levomepromazine maleate | 17086-29-2
中文名称
——
中文别名
——
英文名称
levomepromazine maleate
英文别名
Levomepromazin maleat;rac Methotrimeprazine Maleate Salt;(Z)-but-2-enedioic acid;3-(2-methoxyphenothiazin-10-yl)-N,N,2-trimethylpropan-1-amine
CAS
17086-29-2
化学式
C4H4O4*C19H24N2OS
mdl
——
分子量
444.552
InChiKey
IFLZPECPTYCEBR-BTJKTKAUSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:192 °C
-
溶解度:可溶于DMSO(少许)、甲醇(少许)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):4.21
-
重原子数:31
-
可旋转键数:7
-
环数:3.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.3
-
拓扑面积:116
-
氢给体数:2
-
氢受体数:8
反应信息
-
作为反应物:描述:参考文献:名称:左美丙嗪在不同溶剂中的光氧化机理摘要:不需要的光诱导反应是众所周知的大多数丙嗪药物的不良反应,包括左美丙嗪(LPZ、Levoprome® 或 Nozinan®)。这种药物在精神病学中主要用于治疗精神分裂症和其他分裂情感障碍。Levomepromazine 的特殊镇静特性使其特别适用于精神科重症监护。然而,它在有氧条件下在 UV-A 和 UV-B 光下是光不稳定的,导致其形成亚砜。乙腈 (MeCN) 中的 LPZ 光化学与甲醇 (MeOH) 和磷酸盐缓冲溶液 (PBS, pH = 7.4) 中的光化学完全不同。在有氧条件下,PBS 和 MeOH 中的主要光产物是左美丙嗪亚砜 (LPZSO),尽管在水性环境中的量要高得多。MeCN 中相应的主要光产物无法表征。LPZ 在 PBS、MeOH 和 MeCN 中的破坏量子产率分别为 0.13、0.02 和 <10-3。进一步证明 LPZSO 不是由单线态氧与基态 LPZ 反应形成的。这种氧化产物实际上是由LPZDOI:10.1111/php.12147
-
作为产物:描述:参考文献:名称:左美丙嗪在不同溶剂中的光氧化机理摘要:不需要的光诱导反应是众所周知的大多数丙嗪药物的不良反应,包括左美丙嗪(LPZ、Levoprome® 或 Nozinan®)。这种药物在精神病学中主要用于治疗精神分裂症和其他分裂情感障碍。Levomepromazine 的特殊镇静特性使其特别适用于精神科重症监护。然而,它在有氧条件下在 UV-A 和 UV-B 光下是光不稳定的,导致其形成亚砜。乙腈 (MeCN) 中的 LPZ 光化学与甲醇 (MeOH) 和磷酸盐缓冲溶液 (PBS, pH = 7.4) 中的光化学完全不同。在有氧条件下,PBS 和 MeOH 中的主要光产物是左美丙嗪亚砜 (LPZSO),尽管在水性环境中的量要高得多。MeCN 中相应的主要光产物无法表征。LPZ 在 PBS、MeOH 和 MeCN 中的破坏量子产率分别为 0.13、0.02 和 <10-3。进一步证明 LPZSO 不是由单线态氧与基态 LPZ 反应形成的。这种氧化产物实际上是由LPZDOI:10.1111/php.12147
文献信息
-
Kuzmicka, L.; Puzanowska-Tarasiewicz, H.; Tarasiewicz, M., Pharmazie, 1988, vol. 43, # 4, p. 288 - 289作者:Kuzmicka, L.、Puzanowska-Tarasiewicz, H.、Tarasiewicz, M.DOI:——日期:——
表征谱图
-
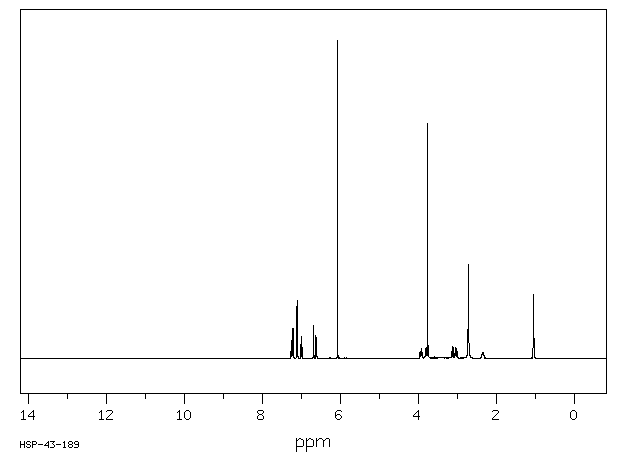
氢谱1HNMR
-
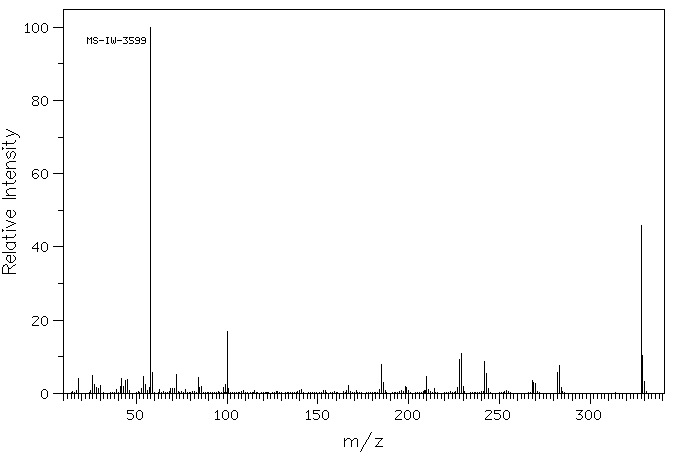
质谱MS
-
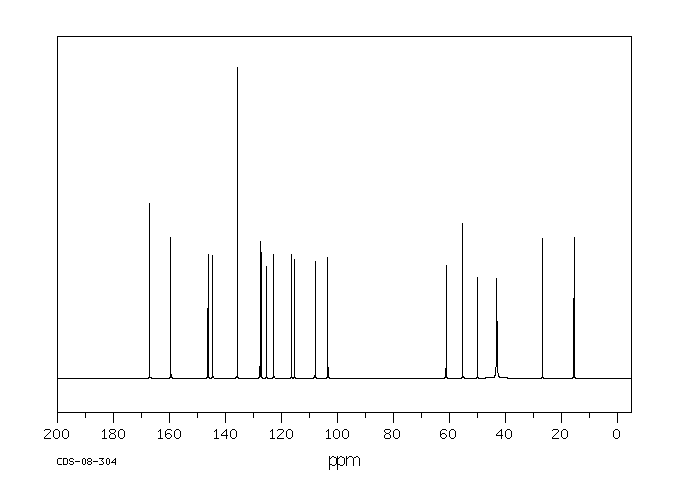
碳谱13CNMR
-
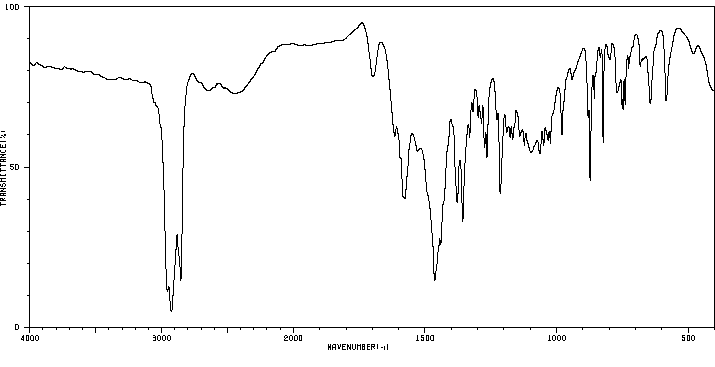
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
高氟奋乃静
马来酸甲哌丙嗪
马来酸奋乃静
马来酸乙巯拉嗪
锁匹达新
醋酸奋乃静
醋异丙嗪
酒石酸异丁嗪
还原亚甲蓝
达赛马嗪
螺氯丙嗪
莫雷西嗪亚砜
茶氯酸异丙嗪
苹果酸硫乙拉嗪
苯达莫司汀杂质A
苯甲酸2-(2H-1,4-苯并噻嗪-3-基)酰肼
苯甲酸,4-硝基-2-[[3-(三氟甲基)苯基]氨基]-
苯甲酰基氧基甲基-[3-(2-氯吩噻嗪-10-基)丙基]-二甲基氯化铵
苯并噻嗪-5-氧化
苯并噻嗪-5-正离子,3,7-二(二甲氨基)-4-碘-,氯化
苯并噻嗪,10-(2-(4-丙基-1-哌嗪基)丙基)-
苯并[b]吩噻嗪-12-基(苯基)甲酮
苯并[a]吩噻嗪-5-酮
苯丙嗪
苄酰基无色亚甲基兰
芬诺宁
芬乙嗪
舒多昔康
羟乙哌氟嗪
美索哒嗪
美索丙嗪
美洛昔康钾盐
美洛昔康钠
美洛昔康-d3
美洛昔康
美托奋乃酯
美托哌丙嗪酸
美托哌丙嗪
美托咪嗪-d6
美喹他嗪亚砜
美喹他嗪
磺达嗪
硫堇(劳氏紫)
硫利达嗪杂质A(EP)
硫利达嗪N-氧化物
硫利达嗪-5-亚砜
硫利达嗪
硫代哒嗪-d35-亚砜
硫丙拉嗪
盐酸诺美丙嗪