B-萘基丙酸酯 | 13080-43-8
中文名称
B-萘基丙酸酯
中文别名
——
英文名称
2-naphthyl propionate
英文别名
β-Naphthylpropionat;naphthalen-2-yl propanoate
CAS
13080-43-8
化学式
C13H12O2
mdl
MFCD00051170
分子量
200.237
InChiKey
KVMXEPJRCAPKJL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
BEILSTEIN
——
EINECS
——
-
物化性质
-
计算性质
-
ADMET
-
安全信息
-
SDS
-
制备方法与用途
-
上下游信息
-
文献信息
-
表征谱图
-
同类化合物
-
相关功能分类
-
相关结构分类
物化性质
-
熔点:48-51 °C
-
沸点:324.0±11.0 °C(Predicted)
-
密度:1.126±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted)
计算性质
-
辛醇/水分配系数(LogP):3.2
-
重原子数:15
-
可旋转键数:3
-
环数:2.0
-
sp3杂化的碳原子比例:0.153
-
拓扑面积:26.3
-
氢给体数:0
-
氢受体数:2
安全信息
-
海关编码:2915509000
SDS
反应信息
-
作为反应物:参考文献:名称:Structural Characterization and Function Determination of a Nonspecific Carboxylate Esterase from the Amidohydrolase Superfamily with a Promiscuous Ability To Hydrolyze Methylphosphonate Esters摘要:The uncharacterized protein Rsp3690 from Rhodobacter sphaeroides is a member of the amidohydrolase superfamily of enzymes. In this investigation the gene for Rsp3690 was expressed in Escherichia coli and purified to homogeneity, and the three-dimensional structure was determined to a resolution of 1.8 angstrom. The protein folds as a distorted (beta/alpha)(8)-barrel, and the subunits associate as a homotetramer. The active site is localized to the C-terminal end of the beta-barrel and is highlighted by the formation of a binuclear metal center with two manganese ions that are bridged by Glu-175 and hydroxide. The remaining ligands to the metal center include His-32, His-34, His-207, His-236, and Asp-302. Rsp3690 was shown to catalyze the hydrolysis of a wide variety of carboxylate esters, in addition to organophosphate and organophosphonate esters. The best carboxylate ester substrates identified for Rsp3690 included 2-naphthyl acetate (k(cat)/K-m = 1.0 x 10(5) M-1 s(-1)), 2-naphthyl propionate (k(cat)/K-m = 1.5 x 10(5) M-1 s(-1)), 1-naphthyl acetate (k(cat)/K-m = 7.5 x 10(3) M-1 s(-1)), 4-methylumbelliferyl acetate (k(cat)/K-m = 2.7 x 10(3) M-1 s(-1)), 4-nitrophenyl acetate (k(cat)/K-m = 2.3 x 10(5) M-1 s(-1)), and 4-nitrophenyl butyrate (k(cat)/K-m = 8.8 x 10(5) M-1 s(-1)). The best organophosphonate ester substrates included ethyl 4-nitrophenyl methylphosphonate (k(cat)/K-m = 3.8 x 10(5) M-1 s(-1)) and isobutyl 4-nitrophenyl methylphosphonate (k(cat)/K-m = 1.1 x 10(4) M-1 s(-1)). The (S-p)-enantiomer of isobutyl 4-nitrophenyl methylphosphonate was hydrolyzed 10 times faster than the less toxic (R-p)-enantiomer. The high inherent catalytic activity of Rsp3690 for the hydrolysis of the toxic enantiomer of methylphosphonate esters make this enzyme an attractive target for directed evolution investigations.DOI:10.1021/bi5004266
-
作为产物:描述:三甲基(2-萘基)硅烷 、 异丁酸 在 palladium diacetate 、 [双(三氟乙酰氧基)碘]苯 作用下, 以 溶剂黄146 为溶剂, 反应 17.0h, 以73%的产率得到B-萘基丙酸酯参考文献:名称:Palladium-Catalyzed Desilylative Acyloxylation of Silicon–Carbon Bonds on (Trimethylsilyl)arenes: Synthesis of Phenol Derivatives from Trimethylsilylarenes摘要:A strategy for desilylative acetoxylation of (trimethylsilyl)-arenes has been developed in which (trimethylsilyl)arenes are converted into acetoxyarenes. The direct acetoxylation is performed in the presence of 5 mol % of Pd(OAc)(2) and PhI(OCOCF3)(2) (1.5 equiv) in AcOH at 80 degrees C for 17 h. The acetoxyarenes are obtained in good to high yields (67-98%). The synthetic utility is demonstrated with a one-pot transformation of (trimethylsilyearenes to phenols by successive acetoxylation and hydrolysis. Furthermore, desilylative acyloxylation of 2-(trimethylsilyl)-naphthalene using several carboxylic acids has been conducted.DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b02336
文献信息
-
Electrostatic catalysis by ionic aggregates: scope and limitations of Mg(ClO4)2 as acylation catalyst作者:Asit K Chakraborti、Lalima Sharma、Rajesh Gulhane、ShivaniDOI:10.1016/j.tet.2003.08.007日期:2003.9Alkali and alkaline earth metal perchlorates exhibit electrostatic catalysis in the activation of anhydrides for the acylation reaction. Perchlorates with higher values of the charge-size function of the metal ion exhibit better catalytic activity following the order Mg(ClO4)2>Ba(ClO4)2>LiClO4. Acylation of structurally diverse phenols, thiols, alcohols, and amines have been carried out with stoichiometric
-
Magnesium Bistrifluoromethanesulfonimide as a New and Efficient Acylation Catalyst作者:Asit K. Chakraborti、ShivaniDOI:10.1021/jo0605142日期:2006.7.1room temperature and in short times. Electron-deficient and sterically hindered phenols provided excellent yields. The catalyst was found to be general for acylation with other anhydrides, such as propionic, isobutyric, pivalic, chloroacetic, and benzoic anhydrides. The rate of acylation was influenced by the electronic and steric factors associated with the anhydride. The reaction with less electrophilic
-
Indium(III) chloride as a new, highly efficient, and versatile catalyst for acylation of phenols, thiols, alcohols, and amines作者:Asit K. Chakraborti、Rajesh GulhaneDOI:10.1016/s0040-4039(03)01641-1日期:2003.8Indium(III) chloride efficiently catalyses the acylation of structurally diverse phenols, alcohols, thiols, and amines under solvent free conditions. Acid sensitive alcohols are smoothly acylated without competitive side reactions. Acylation of 2-hydroxynaphthalene is carried out with carboxylic acids adopting the mixed anhydride protocol using trifluoroacetic anhydride.
-
Na2CO3-Catalyzed O-Acylation of Phenols for the Synthesis of Aryl Carboxylates with Use of Alkenyl Carboxylates作者:Xiao-Yu Zhou、Xia ChenDOI:10.1055/s-0037-1610265日期:2018.10phenol and its derivatives has been developed. The procedure provides an efficient catalysis system for the preparation of aryl carboxylates with alkenyl carboxylates as acyl reagents. The reaction proceeded smoothly by using Na2CO3 as the catalyst in MeCN to produce the corresponding aryl carboxylates in good to excellent yields.
-
METHOD FOR PRODUCING CARBOXYLIC ACID AMIDE申请人:Tomokawa Junichi公开号:US20130123505A1公开(公告)日:2013-05-16A carboxamide can be produced in a high yield by a method for producing a carboxamide, for example, represented by formula (4): (wherein R 1 and R 3 are as defined below), the method comprising a step of allowing a carboxylic acid ester represented by formula (1): (wherein R 1 represents an optionally substituented C 1 -C 20 hydrocarbon group or an optionally substituented C 3 -C 20 heterocyclic group, and R 2 represents an optionally substituented C 1 -C 20 hydrocarbon group), an amine represented by formula (2): R 3 —NH 2 (2) (wherein R 3 represents a hydrogen atom or an optionally substituented C 1 -C 20 hydrocarbon group), and a formamide compound represented by formula (3): (wherein R 3 is as defined above) to react in the presence of a metal alkoxide.
表征谱图
-
氢谱1HNMR
-
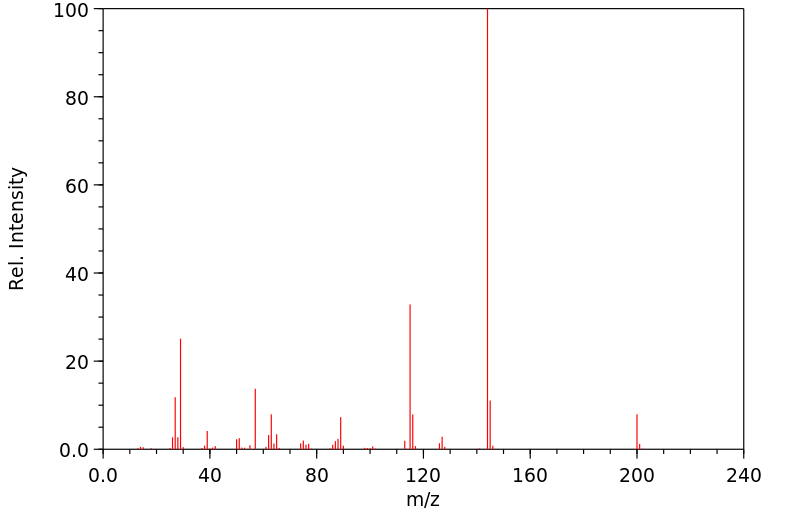
质谱MS
-
碳谱13CNMR
-
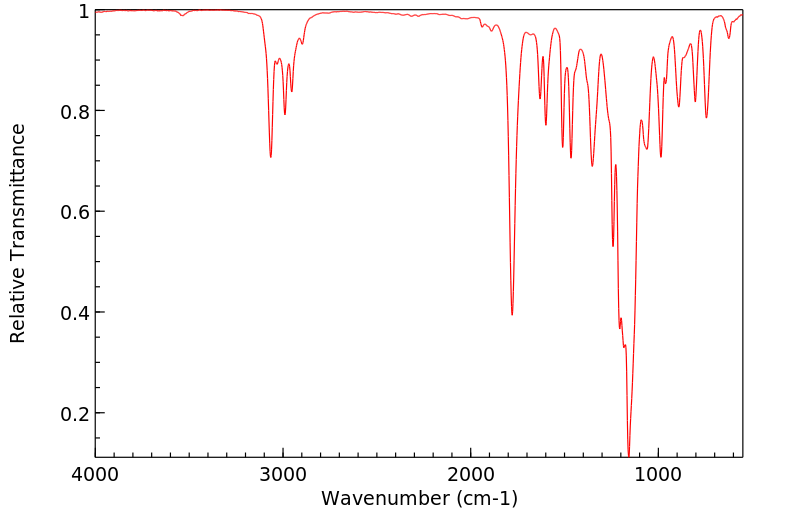
红外IR
-
拉曼Raman
-
峰位数据
-
峰位匹配
-
表征信息
同类化合物
(S)-溴烯醇内酯
(R)-3,3''-双([[1,1''-联苯]-4-基)-[1,1''-联萘]-2,2''-二醇
(3S,3aR)-2-(3-氯-4-氰基苯基)-3-环戊基-3,3a,4,5-四氢-2H-苯并[g]吲唑-7-羧酸
(3R,3’’R,4S,4’’S,11bS,11’’bS)-(+)-4,4’’-二叔丁基-4,4’’,5,5’’-四氢-3,3’’-联-3H-二萘酚[2,1-c:1’’,2’’-e]膦(S)-BINAPINE
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二甲基苯基)-4-羟基-4-氧化物-萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷
(11bS)-2,6-双(3,5-二氯苯基)-4羟基-4-氧-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧磷杂七环
(11bR)-2,6-双[3,5-双(1,1-二甲基乙基)苯基]-4-羟基-4-氧化物-二萘并[2,1-d:1'',2''-f][1,3,2]二氧杂磷平
黄胺酸
马兜铃对酮
马休黄钠盐一水合物
马休黄
食品黄6号
食品红40铝盐色淀
飞龙掌血香豆醌
颜料黄101
颜料红70
颜料红63
颜料红53:3
颜料红5
颜料红48单钠盐
颜料红48:2
颜料红4
颜料红261
颜料红258
颜料红220
颜料红22
颜料红214
颜料红2
颜料红19
颜料红185
颜料红184
颜料红170
颜料红148
颜料红147
颜料红146
颜料红119
颜料红114
颜料红 9
颜料红 21
颜料橙7
颜料橙46
颜料橙38
颜料橙3
颜料橙22
颜料橙2
颜料橙17
颜料橙 5
颜料棕1
顺式-阿托伐醌-d5
雄甾烷-3,17-二酮