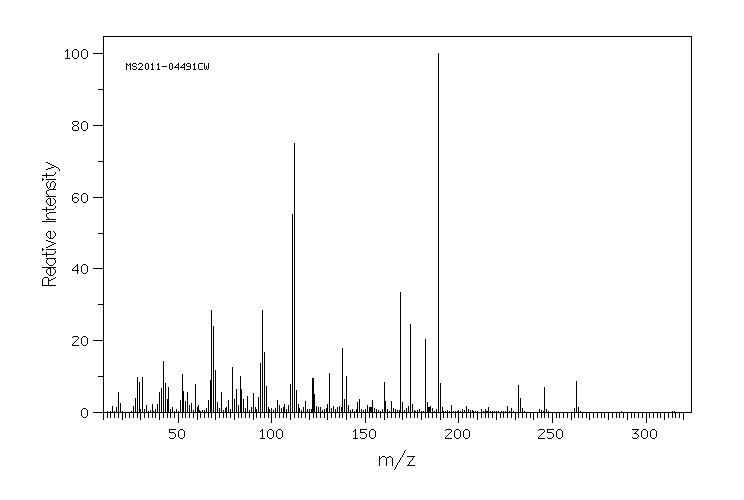
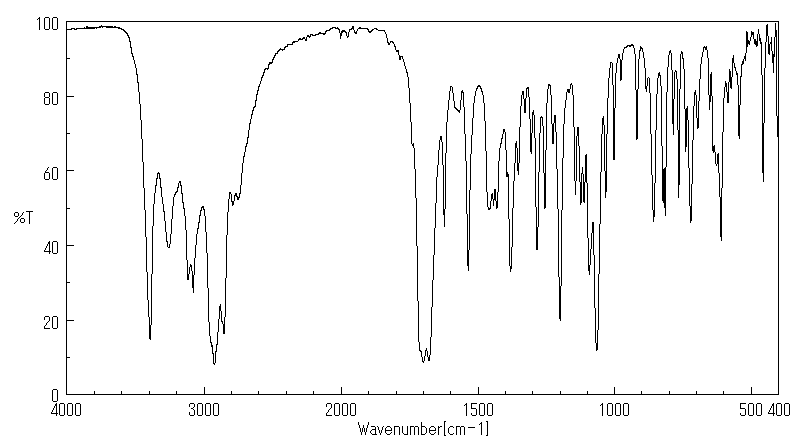
毒理性
◉ 母乳喂养期间使用总结:大多数来源认为,在母亲抗肿瘤药物治疗期间,母乳喂养是禁忌的。在间歇性吉西他滨治疗期间,如果有一个适当的禁乳期,可能可以安全地进行母乳喂养;制造商建议在最后一次给药后至少禁乳1周。化疗可能会不利地影响母乳的正常微生物组和化学成分。[1] 在怀孕期间接受化疗的妇女更有可能在哺乳婴儿时遇到困难。[2]
◉ 对哺乳婴儿的影响:截至修订日期,未找到相关已发布信息。
◉ 对泌乳和母乳的影响:对74名在怀孕第二或第三季度在一个中心接受癌症化疗的妇女进行了电话随访研究,以确定她们产后是否成功进行母乳喂养。只有34%的妇女能够完全用母乳喂养她们的婴儿,而66%的妇女报告遇到母乳喂养困难。这与22位在怀孕期间被诊断但未接受化疗的母亲91%的母乳喂养成功率形成了对比。其他具有统计学意义的相关性包括:1. 有母乳喂养困难的母亲平均接受了5.5个周期的化疗,而没有困难的母亲平均接受了3.8个周期;2. 有母乳喂养困难的母亲在怀孕期间平均比没有困难的母亲早3.4周接受第一次化疗周期。在接受了含氟尿嘧啶方案的9名妇女中,有8名遇到了母乳喂养困难。[2]
◉ Summary of Use during Lactation:Most sources consider breastfeeding to be contraindicated during maternal antineoplastic drug therapy. It might be possible to breastfeed safely during intermittent gemcitabine therapy with an appropriate period of breastfeeding abstinence; the manufacturer recommends an abstinence period of at least 1 week after the last dose. Chemotherapy may adversely affect the normal microbiome and chemical makeup of breastmilk.[1] Women who receive chemotherapy during pregnancy are more likely to have difficulty nursing their infant.[2]
◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants:Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date.
◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk:A telephone follow-up study was conducted on 74 women who received cancer chemotherapy at one center during the second or third trimester of pregnancy to determine if they were successful at breastfeeding postpartum. Only 34% of the women were able to exclusively breastfeed their infants, and 66% of the women reported experiencing breastfeeding difficulties. This was in comparison to a 91% breastfeeding success rate in 22 other mothers diagnosed during pregnancy, but not treated with chemotherapy. Other statistically significant correlations included: 1. mothers with breastfeeding difficulties had an average of 5.5 cycles of chemotherapy compared with 3.8 cycles among mothers who had no difficulties; and 2. mothers with breastfeeding difficulties received their first cycle of chemotherapy on average 3.4 weeks earlier in pregnancy. Of the 9 women who received a fluorouracil-containing regimen, 8 had breastfeeding difficulties.[2]
来源:Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed)