2-N-isonicotinoyl-hydrazide-1,4-naphthoquinone | 22360-15-2
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
2-N-isonicotinoyl-hydrazide-1,4-naphthoquinone
英文别名
2-N'-(1,4-dihydro-1,4-dioxonaphthalen-2-yl)isonicotinohydrazide;N'-(1,4-dioxonaphthalen-2-yl)pyridine-4-carbohydrazide
CAS
22360-15-2
化学式
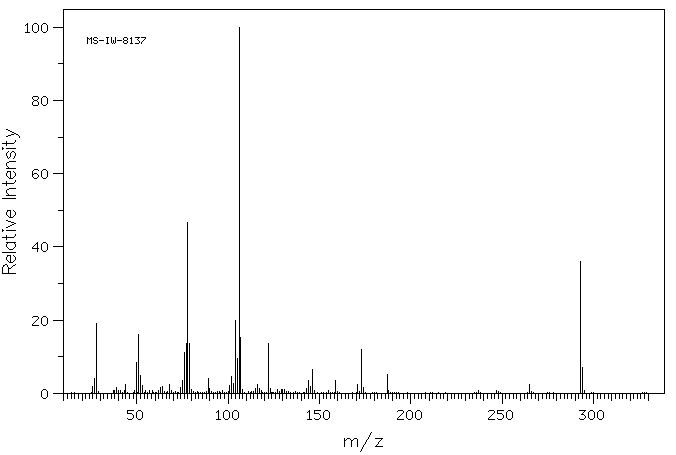
C16H11N3O3
mdl
——
分子量
293.282
InChiKey
BLPSOVCUUGYMIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
沸点:468.8±45.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.42±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):1.28
-
重原子数:22.0
-
可旋转键数:3.0
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.0
-
拓扑面积:88.16
-
氢给体数:2.0
-
氢受体数:5.0
反应信息
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:新功能化的1,4-萘醌衍生物的合成及其对四氧嘧啶致糖尿病小鼠伤口愈合的影响摘要:萘醌衍生物具有多种药理特性。在这里,我们描述了新的1,4-萘醌衍生物的合成,这些衍生物受Lawone和β-Lapachone的启发,它们对成纤维细胞的体外迁移和糖尿病小鼠皮肤伤口愈合的影响。NMR和FTIR光谱有助于化学成分的表征,并证明了在合成四种不同的衍生物(2-溴-1,4-萘醌(称为衍生物S3),2-N-苯基氨基-1,4-萘醌(衍生物S5),2-N-异烟酰酰肼-1,4-萘醌(衍生物S6)和1-N-异烟酰酰-[2-羟基-3-(3-甲基-2-丁烯基)]-1 ,4-萘醌(衍生物S7)。我们的结果表明,衍生物S3,S5,S6和S7对3T3成纤维细胞系无毒。在刮擦试验中,衍生物S3和S6而非成纤维细胞S5和S7刺激成纤维细胞的迁移。与未治疗的糖尿病小鼠相比,S3,S6和S7治疗可加速伤口闭合。但是,与衍生物S6相比,衍生物S3最适合刺激上皮形成,从而增加了角质形成细胞层和血管的数量,并减少了弥DOI:10.1016/j.cbi.2018.06.007
文献信息
-
Computer-aided design of 1,4-naphthoquinone-based inhibitors targeting cruzain and rhodesain cysteine proteases作者:Leandro Rocha Silva、Ari Souza Guimarães、Jadiely do Nascimento、Igor José do Santos Nascimento、Elany Barbosa da Silva、James H. McKerrow、Sílvia Helena Cardoso、Edeildo Ferreira da Silva-JúniorDOI:10.1016/j.bmc.2021.116213日期:2021.7
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
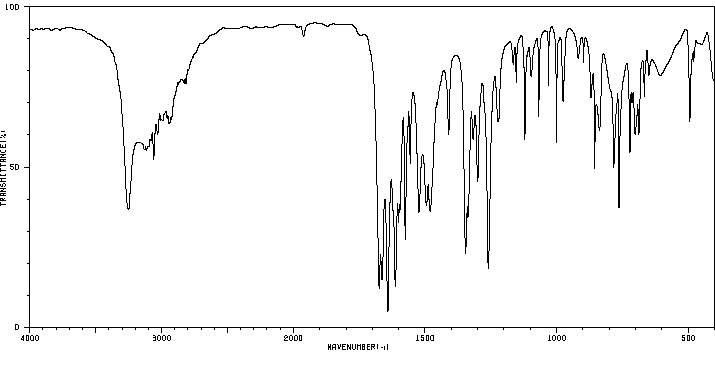
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮