称:Nitrosation of 1,3-diarylureas with nitrosyl chloride, dinitrogen trioxide and dinitrogen tetroxide in dimethylformamide.摘要:用亚硝基氯或三氧化二氮在二甲基甲酰胺中对1,3-二芳基脲(Ia-f)进行亚硝化反应,获得了1,3-二芳基-1-亚硝脲(IIa-f),产率为59-96%;而用四氧化二氮对1,3-二芳基脲(Ia, c-f)进行亚硝化,同样获得了1,3-二芳基-1-亚硝脲(IIa, c-f),产率为75-91%。然而,使用四氧化二氮对1,3-二(4-甲氧基苯基)脲(Ib)在二甲基甲酰胺中进行亚硝化反应,形成了1-(4-甲氧基-2-硝基苯基)-3-(4-甲氧基苯基)脲(III),产率为60%;而用过量四氧化二氮进行亚硝化,则获得了1,3-二(4-甲氧基-2-硝基苯基)脲(IV),产率为42%。DOI:10.1248/cpb.31.41
文献信息
-
One-pot synthesis of azo compounds in the absence of acidic or alkaline additives作者:Ting-Ting Liu、Jiao-Zhao Yan、Xin-Wang Cheng、Pan Duan、Yao-Fu ZengDOI:10.1177/1747519820964182日期:2021.5A one-pot method for the synthesis of azo compounds by the reaction of β-naphthol with aryl amines using t-BuONO as the nitrosonium source in DCM at room temperature was developed. This method feat...开发了一种以 t-BuONO 作为亚硝鎓源在室温下在 DCM 中通过 β-萘酚与芳胺反应合成偶氮化合物的一锅法。这种方法壮...
-
Studies of chelation. Part 9. Cobalt complexes of 1-[(substituted phenyl)azo]-2-naphthol and 1-[(substituted phenylimino)methyl]-2-naphthol ligands. Tautomerism and reactivity作者:Joseph A. Connor、David J. Fine、Raymond PriceDOI:10.1039/dt9810000559日期:——naphthalene rings is a critical feature of the chelation process. The formation of [Co(R-az)3] from [Co(R-az)2] and from [Co(R-Haz)2X2] in the presence of air occurs easily and is acid catalysed. [Co(R-sb)3] is formed only under vigorously oxidising conditions. The isoelectronic ligands R-Haz and R-Hsb should not be regarded as identical in their reactivity towards cobalt(II).光谱表征(1 H和13 C NMR,IR,拉曼光谱,和UV-可见光)的各种1 - [(取代的苯基)偶氮] -2-萘酚,R-哈兹(R = 4'--ME,4'- OMe,4'-Cl,H,2'-OMe,2'-Me,2'-Cl和2'-Br)和1-[(取代的苯基亚氨基)甲基] -2-萘,R-Hsb( R = 4'- OME,4'--ME,4'-氯,H,4'-BR,4'-CF 3,4'-CN,4'- NO 2,2'-OME,2'-ME ,2'-CHME 2,2'-氯,2'- CN,和2'-NO 2),在固体状态下和在极性和非极性溶剂中的溶液表明,氢键酮互变异构体在极性溶剂中占主导地位。钴(II)盐与R-Haz和R-Hsb在乙醇中反应生成[CoL 2 ],顺式-[Co(HL)2 X 2 ]和fac- [CoL 3 ](L = R-az或R-sb)。这些配合物中的配体的互变异构形式是通过振动光谱法建立的,在[Co(R-az)2
-
Fluorescent azo disperse dyes from 3-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-ol and comparison with 2-naphthol analogs作者:Manjaree A. Satam、Rajesh K. Raut、N. SekarDOI:10.1016/j.dyepig.2012.07.019日期:2013.1Five novel fluorescent azo disperse dyes were synthesized using different diazotized aromatic amines followed by coupling with 3-(1,3-benzothiazol-2-yl)naphthalen-2-ol. These dyes were characterized by FT-IR, 1H NMR and mass spectroscopy. These azo disperse dyes were applied on polyester and their fastness properties were evaluated. A parallel series of dyes using 2-naphthol in place of benzothiazolyl
-
Action mechanism of anti-AH13 activity of 1,3-diaryl-1-nitrosoureas and related compounds.作者:MICHIKO MIYAHARA、MAKOTO MIYAHARA、SHOZO KAMIYADOI:10.1248/cpb.32.564日期:——Administration of 1, 3-diaryl-1-nitrosoureas (I) prolonged the life span of rats inoculated intraperitoneally with ascites hepatoma AH13 cells. Active species produced from compound I were aryl diazonium ion, aryl isocyanate and nitrosonium ion. These species reacted with adenine, guanine, L-lysine, and the SH group of N-acetyl-DL-penicillamine. A possible anti-AH13 action mechanism of 1, 3-diaryl-1-nitrosoureas in proposed to be as follows. The nitrosoureas (I) permeate quickly into the cytoplasm or nucleus, and decompose to give an active intermediate, an aryl diazonium ion, which reacts with nucleic acids of tumor cells to form a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) adduct, followed by tumor cell death. DNA repair of other damaged cells is inhibited by aryl isocyanate and nitrosonium ion liberated from compound I, which reacts with repair enzyme to form carbamoylated and S-nitrosated enzyme.
-
Fe(HSO<sub>4</sub>)<sub>3</sub>as an Efficient Catalyst for Diazotization and Diazo Coupling Reactions作者:Mohammad Rahimizadeh、Hossein Eshghi、Ali Shiri、Zohreh Ghadamyari、Maryam M. Matin、Fatemeh Oroojalian、Parvaneh PordeliDOI:10.5012/jkcs.2012.56.6.716日期:2012.12.20Diazo coupling reactions of aromatic amines with 2-naphthol in a green, efficient and easy procedure is described. Ferric hydrogensulfate catalyses this reaction in water at room temperature and short reaction time with high yields. The antibacterial activities of the synthesized compounds against four pathogenic bacteria are also investigated.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
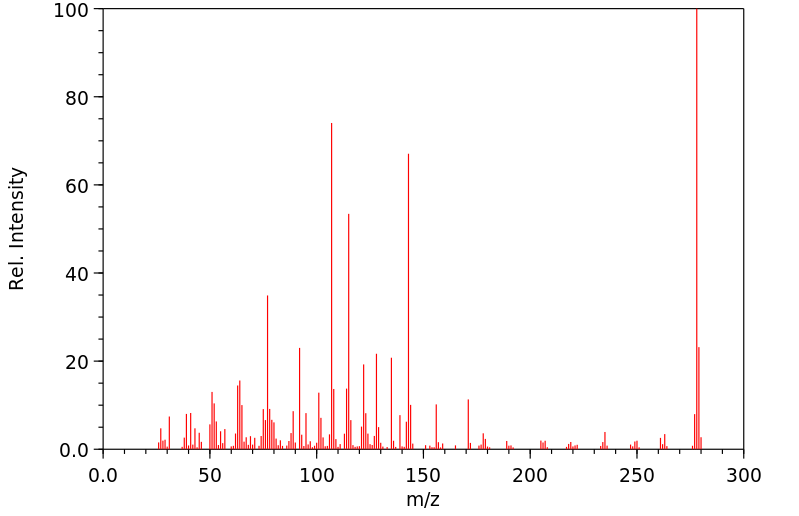
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮